Struggling with a virus-infected computer or unable to uninstall a program? Safe Mode is a method that loads Windows with only the essential files needed to run the system. This mode allows you to perform various troubleshooting tasks that would be difficult or impossible in normal Windows mode. The process of booting into Safe Mode is straightforward, even if you can't start Windows. Refer to Step 1 to learn more about Safe Mode.
Steps
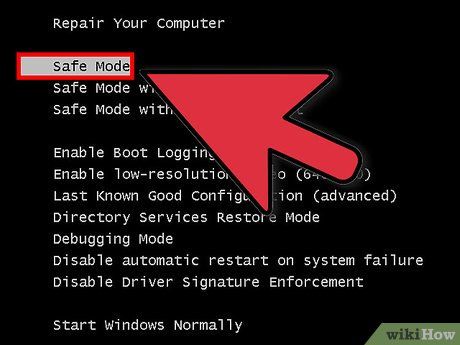
Decide whether Safe Mode is necessary. Safe Mode functions by only allowing the most essential files and drivers to run. Any program not critical for booting the operating system (such as startup software) will be excluded. If you're facing issues with your computer booting up or certain programs malfunctioning right after startup, rebooting in Safe Mode can help troubleshoot the problem.
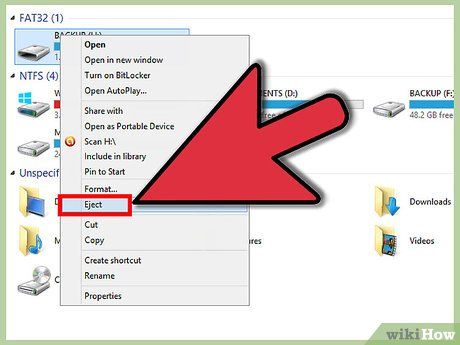
Remove all disks from the computer. This includes CD, DVD, floppy disks, and USB drives. This step prevents any disk from attempting to boot when the computer is restarting.
Boot your computer into Safe Mode. There are two different ways to boot into Safe Mode. You can restart your computer and quickly press the F8 key to access the Advanced Startup menu, or you can configure Windows to automatically boot into Safe Mode. The first method is more convenient if you can't load Windows, while the second is more useful when Windows can boot normally.
- For the first method, press the "F8" key while restarting your computer. Make sure to press F8 before the Windows logo appears (when the screen is still black). If the waiting screen has already shown up, you will need to restart the computer and try again.
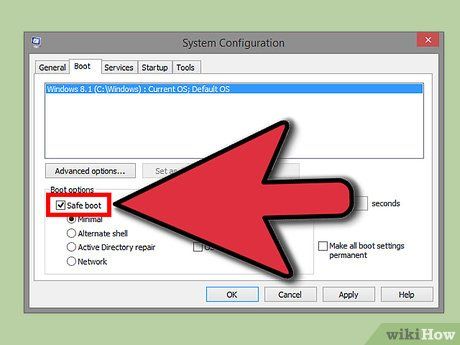
- For the second method, set your computer to boot directly into Safe Mode from Windows. Open the Run dialog (press Windows + R), type "msconfig", and the System Configuration window will appear. Go to the Boot tab and check the “Safe boot” option. This will let you select the type of Safe Mode you want to use, with the most common choices being Minimal and Networking (as explained in the next step).
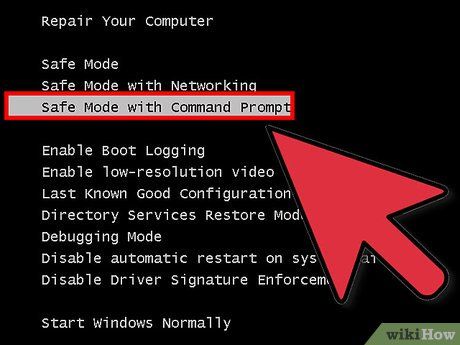
Select the Safe Mode you want to use. After pressing F8, you will be directed to the "Advanced Boot Options" screen. At the top of the list, there will be three different ways to load Safe Mode. If you configured Windows to boot directly into Safe Mode, you won’t see this menu.
- Safe Mode - This is the best option if you’re unsure of which one to choose. It will load the minimal drivers necessary to boot Windows 7. You won’t be able to connect to the internet. This is the "Minimal" option when Windows is set to boot into Safe Mode.
- Safe Mode with Networking - This option loads the same essential drivers as the first option but also loads the necessary processes to enable network connections. Choose this option if you need network access while troubleshooting.
- Safe Mode with Command Prompt - This mode loads similar processes to the first option but grants you immediate access to the command prompt. This option is ideal for advanced users who need to troubleshoot from the command line. Note that you won’t be able to access the graphical environment or Windows.
Wait for the files to load. The next screen will display all the files that are being loaded. At this point, you don’t need to do anything unless a file doesn’t load correctly. If the screen freezes at this stage, note the last successfully loaded file and search online for troubleshooting steps based on that information.
Log into Windows 7. When the login screen appears, sign in to an account with administrator privileges. If there is only one user account on the computer, it's likely that account has administrator rights. If you only have one account and no password, it will log in automatically.
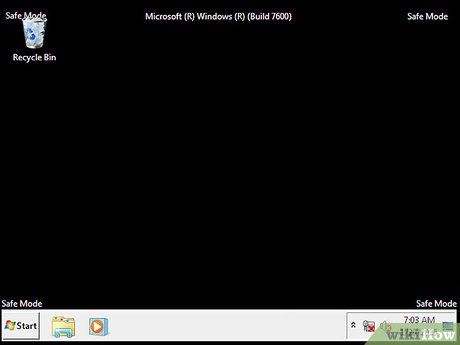
Start troubleshooting. You’ll know that your computer has successfully entered Safe Mode if the words "Safe Mode" appear in all four corners of the screen. Safe Mode is an excellent environment for scanning for viruses and malware, uninstalling faulty programs, and modifying registry entries.
- Once you've finished troubleshooting in Safe Mode, restart the computer to return to normal Windows 7 operation.
- If you set your computer to boot into Safe Mode via the System Configuration window, you will need to open this window again while in Safe Mode and uncheck the “Safe boot” option in the Boot tab. Otherwise, the computer will continue to boot into Safe Mode on restart.
Tips
- Antivirus software runs more efficiently in Safe Mode.
