An algorithm is a series of steps designed to solve a problem or complete a task. Typically, algorithms are written in pseudocode (a simplified version of code) or a mix of natural language and one or more programming languages to develop a program. This guide will show you how to create a complete algorithm to help you build your own application.
Steps

Define the output of the code. What problem are you trying to solve, or what task do you want to accomplish? Once you have a clear idea of the outcome you want to achieve, you can start determining the steps to take in order to reach that result.

Determine the starting point. Identifying the starting and ending points is crucial for outlining the steps of the process. To determine the starting point, ask yourself the following questions:
- What data/input is available?
- Where is this data located?
- What formulas apply to the current problem?
- What rules apply to the available data?
- How are the data values related to each other?

Find the endpoint of the algorithm. Similar to identifying the starting point, you can determine the endpoint by focusing on these questions:
- What have we learned from this process?
- What has changed from the beginning to the end?
- What will be added or removed?
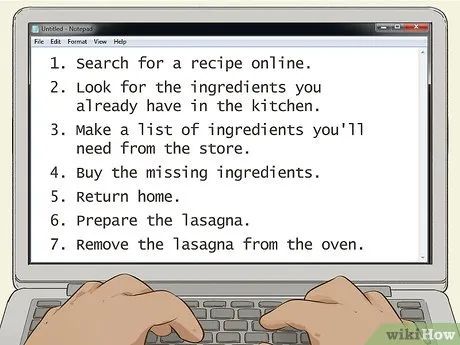
List the steps from start to finish. Start with the major steps. For example, if you want to make lasagna for dinner, once you determine that the starting point is finding the recipe, the result is that you can enjoy a delicious lasagna at 7 PM. The steps are as follows:
- Search for a recipe online.
- Check available ingredients in the kitchen.
- Create a shopping list for missing ingredients.
- Purchase the missing ingredients.
- Return home.
- Prepare the lasagna.
- Take the lasagna out of the oven.

Determine how to complete each step. Now that you have a detailed step-by-step plan, it’s time to figure out how to code each step. What language will you use? What resources are available? What’s the most efficient way to implement each step in that language? Add these code snippets to your algorithm. Expand each step until you have a complete process.
- For example, the first step in the lasagna algorithm is Search for a recipe online. But what does this search entail? List the specific steps:
- Open the computer.
- Ensure the computer is connected to the internet. If not, connect to the internet.
- Open a web browser.
- Enter the search keyword.
- Click on the recipe link.
- Assess if the recipe meets your needs.
- Filter out non-vegetarian recipes.
- Ensure the recipe serves at least five people.
- Repeat some of these steps until you find the right recipe.
- Open the computer.
- Consider the resources you have, like your system’s capabilities for developing the program. In the case of lasagna, let’s assume the person knows how to search for information online and use the oven, etc.

Review the algorithm. Now that your algorithm is written, it’s time to evaluate the process. Your algorithm is designed to accomplish a specific task, and you’ll need it to start writing the program. Answer these questions and address any issues as necessary:
- Does the algorithm solve the problem/accomplish the task?
- Are the input and output clearly defined?
- Does the goal need to be redefined to be broader? Or more specific?
- Can any steps be simplified?
- Does the algorithm provide accurate results?
Tips
- Refer to existing algorithms to inspire the creation of your own.
- Use efficient loops.
- Focus on performance when writing code.
- Don’t forget to define the end point, or your code might break.
