1. Tomatoes
Tomatoes are a staple in many households. They offer numerous health benefits, including improved vision, digestive health, stable blood pressure and blood sugar, better skin, and protection against urinary tract infections. Additionally, tomatoes contain lycopene, which helps protect the body from prostate cancer. Lycopene is an antioxidant known for fighting free radicals, which can destroy harmful and disease-causing cells.
Studies have shown that men who consume about 10 servings of tomatoes per week (roughly 800g) can reduce their risk of prostate cancer by 18%, according to research published in the journal Cancer Epidemiology, Biomarkers, and Prevention. Whether eaten raw or cooked, tomatoes still contain this beneficial compound, but research suggests lycopene is absorbed better when paired with fats, like olive oil.


2. Walnuts
Researchers at the University of Texas have found that walnuts can help reduce the risk of prostate cancer. The study, conducted on mice, showed that only 18% of mice fed one walnut per day developed prostate cancer, compared to 44% of mice not given walnuts. This finding is significant for humans, as prostate cancer is the second leading cause of cancer death in men in the United States.
According to the American Institute for Cancer Research (AICR), "Certain compounds in walnuts, such as alpha-linolenic acid (ALA), omega-3 fatty acids, antioxidants, and phytosterols, are weapons in the fight against cancer." Dr. Reiter, the lead researcher, noted that very few tumors appeared in the mice consuming walnuts, and those that did grow developed more slowly compared to the control group. Dr. Reiter remarked, "We were truly surprised by the effectiveness of walnuts in inhibiting prostate cancer in humans." Walnuts may not only help reduce the risk of prostate cancer but also breast cancer. In a study, mice consuming the human equivalent of 2.4 ounces of walnuts for 18 weeks showed significantly smaller and slower-growing prostate tumors compared to those eating the same amount of fat from other sources.

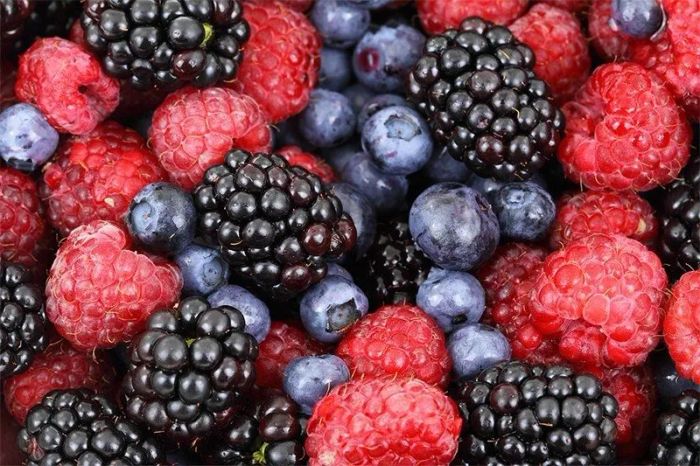
3. Berries
All fruits contain antioxidants that help fight cancer, but they also have relatively high sugar content. Studies have shown that even natural sugars found in fruit can increase the risk of cancer. Berries, especially strawberries, raspberries, and blueberries, are among the top superfoods for prostate health. These fruits are packed with potent antioxidants that combat free radicals, which may help prevent cancer. The high vitamin C content in berries also contributes to preventing prostate enlargement.
A study published in the Annals of Oncology found that people who consumed foods with a high glycemic index had a 26% higher risk of developing prostate cancer compared to those who ate foods with a low glycemic index. Cancer is also linked to oxidative stress—the imbalance between free radicals and antioxidants in the body. By preventing this process, cells are less likely to become cancerous. Many foods, like blueberries, raspberries, and strawberries, are rich in antioxidants and have a low glycemic index, making them effective in fighting oxidative stress.


