The Uncanny Valley theory posits that as robots become more lifelike, the more people begin to feel uneasy about them. With technology advancing rapidly, the distinction between humans and robots is becoming increasingly blurred. Robots now exhibit human-like movement, appearance, and even a certain level of consciousness. There seems to be no limit to how robots can be programmed, what tasks they can be taught to perform, and how lifelike they can appear. This list features some of the latest, most advanced robots and androids currently available.
10. BEAR

While robots are known for enhancing our lives, they also serve to make them safer. The Battlefield Extraction-Assist Robot (BEAR), developed by Vecna Technologies, is designed as a rescue android for high-risk situations. BEAR is capable of transporting heavy objects across rough terrains, including stairs, with remarkable balance and dexterity. Its explosion- and fire-resistant treads and batteries ensure durability in harsh conditions. BEAR can be controlled remotely or via a glove, and is often deployed to enter hazardous areas to rescue injured soldiers, eliminating the need to risk human lives. With a steel frame powered by hydraulics, it can lift up to 236 kilograms (520 lbs), and it uses infrared, night vision, and optical cameras to navigate dangerous environments.
In addition to its impressive heavy-lifting capabilities, BEAR is also capable of handling delicate objects, such as an egg, without damaging it. It can maintain perfect balance while carrying weighty loads that would typically cause other robots to topple. BEAR has evolved significantly from its initial designs, now able to follow complex commands from its operators. Furthermore, it’s equipped with a human-like face to help calm injured individuals. Developers are excited to further enhance BEAR’s abilities to assist both citizens and soldiers in life-threatening situations.
9. BINA48

The Breakthrough Intelligence via Neural Architecture, or BINA48, has quickly gained recognition as one of the most astonishingly realistic androids ever created. Developed by David Hanson of Terasem Movement and modeled after the co-founder’s wife, Bina Rothblatt, BINA48 is not only strikingly similar to a human in appearance, but is also composed of Bina’s actual thoughts, memories, emotions, and feelings.
The creation of BINA48 required more than 100 hours of compiling Bina’s thoughts to upload into the android. As a result, BINA48 can engage in conversations on various intellectual topics, mimicking Bina’s own mannerisms. The robot also has the ability to continually learn, with her vocabulary and knowledge expanding daily as she interacts with people. Although BINA48 currently lacks a full body, her head alone is capable of expressing over 64 different emotions based on the information she processes. While BINA48’s abilities can be unsettling to many, her creators are eager to continue enhancing her technological consciousness. BINA48 is already able to make decisions independently, relying on her past experiences and preferences, and she is also learning to back up her choices with data and reasoning.
8. NAO

When you think of androids, emotional intelligence might not be the first feature that comes to mind. However, the NAO robot is equipped with the unique ability to learn, recognize, interact with humans, and even develop emotions. Standing at only 58 centimeters (23 inches) tall, NAO was created by Aldebaran Robotics.
What sets NAO apart is its high degree of programmability. The University of Hertfordshire is using this flexibility to teach the robot to experience emotions. By enhancing NAO’s ability to recognize and interpret facial expressions and body language, it will form attachments to those it interacts with most frequently. Through observation—much like a young child—NAO will learn to express emotions such as anger, fear, sadness, excitement, pride, and happiness, as well as when and how to apply them in real-world situations. Beyond emotions, NAO is capable of learning other skills like writing and speaking different languages. NAO has been utilized as a teacher, visitor for children, and has also hosted comedy shows, groomed cats, assisted in research, played soccer, and worked in hospitals. Researchers are eager to explore the endless possibilities for this small but dynamic robot.
7. HRP-4C

Until now, the androids featured in this list have been clearly robotic, but the HRP-4C (Miim) takes things a step further with an astonishing resemblance to a real human. Developed by the Japanese company AIST, Miim was designed to resemble a typical young Japanese woman. She stands at 157 centimeters (5.2 feet) and weighs 43 kilograms (95 pounds), with the capability to recognize faces, speech, and ambient sounds.
What makes Miim particularly remarkable is her ability to replicate human facial expressions and movements with incredible precision. She’s often described as 'super-realistic' and even has the talent to dance. When Miim made her debut on the catwalk in 2009, photographers eagerly captured images of her striking poses, smiling, and even pouting. The designers at AIST revealed that they chose to make her face hyper-realistic, but avoided giving her a similarly detailed body, fearing it might be 'too creepy.'
6. PARO

Who can resist the charm of baby harp seals? The Japanese company AIST certainly couldn’t: They’ve created a remarkably lifelike robotic seal named PARO, designed for therapeutic purposes. PARO interacts with people in ways similar to a real baby seal by moving its head and flippers, and making sounds. It uses five sensors (audio, light, tactile, posture, and temperature) to assess its environment. What makes PARO such an effective therapeutic companion (besides its cuteness) is that it remembers how it’s treated and responds accordingly. For instance, if you hug it after it squeaks in a certain way, it will squeak like that more often. However, if it makes movements or sounds you don’t like and you scold it, PARO learns not to repeat those actions, which might be a bit eerie in some scenarios.
PARO holds the Guinness record as the world's most therapeutic robot, thanks to the positive social and psychological effects it has on patients. Not only does it reduce stress, but it also enhances interaction between patients and caregivers. PARO is used in various settings, including hospitals and nursing homes, offering patients the comforting presence of a pet without the hassle of upkeep. It can also express emotions to its caregivers, and remains the top 'robopet' for therapy.
5. FACE

