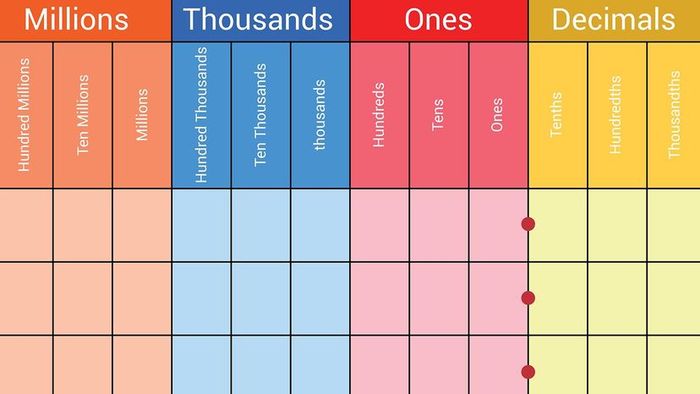
 This chart illustrates how different parts of a number align with their respective value categories. zizou7 / Shutterstock
This chart illustrates how different parts of a number align with their respective value categories. zizou7 / ShutterstockUnderstanding place values is a key aspect of mathematics and the number system, especially when working with whole and decimal numbers. A place value chart serves as a valuable tool, helping students visualize the location of each digit in a number and grasp its real value within that number's context.
For instance, the place value system can help identify which digit in a large whole number represents the ones, tens, hundreds, thousands, millions, or billions places. It can also assist in figuring out which digit to the right of the decimal point is in the tenths, hundredths, or thousandths places in a small decimal number.
Let's dive deeper into the concept of a place value chart and explore some helpful tips for using it effectively.
What Exactly Is a Place Value Chart?
A place value chart (also referred to as a decimal place value chart or place value table) is a graphical tool that helps students understand place value in numbers. It does this by visually depicting the position of each digit in a number, showing how each digit's value is determined by its place within the number.
Place value charts are typically divided into two main sections: the whole number section and the fractional section. These sections are separated by a decimal point, which plays a vital role in differentiating whole numbers from decimal fractions.
Understanding Face Value vs. Actual Value
By using a place value chart, students can shift their focus from a digit's face value to understanding how it contributes to the overall value of the number.
For instance, take the number 3,912.487. Students can place the digit 3 in the thousands column, 9 in the hundreds column, 1 in the tens column, 2 in the ones column, 4 in the tenths column, 8 in the hundredths column, and 7 in the thousandths column.
The chart helps clarify the distinction between a digit's face value and its actual value within a number. In this case, the place value of 4 is 0.4 — whereas in 4,815, the place value of 4 becomes 4,000.
The Whole Number Section of a Place Value Chart
The whole number section of a place value chart refers to everything located to the left of the decimal point in a number or decimal number.
Beginning from the right, the first column in a place value chart without a decimal point is the ones place, followed by the tens place, hundreds place, thousands place, ten thousands place, hundred thousands place, and continuing on to the billions place or even further.
Each step to the left multiplies the value of the digit by ten times the value of the digit to its right. For instance, in the number 5,674, the digit 4 is in the ones place, 7 is in the tens place, 6 is in the hundreds place, and 5 is in the thousands place.
The Decimal Section of a Place Value Chart
The fractional section of a place value chart comes into play when working with place values in decimal numbers. Digits to the right of the decimal point represent the tenths, hundredths, thousandths, and other places. Each position to the right reduces the value of the digit by a factor of ten compared to the position to its left.
By adhering to place value chart principles, students can grasp how a digit’s value diminishes as it shifts further to the right of the decimal point.
Incorporating Place Value Charts in Teaching
Decimal place value charts are specifically created to assist students in writing numbers that feature a decimal point while also enhancing their overall understanding of the number system. These charts clarify how the decimal point acts as a separator between the whole number part and the fractional part of a number.
Teachers can utilize place value charts as valuable educational tools when teaching students about place values. This is particularly useful when introducing children to small or large numbers, as well as decimal numbers.
By using place value charts, children can practice accurately writing numbers and build their confidence in working with a range of numbers. For example, a teacher may incorporate a printable place value chart in lessons or provide exercises where students place digits into the appropriate columns.