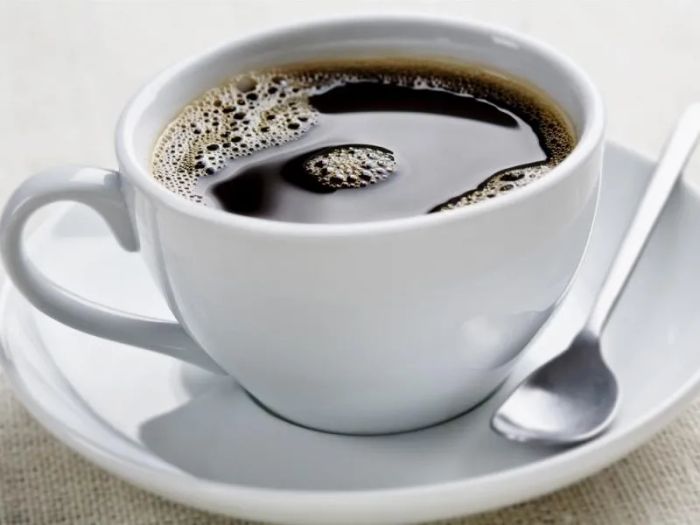
4. Coffee
According to a recent study published in the British Medical Journal (BMJ), drinking a few cups of coffee daily can help men reduce the risk of prostate cancer and improve survival rates if diagnosed with the disease. In this new research, experts from the Chinese University of Medical Sciences analyzed data from over 1 million men (including nearly 58,000 prostate cancer patients) across 16 studies conducted in North America, Europe, and Japan up to September 2020. The results showed that compared to those who drank little or no coffee (less than 2 cups per day), those who consumed more coffee had a 9-12% reduced risk of developing prostate cancer.
Notably, for those already diagnosed with the disease, daily coffee consumption could reduce the risk of death by up to 16%. To confirm these findings, scientists tested both caffeinated and decaffeinated coffee extracts on prostate cancer cells in the lab. Observations showed that the caffeinated extract significantly slowed the growth and spread of cancer cells, while the decaffeinated extract had no similar effect. This suggests that the cancer-preventing benefits of coffee are attributed to caffeine, not other compounds.


5. Carrots
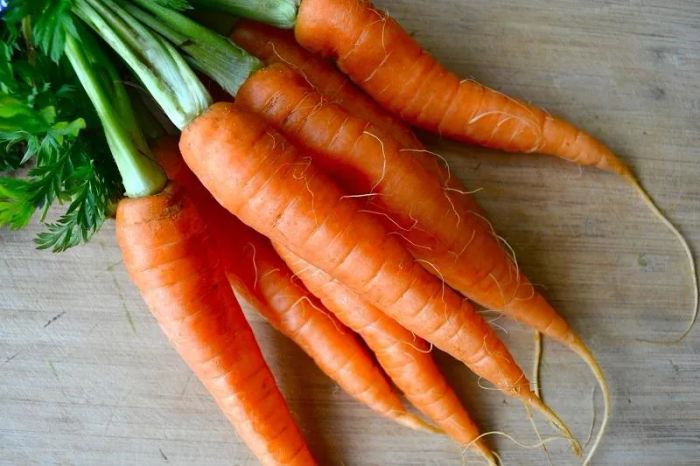
Carrots have long been known for their benefits to eye health. Recent research from Zhejiang University (China) has found that regular consumption of carrots can reduce men’s risk of developing prostate cancer by 18%. The study analyzed and combined results from 10 global studies, focusing on the anti-cancer properties of carrots. Most of these studies compared prostate cancer rates between two groups: those who ate carrots 3-5 times a week and those who ate them once a week or less.
When the research results were synthesized, the team concluded that carrots play a significant role in reducing the incidence of prostate cancer, even when factoring in other risk-increasing factors (such as obesity). It is known that the risk of cancer increases with age (men over 50 are more likely to develop tumors) and genetic factors (a family history of the disease). Although the exact mechanism by which carrots lower cancer risk is not fully understood, scientists believe this effect may be due to carotenoids, such as beta-carotene and lycopene, which give carrots their orange color. These compounds have long been proven to be potent anti-cancer agents by inhibiting free radicals that damage cells.


