From tiny black holes to the warping of space-time itself, from galaxies devouring one another to unseen matter that defies detection... space is filled with perplexing wonders. Here are ten of the most puzzling, sourced from MSN and Space.com:
10. Quasars

These luminous objects emanate from the farthest reaches of the observable universe, acting as reminders of the early, turbulent stages of our cosmos. Quasars emit more energy than the combined total of hundreds of galaxies. Scientists generally believe that these intense energy sources are massive black holes at the cores of distant galaxies. The image here shows quasar 3C 273, taken in 1979.
If you're looking for an awesome Halloween costume, check out the WALTER M. SCHIRRA One-piece Flight Training Suit available on Amazon.com!
Quantum physics reveals that, contrary to what we might think, what appears to be empty space is actually a dynamic mixture of “virtual” subatomic particles, continually appearing and disappearing. These brief-lived particles imbue every cubic centimeter of space with energy, which, as per general relativity, generates an anti-gravitational effect that causes space to stretch. However, the true cause of the universe's accelerating expansion remains a mystery.
8. Anti-matter
Much like Superman’s rival, Bizarro, the particles that make up ordinary matter have their opposite counterparts. For instance, an electron carries a negative charge, but its anti-matter counterpart, the positron, carries a positive charge. When matter and anti-matter collide, they annihilate each other, converting their mass into pure energy, as described by Einstein’s famous equation E=mc2. Some futuristic spacecraft designs are even considering anti-matter engines.
7. Mini Black Holes
According to a bold new theory known as the “braneworld” theory of gravity, there may be thousands of minuscule black holes scattered throughout our solar system, each no larger than an atomic nucleus. Unlike their larger counterparts, these tiny black holes are remnants from the Big Bang, and due to their proximity to a fifth dimension, they influence space-time in a unique manner.
6. Cosmic Microwave Background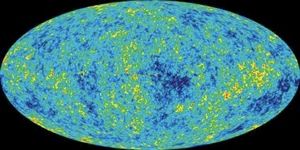
The Cosmic Microwave Background (CMB) is radiation from the early universe, a relic from the Big Bang. It was first detected in the 1960s as a faint radio signal that seemed to come from every point in space. The CMB is widely considered one of the strongest pieces of evidence supporting the Big Bang theory. Recent precise data from the WMAP project show that the CMB has a temperature of -455 degrees Fahrenheit (-270 degrees Celsius).
Click here to access 40,000 movies and TV shows with Amazon Prime Instant Video – 30 day free trial at Amazon.com!
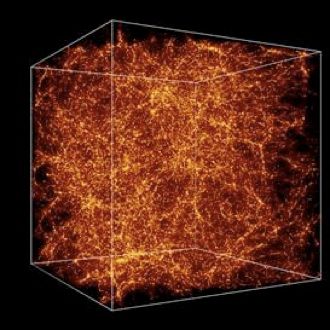
Scientists believe dark matter constitutes most of the matter in the universe, though it remains invisible and cannot be detected by current technology. Potential candidates for dark matter include lightweight neutrinos and unseen black holes. Some researchers even question the existence of dark matter, proposing that the phenomena attributed to it might actually be better understood through a deeper understanding of gravity.
4. Exoplanets
Before the early 1990s, the only known planets were those within our own solar system. Since then, astronomers have discovered over 190 exoplanets (as of June 2006). These planets range from massive gas giants that almost qualify as stars to smaller, rocky planets orbiting faint red dwarf stars. Despite extensive searches, no planets resembling Earth have been found yet. However, many astronomers are optimistic that advancing technology will soon uncover Earth-like worlds.
3. Gravity Waves
Gravity waves are ripples in the very fabric of space-time, a concept predicted by Albert Einstein’s general theory of relativity. These waves travel at the speed of light, but their effects are so minuscule that only enormous cosmic events, such as the merging of black holes, are expected to produce detectable waves. LIGO and LISA are advanced detectors designed to capture these elusive phenomena.
2. Galactic Cannibalism
Galaxies, like life on Earth, can consume each other and evolve over time. Andromeda, the Milky Way's neighbor, is currently devouring one of its satellite galaxies. Over a dozen star clusters, the remnants of past galactic feasts, are scattered across Andromeda. The image above depicts a simulation of the collision between Andromeda and our own galaxy, an event expected to occur in about 3 billion years.
1. Neutrinos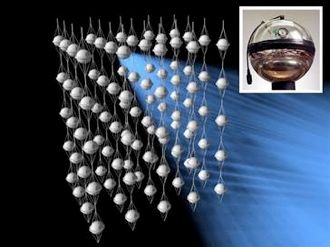
Neutrinos are elementary particles that have no electric charge and almost no mass, allowing them to pass through entire mountains of lead without being stopped. These ghostly particles are continuously passing through your body right now. Neutrinos are created in the core of healthy stars as well as during the explosive deaths of stars in supernovae. Neutrino detection projects, like IceCube, have placed sensors deep underground, beneath oceans, and even in massive blocks of ice to capture these elusive particles.
Sources: Space.com
Technorati Tags: science, space
