When you're unable to boot into Windows or simply want to explore alternative file management methods, you can always use Command Prompt (CMD) to transfer data from your hard drive to a USB. For copying individual files, you can use the copy command. However, if you want to copy an entire directory, including subfolders and files within, it's better to use the xcopy command. This guide explains how to use both copy and xcopy to copy files and folders using Windows Command Prompt.
Steps
Open Command Prompt. If you haven't done this yet, you can access Windows Command Prompt as follows:
- Press Windows key + S to open the search bar.
- Type cmd into the search bar.
- If you need to copy system files, right-click on Command Prompt and select Run as administrator.
- You don't need to do this if you've booted into recovery mode, as you'll always have administrative access to Command Prompt.
- If you're copying personal files, such as images or documents, simply click on Command Prompt.
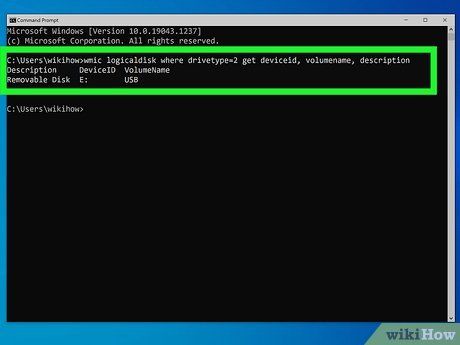
Find the USB drive letter. If you already know the drive letter (e.g., E or F), you can skip this step. Otherwise, follow these steps to locate the drive letter:
- Enter or paste this command after the prompt:wmic logicaldisk where drivetype=2 get deviceid, volumename, description
- Press Enter.
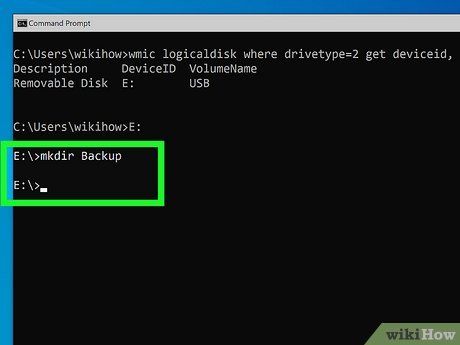
Create a new directory on the USB drive (optional). If you want to copy files into a specific folder instead of the root directory of the USB, you can create a folder using Command Prompt. Here’s how:
- Type cd F: (if the USB drive is not F:, replace it with the correct drive letter) and press Enter.
- Type mkdir foldername and press Enter (replace foldername with the name you want for the new folder).
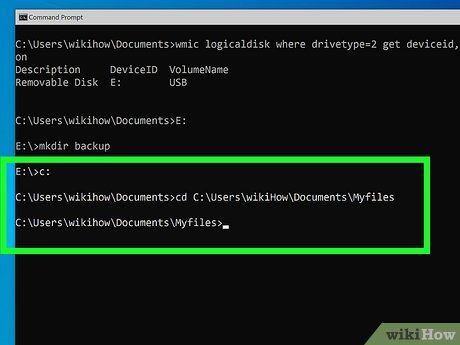
Navigate to the folder containing the files you want to copy. For example, if you want to copy the contents of your personal Documents folder, you can open it by typing cd C:\Users\yourname\Documents.
- If the folder name contains spaces, such as C:\Users\yourname\personal files, enclose the entire path in quotes like this: cd "C:\Users\yourname\personal files.
- To view all files in the folder, type dir and press Enter.
- Type dir and press Enter to see the current files and folders. All folders are marked as ''<DIR>'' to indicate they are directories, not files.
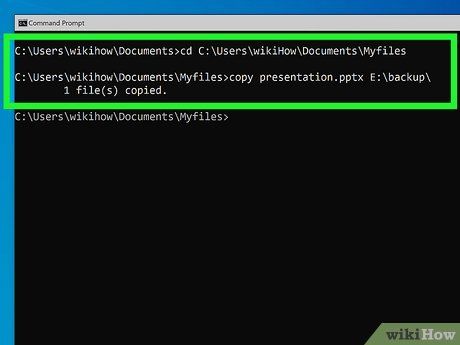
Use the copy command to copy individual files. If you want to copy a single file (without folders) to the USB, the simplest method is to use the copy command. Here’s how:
- When using the copy command, enter the following: copy sourcefolder destinationfolder. For example, to copy the file cats.docx from a folder to the Pets folder on a USB with the drive letter F:, the command would be:
- copy cats.docx F:\Pets\
- If you want to copy multiple individual files with the same extension (e.g., .docx) to the Pets folder on the USB, type copy *.docx F:\Pets\.
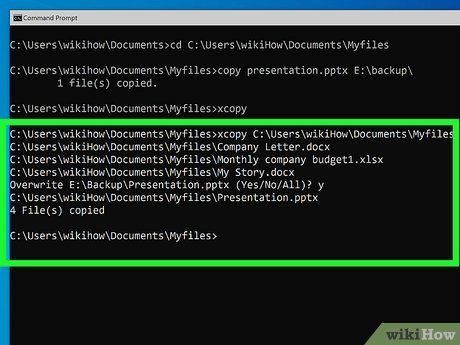
Use the xcopy command to copy entire folders, including all files and subfolders. If you want to back up an entire folder to the USB or copy multiple files, using the xcopy command is the best approach. For example, to copy the folder C:\Users\yourname\personal files, including all its contents, to drive F, follow these steps:
- xcopy "C:\Users\yourname\personal files\" F:\ /e /h /r
- The backslash \ at the end of the first path instructs xcopy to copy the folder, not individual files.
- Add /e to ensure xcopy copies all subfolders.
- Add /h to include hidden files in the copy.
- Add /r to copy read-only files.