6. Pomegranate Juice
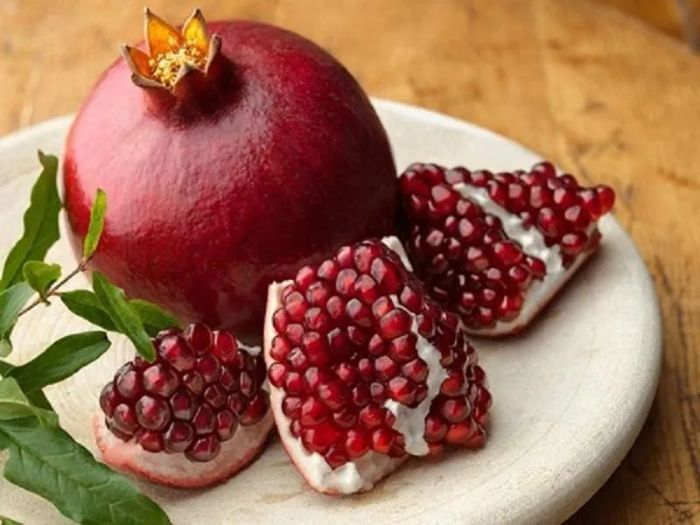
Pomegranate juice is rich in phenolic compounds with potent antioxidant properties. Recently, researchers in Italy have shown that pomegranate can help prevent heart disease in mice by inhibiting the buildup of oxidized fat deposits on artery walls. Dr. Hasan Mukhtar and colleagues at the University of Wisconsin (USA) added pomegranate juice to prostate cancer cells in culture. They observed that the growth of the cancer cells was slowed significantly as the concentration of pomegranate juice increased. The researchers then injected these cancer cells into mice and fed them pomegranate juice.
The researchers noted that in these mice, the cancerous tumors developed more slowly, were smaller in size, and the mice lived longer. Prostate cancer is most commonly diagnosed in men over 50, with 30,000 new cases reported annually in France alone. According to Dr. Mukhtar, there is still a long way to go before pomegranate juice can be used as a preventive or treatment option for prostate cancer. First, it is essential to identify the specific compounds in pomegranates with anti-cancer properties and understand how they work, followed by testing in animals and humans.


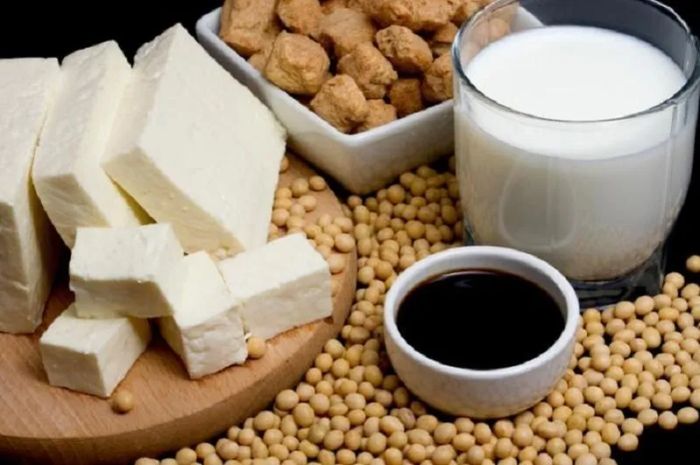
7. Soybeans
Prostate cancer, which leads cancer rates among men, is a disease that causes constant concern. Not only does it impact physical health, but it also silently shortens the average lifespan of men worldwide. Regular consumption of soybeans can reduce men's risk of developing this common male disease. Studies on prostate cancer patients show that eating soy-based foods can lower PSA levels. PSA is a protein primarily produced in the prostate, and while it is normally present in small amounts in the blood, elevated PSA levels are a sign of prostate cancer.
A meta-analysis of 24 epidemiological studies from both Asia and the West revealed that men who consume soy daily have a 25% lower risk of prostate cancer compared to those who do not consume soy. With modern research debunking the myth that soy decreases male vitality, men can now confidently incorporate soy-based foods into their diet to protect their health.


