Get this issue sorted out with our comprehensive troubleshooting guide.
The "Power surge on the USB port" error that appears on a Windows computer typically means a USB device is drawing more power than the port can supply. This article from Mytour will guide you through resolving the "Power surge on a USB port" warning in Windows.
This error suggests that a USB device attached to your computer requires more power than the USB port can deliver. Try connecting the device to another USB port, using a different cable, or checking for updates. If the problem persists, consider using a powered USB hub.
Identify the cause.
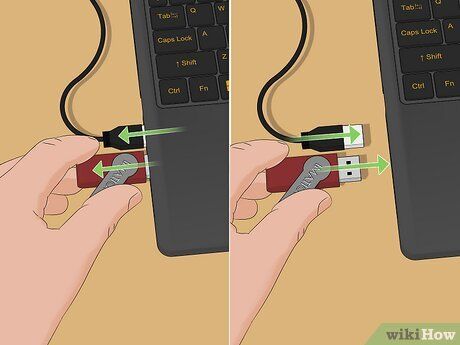
Inspect all USB devices attached to your computer. Unplug all USB devices from your computer and reconnect them one by one. Observe if the error message reappears when a specific device is connected. If "Power Surge on the USB port" appears, you'll know which device or port is the source of the issue.

The USB cable might be malfunctioning. Inspect the cable for any visible damage or exposed wires. Check the USB connector for dirt, debris, or bent pins. If you can, test the device with another cable. If it works fine with a different cable, the issue lies with the original one.
Test a different device with the faulty port.

Test the error with a different device. If the error only appears when using a particular device, it may be faulty.
- Some USB devices require an external power source. Ensure that your USB device is properly powered.
Perform a power cycle on your computer.

Your computer may need to be rebooted. Sometimes, performing a power reset can clear the computer’s memory and eliminate residual power, fixing minor bugs or glitches. To power cycle your computer, turn it off and disconnect it from the power source. If possible, remove the battery. Press and hold the power button for about 10 seconds to release all power. Then reconnect the power and restart your computer to see if the issue is resolved.
Update your USB drivers.
Your USB drivers might be outdated or corrupted. Updating your USB drivers can resolve bugs and improve system stability. The easiest way to update your drivers is via
Windows Update. Follow these steps to update Windows and drivers:
- Click the Start menu.
- Click the Gear/Settings icon.
- Click Update & Security (Windows 10 only).
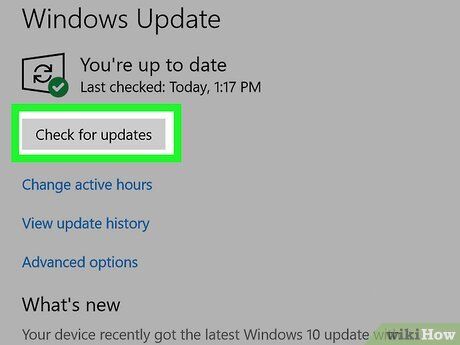
- Click Windows Update.
- Click Check for Updates.
- Follow the prompts to install any necessary updates.
Reinstall your USB drivers.
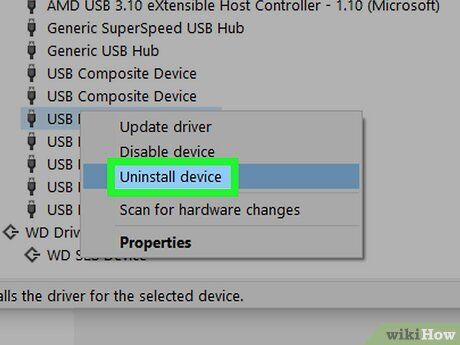
Uninstall and reinstall your drivers. Reinstalling the USB drivers might resolve any issues with your current drivers, including the "Power surge on the USB port" error. When you
uninstall the drivers, Windows will automatically reinstall them upon restart.
- Right-click the Windows Start menu.
- Select Device Manager.
- Scroll down and expand the "Universal Serial Bus Controllers" section.
- Right-click a USB device and choose Uninstall device.
- Repeat for all USB devices.
- Restart your computer.
Run a Windows troubleshooter.
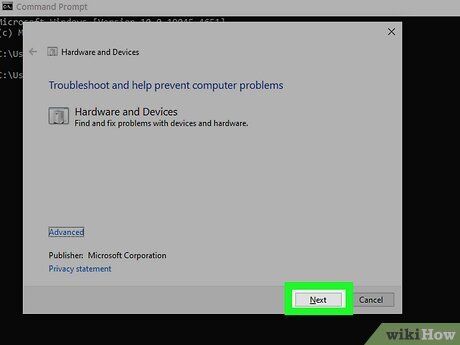
Run a hardware diagnostic tool in Windows. You can use the following steps to run the built-in Windows diagnostic tool to check your hardware and devices:
- Click the Windows Start menu.
- Type CMD.
- Open the Command Prompt.
- Type msdt.exe -id DeviceDiagnostic and press Enter.
- Click Next in the bottom-right corner.
- Follow the instructions if any issues are found.
Modify your power settings.
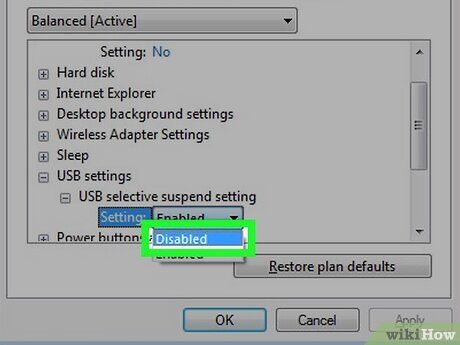
Your power settings might be insufficient. Your USB port may not be supplying enough power. Adjusting your power settings in the Control Panel could help:
- Click the Windows Start button.
- Type Control Panel.
- Open the Control Panel.
- Click Hardware & Sound.
- Click Power Options.
- Select High Performance.
- Click Change plan settings next to "High Performance."
- Click Change advanced power settings.
- Expand the "USB settings" menu.
- Expand the "USB selective suspend settings" menu.
- Ensure all selective suspend settings are turned off.
- Click Apply.
Use a powered USB hub.

