Oral Rehydration Salt (ORS) is a special solution made from sugar, salt, and clean water. It helps replace the fluids lost due to diarrhea or vomiting. Research shows that ORS is effective for rehydration via intravenous fluids when treating dehydration. You can purchase pre-packaged ORS solutions like Pedialyte®, Infalyte®, and Naturalyte®. Alternatively, you can prepare the solution at home using water, salt, and sugar.
Steps to Prepare ORS
Making Your Own ORS Solution
Wash your hands. Thoroughly wash your hands with soap and water before preparing the solution. Make sure you have a clean bottle or jar ready for use.
Gather the ingredients. To prepare the ORS solution, you will need:
- Refined salt (such as kosher salt, iodized salt, or sea salt)
- Clean water
- Sugar (granulated or powdered)
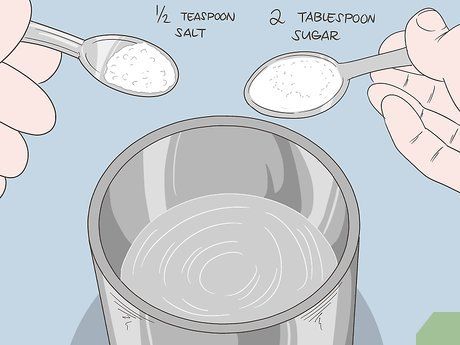
Mix the dry ingredients. Add half a teaspoon of salt and 2 teaspoons of sugar into a clean container. You can use either granulated or powdered sugar.
- If you don’t have a teaspoon, you can use a handful of sugar and a pinch of salt, but this method is not precise and is not recommended.
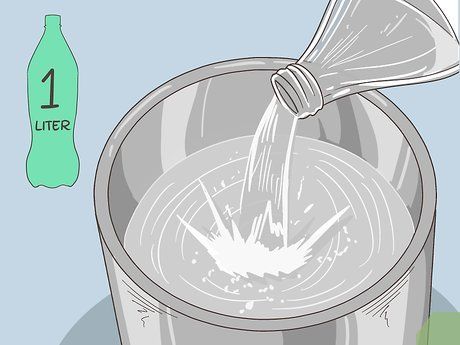
Add one liter of clean drinking water. If you can't measure one liter, use 5 cups of water (each cup around 200ml). Only use clean water. It can be bottled or freshly boiled and cooled.
- Make sure to only use water. Milk, broth, fruit juices, or soft drinks should not be used as they will reduce the effectiveness of the ORS solution. Do not add extra sugar.
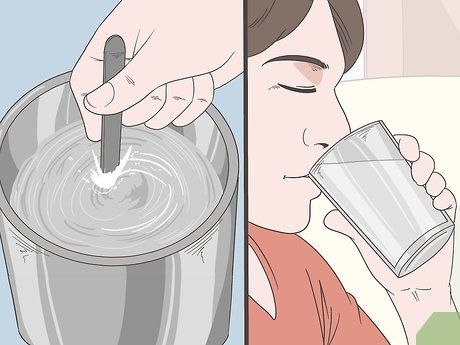
Stir well and drink. Use a spoon or whisk to mix the ORS powder into the water. After about a minute of continuous stirring, the solution will completely dissolve. Now it’s ready to drink.
- The ORS solution can be stored in the fridge for up to 24 hours. Do not store it for longer.
Understanding the ORS Solution

Consult a doctor if you need to take ORS. If you experience severe diarrhea or vomiting, your body loses fluids, leading to dehydration. You may notice symptoms such as increased thirst, dry mouth, drowsiness, less frequent urination, dark yellow urine, headaches, dry skin, and dizziness. If you experience these symptoms, contact your doctor. You may be advised to use ORS if these symptoms are not severe.
- If left untreated, dehydration can worsen. Severe dehydration signs include: very dry mouth and skin, darker or brownish urine, loss of skin elasticity, slow pulse, sunken eyes, seizures, extreme weakness, and even coma. If you or someone you are caring for shows these signs of severe dehydration, call emergency services immediately.