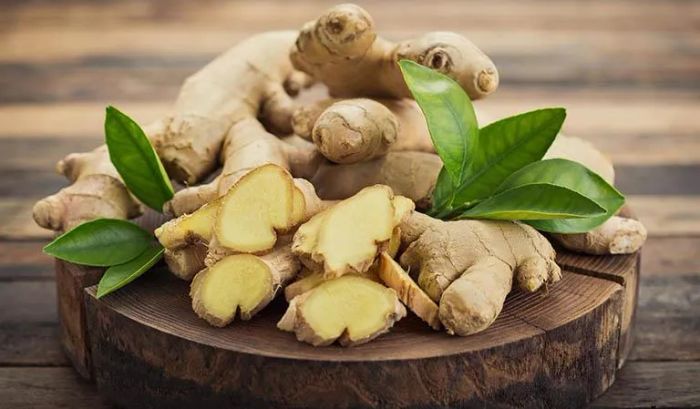
8. Ginger
With its antibacterial and anti-inflammatory properties, ginger is highly effective in treating prostate cancer. When consumed regularly, ginger helps slow the growth of cancer cells. It's also beneficial for patients undergoing chemotherapy, as it can alleviate side effects like nausea and vomiting. Recent research from Georgia State University has demonstrated that certain natural plants, including ginger, can inhibit cancer cell growth without harming the body. Ginger extracts, specifically, have shown promise in treating prostate cancer, a common illness among men.
In 17 studies conducted on both animals and humans, experts found that ginger not only reduces tumor size but also prevents and slows the metastasis of cancer cells to other parts of the body. Notably, when ginger extract was applied to prostate cancer cells in a petri dish, it inhibited the growth and slowed the cell division process. Some cancer cells even shrank and were destroyed.


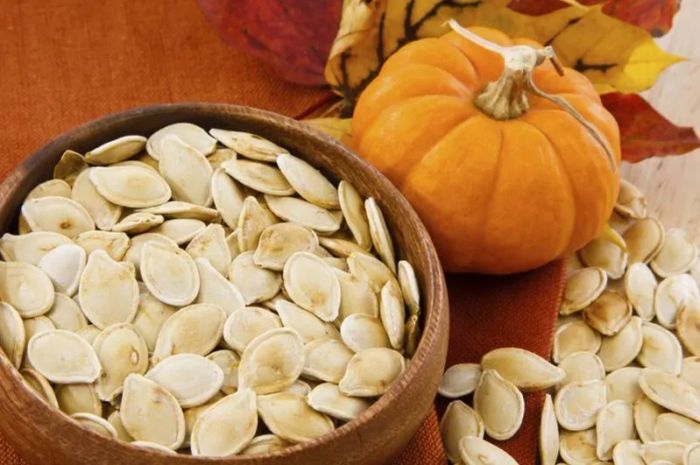
9. Pumpkin Seeds
Pumpkin seeds play a crucial role in treating a range of conditions affecting the prostate and bladder. Rich in zinc, pumpkin seeds help boost the body's immune system. Additionally, scientific evidence shows that pumpkin seeds aid in detoxifying the body. According to Health Sina, pumpkin seeds are highly nutritious and offer numerous health benefits. Recent studies have revealed that these seeds help protect the prostate in men. American scientists recommend consuming about 50 grams of pumpkin seeds daily (equivalent to 20-25 seeds, each weighing an average of 68 mg) to effectively prevent prostate issues.
Researchers explain that prostate secretion functions are dependent on fatty acids. Since pumpkin seeds are rich in fatty acids, they help maintain optimal prostate function. Furthermore, these seeds contain active compounds that reduce inflammation in the prostate, thus helping to prevent prostate cancer. Pumpkin seeds have also been shown to improve sperm quality. Experts note that pumpkin seeds contain a high amount of zinc, which, according to Western medicine, not only benefits the prostate but also increases sperm count. Traditional Chinese medicine also asserts that foods rich in zinc can enhance male fertility. In addition to pumpkin seeds, other zinc-rich foods like chestnuts and peanuts can also contribute to improved sperm quality.