Try connecting your device through a USB hub instead of directly to the port. A USB hub lets you connect multiple devices to a single USB port. If your device is not receiving enough power, a
powered USB hub (one that requires its own power supply) with fast-charging ports could provide sufficient power for your device.
Check your BIOS/UEFI settings.
Your BIOS settings might not be configured correctly. The process to enter the BIOS depends on your computer model. Usually, your computer will display a message indicating which key to press during startup (typically F1, F2, DEL, ESC, etc.). Once inside, check the USB-related settings (such as "Legacy USB support" and "USB 3.0 Configuration Pre-OS") and ensure they're enabled and set properly. The BIOS menu differs by model. If you're unsure how to
enter the BIOS, follow these steps within Windows:
- Click the Windows Start menu.
- Click the Gear/Settings icon.
- Click Update & Security (Windows 10) or System (Windows 11).
- Click Recovery.
- Click Restart Now under "Advanced startup."
- Click Troubleshoot.
- Click Advanced options.
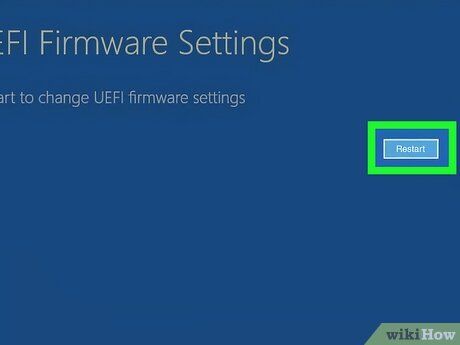
- Click UEFI Firmware settings.
- Click Restart.
Get your computer professionally serviced.

Take your computer for professional repair. If the error persists despite your efforts, the issue might be a hardware problem with your motherboard affecting the USB ports. Reach out to the point of sale or the manufacturer to check if your device is still covered under warranty. If it's not, consider taking your computer to an authorized repair service.











