This article provides a guide on accessing a website's HTML source to find login information. While most websites allow you to view their HTML through a browser, the majority do not store administrator passwords or other login details in the HTML. Websites that expose such information are typically in the early stages of development.
Steps
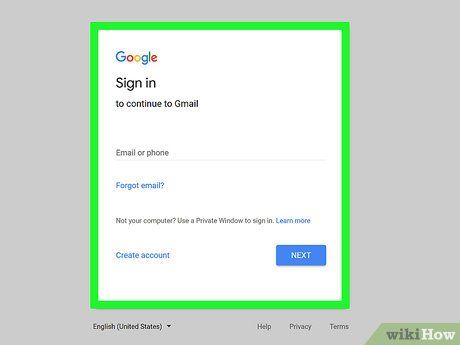
Understand that this method is ineffective for most websites. Unless a website is built using extremely basic HTML security measures, passwords and login credentials are usually stored in encrypted formats that cannot be accessed by simply viewing the website's HTML.
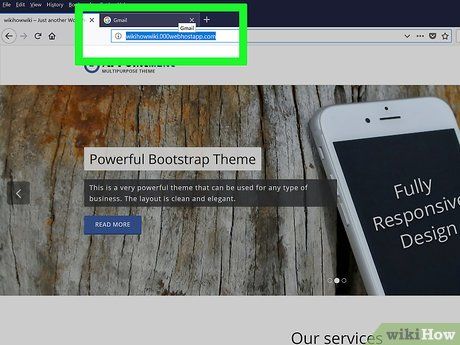
Open the website. Navigate to the website you want to hack using a browser like Chrome, Firefox, or Safari.
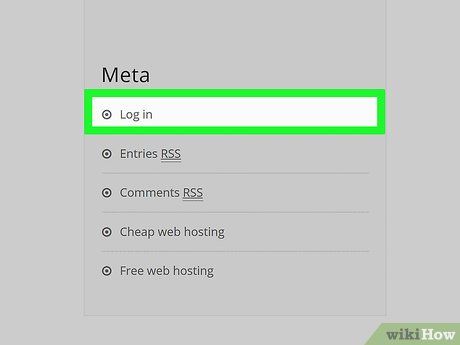
Access the "Login" section. If the website has a dedicated login area, click on the Log In or Sign In link to navigate there.
- If the login screen is already displayed (or if the login section is on the homepage), you can skip this step.
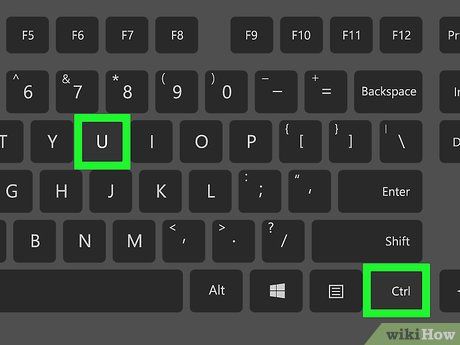
Open the website's source code. Each browser has a different method, but the simplest way to view the HTML of a website is by pressing Ctrl+U (on Windows) or ⌘ Command+U (on Mac). This opens a new tab with the website's source code.
- If using Microsoft Edge, you’ll need to click the Elements tab in the displayed menu to view the HTML.

Activate the "Search" feature. On the source code tab, press Ctrl+F (on Windows) or ⌘ Command+F (on Mac) to bring up the search bar at the top-right corner of the window.
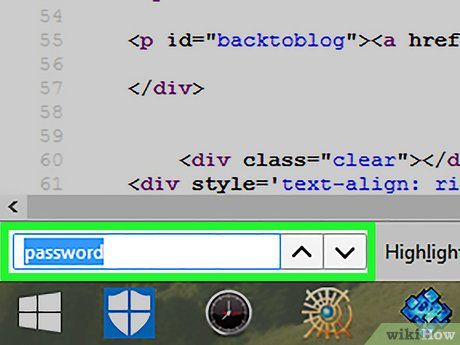
Search for login credentials. Type password into the search bar and review the highlighted results. If nothing appears, try searching for pass and repeat the process. Do the same for user, username, login, and other keywords related to login information.
- If you’re attempting to hack the website using administrator credentials, the username might be "admin" or "root".
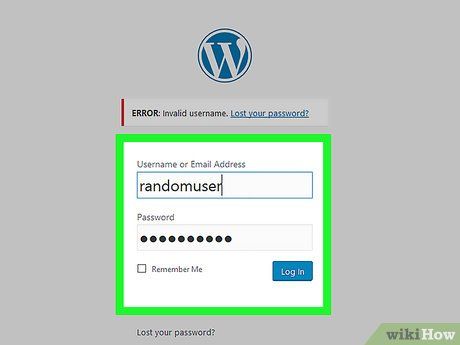
Attempt entering incorrect credentials. If searching through the HTML yields no results, try the following:
- Close the source tab.
- Enter random characters into the username (or email) and password fields.
- Click the Log In button.
- Reopen the source code by pressing Ctrl+U or ⌘ Command+U.
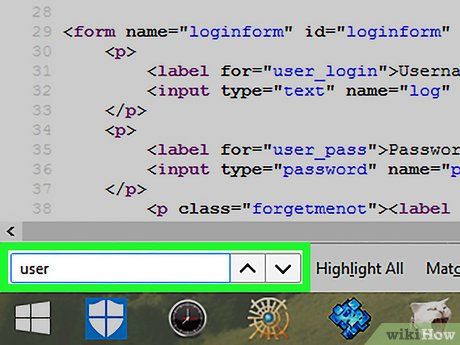
Continue searching for login details. After updating the source code to reflect the content displayed when incorrect credentials are entered, you can use the search bar to look for keywords related to login information.
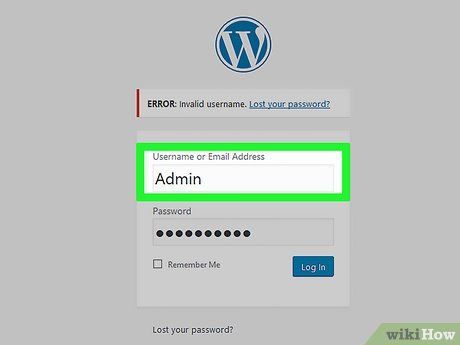
Enter the login credentials found on the page. If you manage to locate a username and password within the HTML, try entering them into the website's login section. If no error message appears, you’ve successfully found the correct credentials.
- Again, the likelihood of finding usable login information in the HTML is extremely low.
Tips
- If you want to practice HTML hacking techniques, the website "Hack This Site" offers practical examples to help you understand basic hacking methods and real-world challenges. You’ll need to create an account before participating in the challenges on Hack This Site.
- Learning HTML will give you a slight advantage when reviewing the source code of your chosen website.
- In addition to login fields, try searching for other input fields, comments, or any areas where you can insert content. You can then input HTML, CSS, or JS. However, avoid hacking—this is just an example.
Warnings
- You cannot edit a website's HTML through your browser unless you have access to the server used to upload the website's HTML files.