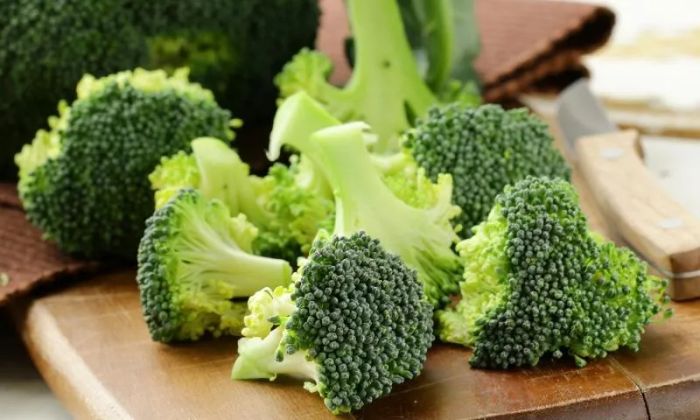
10. Broccoli
Prostate cancer is the second most common cancer diagnosed in men worldwide. Studies show that the sulforaphane in broccoli works by influencing large non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs), offering a new approach to prevent or slow the progression of malignant cells. One particular lncRNA, LINC01116, is found to be upregulated in prostate cancer cells, but its levels can be reduced through treatment with sulforaphane.
Research indicates that sulforaphane treatment may help normalize lncRNA levels. The effect of diet on lncRNA expression is still not fully understood. In this study, when LINC01116 was disrupted, the risk of prostate cancer cells forming colonies was reduced by four times. Researchers believe this study supports the idea that lncRNAs are an exciting new avenue for cancer prevention research, and dietary chemicals may alter their expression.


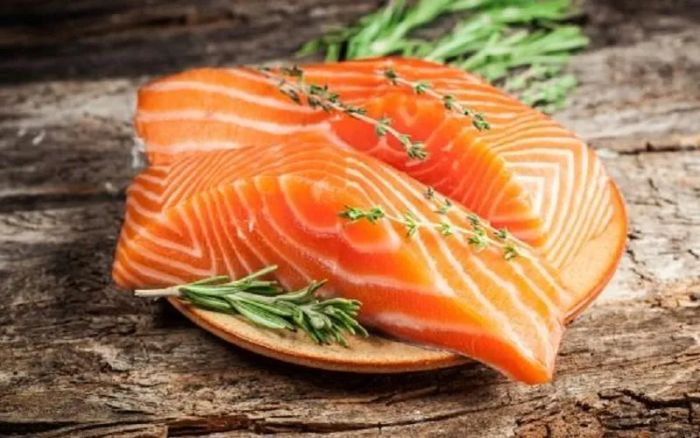
11. Salmon
Prostate cancer is one of the most common cancers affecting men worldwide. Some easily accessible foods can help reduce the risk of developing this disease. While there is no definitive way to prevent prostate cancer, incorporating certain foods into your daily diet can strengthen your immune system and lower your risk, including salmon.
“Men who follow a Mediterranean diet are less likely to develop prostate cancer,” says Lisa Cimperman, a nutrition expert at the Institute of Nutrition and Dietetics. A key component of the Mediterranean diet is fish, especially fatty fish like salmon. Salmon is rich in omega-3 fatty acids, a type of unsaturated fat that has been proven to help prevent prostate cancer. Other fatty fish like sardines, mackerel, and halibut are also rich in omega-3s.

12. Brazil Nuts
“One of the key minerals that helps prevent prostate cancer is selenium,” Espinosa adds. Selenium levels tend to decline with age. Studies show that men with higher selenium levels are less likely to develop prostate cancer. Brazil nuts are an excellent source of selenium: Just 6-8 nuts contain more than 700% of the daily selenium requirement. Consuming Brazil nuts has been linked to a reduced risk of prostate cancer.
A study published in the National Cancer Institute Journal found that selenium in these nuts may help reduce the risk of stomach and esophageal cancers. Other studies suggest that it also has the potential to combat breast, prostate, lung, and colon cancers. Additionally, selenium in Brazil nuts is beneficial in reducing the risk of heart disease by combating inflammation and oxidative stress, factors that contribute to plaque buildup in arteries, leading to coronary artery disease and heart attacks.