While many scientists avoid creating robots that closely resemble humans due to the Uncanny Valley theory, researchers at the University of Pisa are determined to challenge that concept. They’ve developed a robot called FACE, which is groundbreaking for its ability to mimic realistic human expressions. Unlike most robots that can express just five or six basic emotions, FACE can replicate these emotions (happiness, sadness, disgust, amazement, indifference, and fear) as well as the nuanced emotions that exist between them. Equipped with 32 motors in its face and upper body, FACE can produce lifelike human-like expressions. Researchers hope that FACE will be useful in various fields, including teaching children with autism to interpret emotions through facial expressions.
4. Actroid

While the HRP-4C is known for its highly realistic humanoid face, the Actroid takes it a step further with a lifelike body and even more sophisticated human-like behaviors. Created by Kokoro Company Ltd., the Actroid has undergone several iterations. Its air-powered actuators, strategically placed in the upper body, enable it to react to different forms of tactile stimuli. For instance, if it senses an approaching slap, it can quickly move out of the way or even retaliate, while a tap on the shoulder will be met with a more relaxed response. Actroid is also capable of subtle human-like movements, including head and eye gestures, and even simulates breathing.
Actroids can be programmed to learn additional human movements, although their movement capabilities are limited, and they must be securely supported in a sitting or standing position. In addition to the original Actroid model, Repliee Q-1, Kokoro developed Repliee R-1, which takes the form of a young Japanese girl. Kokoro, alongside Osaka University, has a goal of creating robots so realistic that people won't realize they're interacting with one. The results are impressive: many people mistake Actroids for humans during the first few minutes of interaction. Some even forget they're conversing with a robot due to how naturally they move and react. Another notable creation is Geminoid, a robot developed and designed by Hiroshi Ishiguro.
3. ASIMO

Created by Honda, ASIMO (Advance Step In Innovative Mobility) was first introduced to the world in October 2000. While it's not particularly imposing—standing at just 1.3 meters (4.3 ft) tall and weighing 54 kilograms (119 lbs)—what makes ASIMO remarkable is its impressive functionality. Designed as a personal assistant, ASIMO’s purpose is to aid those who are unable to assist themselves. Powered by a battery, ASIMO doesn’t think on its own, but can be controlled through a computer, a controller, or even voice commands.
At first glance, it might seem like a typical robot, but ASIMO takes it further with the ability to recognize and interact with people. It can sense postures, gestures, sounds, and even faces. For example, if you enter a room, ASIMO will turn to face you and shake your hand if you extend it. It can even distinguish between up to 10 different people. ASIMO has been featured at various conventions and currently performs in a show at Disneyland. Despite not being the most cutting-edge robot, ASIMO’s capabilities and humanoid traits keep it relevant among the latest generation of androids.
2. Atlas
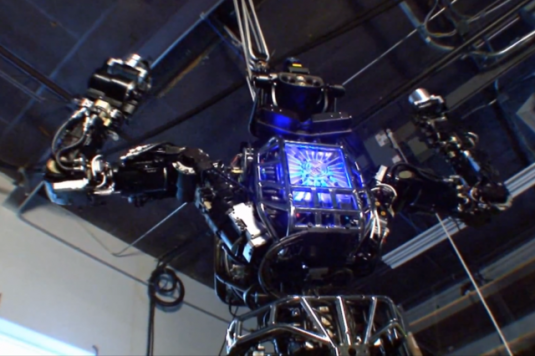
On July 11, DARPA unveiled one of the most advanced robots to date—Atlas. Standing nearly two meters (six feet) tall and weighing around 150 kilograms (330 lbs), Atlas was developed by Boston Dynamics to serve as a humanoid responder in hazardous situations, such as nuclear disasters. It is scheduled to take part in DARPA’s robot challenge in December, with Boston Dynamics continuing to refine its software.
Although Atlas already looks like it belongs in a sci-fi movie, things get even more impressive when you realize what it can actually do. With 28 hydraulic joints in its arms, legs, torso, and head, along with various sensors and a real-time onboard computer, Atlas can sense and respond to its surroundings with remarkable precision. It can perform basic tasks like walking, grabbing, turning, and providing visual feedback, but it can also do more complex tasks such as climbing ladders, driving a car, and attaching a fire hose to a valve. Thanks to its advanced sensors and real-time computer, Atlas can even map and analyze its environment from a distance. DARPA’s robot challenge is designed to push robotics like Atlas to new heights, and the organization is confident that the robot’s capabilities will soon extend to real-world applications as well.
1. Morpheus

Controlling a robot with a joystick or gestures is one thing, but what if you could control it just by thinking? Mind-controlled robotics is a growing field, and it has already been applied to small drones. One such breakthrough is the robot known as Morpheus, which can follow commands based solely on thoughts. The process uses a non-invasive swim cap embedded with electrodes, boasting an impressive success rate of up to 94 percent. This is a significant improvement over previous systems that required electrodes to be surgically implanted in the operator’s skull. Developed by Rajesh Rao at the University of Washington, Morpheus is expected to offer a range of applications, including companionship, assistance, and rescue missions.
