Hemorrhoids are a condition where the veins in the lower rectum and anus become swollen and inflamed. It's a common condition, with about 50% of adults in the U.S. facing hemorrhoids at least once before the age of 50. The condition arises due to increased pressure on the veins in the lower rectum and anus, causing them to swell. The most common symptoms include painless bleeding during bowel movements, rectal or anal pain, itching, and/or soft lumps near the anus. There are various home remedies and medical treatments to manage hemorrhoids and their pain.
Steps
Home Treatment for Hemorrhoids
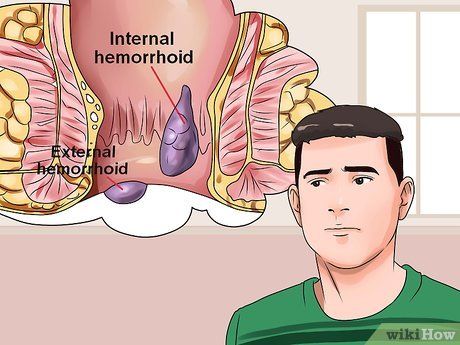
- Internal hemorrhoids develop in the lower rectum and generally do not cause pain as the rectum lacks pain receptors. You may not realize you have internal hemorrhoids until you notice blood in your stool or observe hemorrhoids protruding from the anus.
- Painful symptoms are often a sign of external hemorrhoids, which develop under the skin around the anus. If a blood clot forms in the hemorrhoid, it is called a “thrombosed hemorrhoid,” and the pain is often described as severe and sudden. The patient may see or feel a lump around the anus. The blood clot usually dissolves over time, leaving excess skin protruding from the anus.

- Gently pat the anal area dry with a towel or use a hair dryer to ensure it is completely dry after the bath.

- After using the cold compress, gently dry the area with a towel or use a hair dryer to avoid moisture.

- Use Tucks medicated pads, which can be applied up to 6 times a day to the irritated hemorrhoid area to relieve pain and itching. These pads contain witch hazel, known for its soothing and anti-inflammatory properties.
- Preparation H cream acts as a topical anesthetic, helping to constrict blood vessels and protect the skin effectively in hemorrhoid treatment. It blocks pain signals from the nerve endings in the anal area and helps reduce swelling and inflammation.
- Creams or suppositories containing hydrocortisone, a strong anti-inflammatory steroid, can be useful for treating hemorrhoids. However, hydrocortisone should only be used for a maximum of 7 days to avoid thinning the skin around the anus.
- Pramoxine, available in both prescription and over-the-counter forms, is another topical anesthetic used for hemorrhoid treatment.

- Acetaminophen can be taken at 650-1000 mg every 4-6 hours, not exceeding 4 grams in 24 hours.
- Ibuprofen can be taken at 800 mg, up to 4 times a day.
- Aspirin can be taken at 325-650 mg every 4 hours as needed, not exceeding 4 grams in 24 hours.

Receive medical treatment
- Seek medical attention immediately if the hemorrhoids cause pain.
- The doctor may suggest changes to your diet and lifestyle before recommending medication or surgery. These changes could include increasing fiber intake and regular exercise.


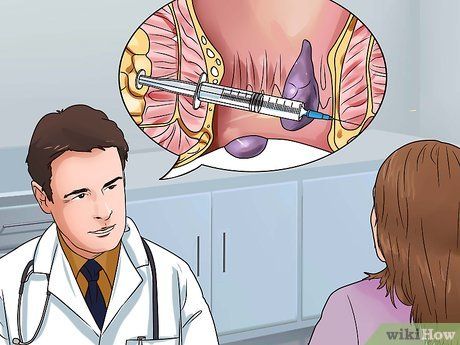
- Some doctors do not recommend sclerotherapy because studies show it is only effective for a short time, and most patients experience a recurrence of hemorrhoids.
- This technique is typically applied to small hemorrhoidal tissue (where rubber band ligation isn't feasible) or combined with rubber band ligation, offering a success rate of up to 97%.
- Patients generally require a short recovery time (1-2 weeks) after the procedure.
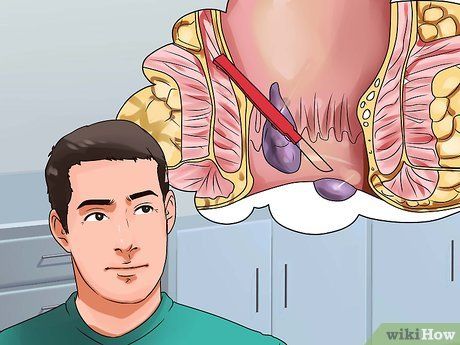
- Hemorrhoidectomy is typically performed for thrombosed internal hemorrhoids, combined internal and external hemorrhoids, or rectal conditions requiring surgery. The procedure is more painful, and recovery time is longer than with other methods.
- The recovery period after a hemorrhoidectomy typically spans 2-3 weeks, with a follow-up visit.

- Compared to traditional hemorrhoidectomy, clamp hemorrhoidectomy has a higher risk of recurrence and rectal prolapse (where the rectum protrudes from the anus). However, it significantly reduces postoperative pain compared to conventional surgery.
Prevention of hemorrhoids
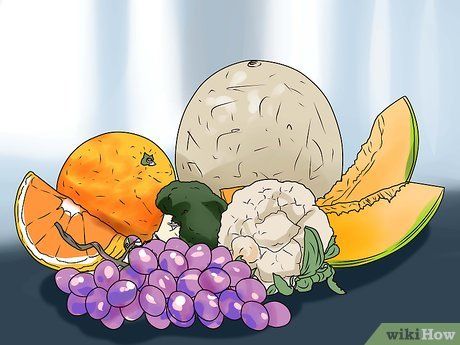
- The recommended fiber intake is around 20-35 g per day, depending on age and gender. Women under 51 need 25 g of fiber daily, while women over 51 need 21 g. Men under 51 need 38 g daily, while men over 51 require 30 g of fiber.
- Additionally, fiber supplements like psyllium husk (Metamucil, Citrucel) can be added to your diet.
- Increase fiber intake gradually to prevent bloating.
- If increasing fiber doesn't alleviate constipation, consider using stool softeners like Colace for short-term relief.


- Try to exercise for at least 30 minutes, five times a week. You can break this into shorter sessions, like 15 minutes twice a day or 10 minutes twice a day if that's easier for you.
- Engage in activities that you enjoy to stay motivated. You can go for a walk after meals, cycle to work, or join an aerobic class a few times a week.

- If after sitting on the toilet for 5 minutes you still can't have a bowel movement, stand up and return later. Prolonged sitting on the toilet can aggravate hemorrhoid symptoms.

Warning
- This article offers information regarding hemorrhoids but is not intended as medical advice. Always consult with a doctor to determine the best treatment for your condition.
- Individuals who experience rectal bleeding while taking blood-thinning medications such as warfarin (Coumadin), clopidogrel (Plavix), enoxaparin (Lovenox), rivaroxaban (Xarelto), dabigatran (Pradaxa), or apixaban (Eliquis) should seek immediate medical assessment.
- Hemorrhoids do not cause abdominal pain, so if rectal bleeding is accompanied by stomach pain, urgent medical care is needed.
- If rectal bleeding is accompanied by dizziness, mild headaches, or fainting, it is important to seek emergency medical care. These symptoms may indicate significant blood loss and could require a blood transfusion.
- If internal hemorrhoids cannot be pushed back into the rectum, immediate medical attention is necessary.
- Severe pain caused by thrombosed hemorrhoids requires urgent medical examination, and if indicated, clot dissolution may be necessary.