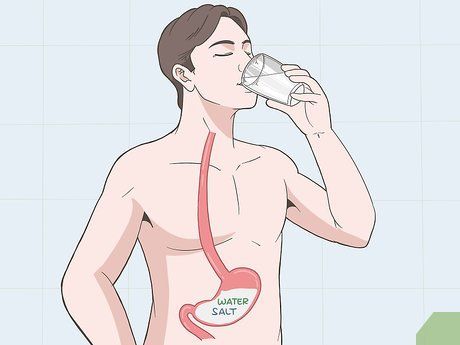
Learn how ORS treats severe dehydration. ORS is designed to replace lost salts and improve your body’s ability to absorb water. When you begin showing early signs of dehydration, you should start drinking ORS. The main goal of this solution is to rehydrate your body. Preventing dehydration is easier by drinking ORS early than waiting for it to become severe and requiring treatment.
- Severe dehydration will require hospitalization and intravenous fluid replacement. However, if detected early, ORS can be prepared at home to treat mild dehydration.
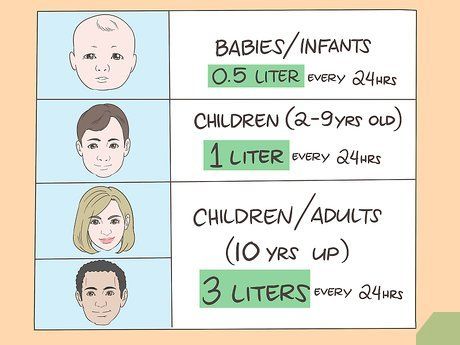
Learn how to drink ORS. Take small sips of ORS water throughout the day. You can drink it during meals. If you vomit, stop drinking ORS for a moment, wait 10 minutes, and then resume. If you are breastfeeding or caring for a baby, continue breastfeeding while using ORS for treatment. You can continue using ORS until diarrhea stops. Here’s the recommended ORS dosage:
- Infants and toddlers: 0.5 liters of ORS within 24 hours
- Young children (2 to 9 years old): 1 liter of ORS within 24 hours
- Children (10 years and older) and adults: 3 liters of ORS within 24 hours
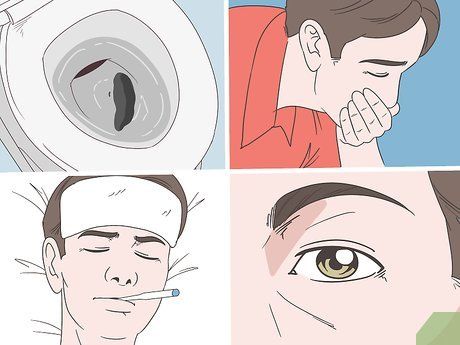
Know when to see a doctor if you have diarrhea. Symptoms should improve within hours of drinking ORS. You’ll urinate more, and your urine should become lighter and clearer. If symptoms do not improve, or if any of the following signs appear, seek medical help immediately:
- Blood in diarrhea or black, tarry stools
- Continuous vomiting
- High fever
- Severe dehydration (feeling dizzy, lethargic, sunken eyes, not urinating for 12 hours)
Advice
- Diarrhea usually stops after three or four days. The real concern is dehydration and nutrient loss in children, which can lead to malnutrition and further dehydration.
- Encourage children to drink as much as possible.
- ORS powder is available for purchase at pharmacies. Each packet contains 22g of powder for a single dose. Follow the instructions on the package to prepare the solution.
- A diet consisting of bananas, rice, apple juice, and toast can aid recovery after diarrhea and may help prevent further dehydration, as these foods are easy to digest.
- If experiencing diarrhea, consider adding zinc supplements. You can take 10 to 20 mg of zinc daily for 10–14 days after diarrhea. This helps replenish the zinc lost and prevent worsening of the condition. Zinc is abundant in seafood like oysters and crab, beef, fortified cereals, and baked beans. These foods may help, but additional zinc supplementation is necessary for severe diarrhea.
Warnings
- Always check if the water used for mixing is clean.
- If diarrhea persists for more than a week, consult a doctor or healthcare professional.
- Never give children antibiotics, tablets, or other medications unless prescribed by a doctor or healthcare professional.
