Leg cramps (sometimes called 'charley horses') are a common ailment, especially among pregnant women, the elderly, and athletes. A leg cramp occurs when a muscle suddenly contracts, causing severe pain that can last anywhere from a few seconds to 10 minutes. You can prevent leg cramps and treat acute ones by immediately moving and massaging the affected area.
Steps
How to Treat Leg Cramps

Move your toes upwards as soon as a leg cramp occurs. Sleeping in a position with a slightly bent knee and toes pointed downwards makes the muscles more likely to cramp. Instead, move and point your toes upwards. Hold each movement for about 2 seconds. Repeat for 30 seconds to 1 minute.

Walk around on your heels. This movement helps to stretch and contract the muscles, providing a massage effect and improving blood circulation to the muscles. Poor circulation can reduce the oxygen supply to the muscles, leading to cramps.

Stretch your calf muscles. Place the foot with the cramp behind your regular foot, about 0.3 meters apart. Bend the knee of the normal leg to help the cramping calf muscle stretch forward.

Stand with your feet shoulder-width apart (60 to 90 cm) against a wall. Make sure your feet are firmly placed on the floor. Place your hands on the wall, about one shoulder width away. Bend your elbows and lean forward. This will stretch your calf muscles. If the pain is intense, you can adjust your position by moving closer or farther from the wall to increase the stretch.

Massage the muscle. Sit down, cross the leg with the cramp over the thigh of your normal leg, and gently massage the muscle. Apply deeper pressure if needed.
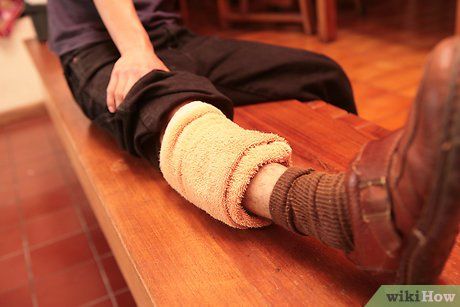
Apply heat to the cramped area. Heat helps to improve blood circulation to the muscles. You can use a warm towel or a heating pad to apply heat to the affected area.

Take a warm bath. If the cramp lasts for over 5 minutes or longer, consider taking a warm bath. This method allows the heat to spread throughout your muscles, which helps alleviate the cramp.
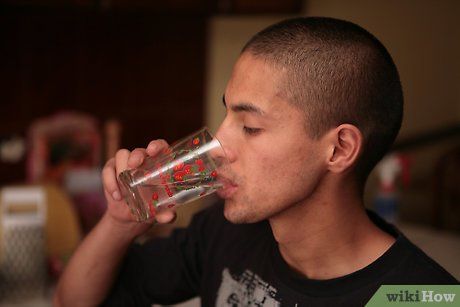
Drink 1/4 to 1/2 liter of water immediately after a cramp. Dehydration is one of the main causes of cramps, whether you're an athlete or not.
- If you experience cramps after exercising, there is a risk of an electrolyte imbalance. Drinking sports drinks with electrolytes can help replenish the lost fluids and restore your body's balance.

Take pain relievers. Medications such as Ibuprofen (Motrin, Advil) or Acetaminophen (Tylenol) may help reduce the pain from leg cramps. Be sure to follow the dosage instructions provided on the label.
Preventing leg cramps

Drink plenty of water daily to lower the risk of dehydration-related cramps. It's recommended that you drink at least 1.9 liters of water each day or more if you're compensating for fluid loss due to illness. Some experts even recommend a higher intake of around 9-13 cups of water daily.
- Diarrhea or other illnesses can cause a significant loss of potassium and water from your body, making you more susceptible to cramps. Recovering from illness is also an essential step in preventing cramps.

Wear shoes with cushioned insoles and flexible soles that mold to the shape of your foot (arch-shaped soles). Wearing ill-fitting shoes can lead to muscle strain or cramps. Consider buying insoles available at pharmacies to add to your shoes for added comfort.

Place a pillow under your knee while lying down. If you lie on your stomach, it is best to raise your legs on the bed for extra support.

Loosen the blanket around your feet. If you sleep on your back and tend to curl up in the blanket, there’s a risk of foot cramps. Try loosening the blanket around your feet to avoid constricting your muscles during sleep.

Stretch your legs, walk, or pedal in place for 5 minutes before bed. This helps to warm up your muscles and enhance circulation.

Engage in regular calf exercises throughout the day. You can strengthen your calves by walking, cycling, or doing yoga. Moderate exercise helps reduce the risk of cramps, while intense workouts might increase the likelihood of muscle tightness.

Consult a doctor about using supplements like quinine, potassium, calcium, or magnesium if you experience frequent or nightly leg cramps. Quinine may help reduce the frequency of leg cramps.
- You might try a small dose of magnesium citrate before bedtime if you frequently suffer from cramps during the night.
Advice
- It's important to note that deficiencies in vitamins, especially magnesium, potassium, and calcium, can cause leg cramps at night. However, you don't necessarily have to rely on supplements. Sometimes eliminating certain foods from your diet can help reduce or even completely prevent nighttime cramps. You can try an elimination method to determine which foods should be eaten or avoided. Additionally, always remember to stay well-hydrated.
- If you experience severe muscle pain after a leg cramp, seek medical assistance or consult a trained healthcare professional. Muscle cramps may lead to muscle spasms or ligament strain, known as a muscle strain.
- If you have pain from muscle spasms or injury following a cramp, apply cold compresses instead of heat. Cold therapy helps reduce inflammation and numbs the affected area.
- Conditions such as neurological disorders, cirrhosis, Sarcoidosis (granuloma disease), peripheral artery disease, and kidney dialysis can contribute to muscle cramps. Certain medications like diuretics, statins, lithium, penicillamine, nifedipine, nicotinic acid, cimetidine, clofibrate, salbutamol, and phenothiazines may also cause cramps.
- Talk to your doctor about wearing support stockings that may help reduce cramps for the elderly or pregnant women in their later stages. These pressure stockings can warm up the legs and improve blood circulation to the feet.
- According to a muscle cramp principle, biting your upper lip is thought to help relieve cramps. However, there is no medical evidence supporting this claim.
- You can use Ibuprofen to alleviate pain.
Warning
- Avoid taking supplements without consulting a healthcare professional.
- Exposure to lead or tetanus bacteria can trigger muscle cramps. See a doctor immediately if you come into contact with either of these situations.
Items You Need
- Hot compress bag
- Water
- Cold compress bag
- Showerhead
- Wall
