Warning: Beer products are only for individuals over 18 years old.
Based on the information below, you can further consider and manage the amount of alcohol consumption daily or weekly in your body.
1. Potential Side Effects of Drinking Beer
Here are 8 reasons scientifically proven why drinking too much beer can lead to some serious health consequences if the drinker exceeds the recommended limit.
1.1 High Blood Sugar Levels
According to scientific research, consuming any type of alcohol, including beer, can affect the amount of glucose in our bodies. After the liver converts glycogen into glucose, it releases this substance into the bloodstream.

At this stage, if you drink more than the recommended amount, the side effects of daily beer consumption can be significant. Specifically, the alcohol in the beverage can induce feelings of hunger. Consequently, you may eat more food, which can lead to higher blood sugar levels.
1.2 Beer as a 'Diuretic'
When you're looking to quench your thirst on a scorching day, a cold glass of beer can be a soothing remedy. The key here is that while the body's natural antidiuretic hormones retain fluids, consuming beer slows down the release of these hormones.
As a result, you may feel the urge to urinate more frequently, especially after drinking a few beers. That's why drinking beer before engaging in any strenuous physical activity is extremely detrimental. Your body will lose fluids through sweat and urine in such situations.
1.3 Heart-Related Issues
Some studies have suggested that beer consumption may be beneficial for the heart. However, you can only reap the benefits of beer under the condition that you drink an appropriate amount. If you're dealing with cardiovascular diseases, drinking too much can weaken your heart health.
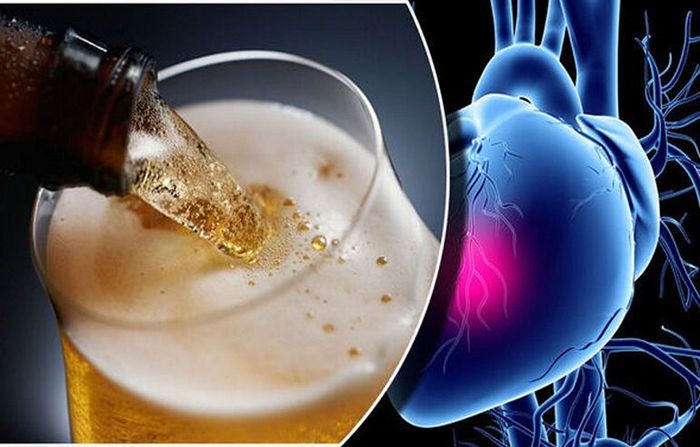
What's worse, consuming high doses of beer over a long period is known to increase the mortality rate among heavy drinkers and frequent binge drinkers.
1.4 Unwanted Weight Gain
Weight loss is another 'deceptive trick' when it comes to the side effects of beer. Compared to craft beer, commercial beer contains fewer nutrients but more calories. If you exceed the recommended amount, all your weight loss efforts will ultimately come to naught.
Specifically, the liver will convert the alcohol in beer into acetate. Subsequently, this compound will be burned for energy. At this point, excessive beer consumption can lead to the accumulation of excess fat in certain parts of the body such as the abdomen and hips. By the end of the day, you may be shocked by the increased weight and a few extra centimeters added to your waistline. Excess weight and obesity can catch you off guard when you drink too much beer.
1.5 Alcohol and Beer Addiction
Alcohol and beer addiction remains the most serious side effect of beer consumption. When dependency reaches a critical point, alcohol and beer will take center stage in your life. As a result, you may neglect or abandon important activities and relationships. You might spend a significant amount of time just thinking about beer, engaging in consumption activities, using beer, or you may have to recover from the effects of drinking alcohol.
1.6 Gluten Sensitivity
Hops and malt, grains (most commonly barley malt) are also essential input materials in the beer production process, alongside water.
Most beer varieties found on the market use barley malt as the main ingredient. And you know what? Barley contains a large amount of gluten, which is a type of protein. If you're diagnosed with gluten sensitivity, drinking beer may cause unwanted symptoms.
1.7 Decline in Sleep Quality
1.5 Decline in Sleep Quality
According to researchers, while having a beer may improve sleep quality, the alcohol in beer is known to have negative impacts on your natural sleep cycle. The more beer you consume and the closer to bedtime, the more likely you are to experience reduced sleep quality. This is because alcohol in beer can trigger the release of stomach acid, potentially increasing the likelihood of acid reflux and other negative effects on sleep quality.
1.8 Beer's Impact on Skin: Acne and Infection
Most beer varieties on the market today contain a substance called furfural. It's an enzyme inhibitor added in the fermentation process of beer production. Our bodies often process alcohol as a type of sugar, so it may contribute to inflammation and widespread acne.
2. How to Minimize Risks from Beer's Side Effects?
After considering the side effects of daily beer consumption, it's advisable to take breaks from regular beer drinking to reduce the risk of dependence. If beer drinking is your hobby, it's best to drink in moderation: a maximum of 2 glasses for men and only 1 glass for women per day.

Another solution is to fill your meals with healthy foods. Vegetables, fish, and lean meats tend to be low in calories. Additionally, they're excellent choices to make us feel full, reducing the likelihood of reaching for unhealthy foods during beer sessions.
Your body won't store too much fat unless you consume more calories than you burn. Therefore, you can mitigate the side effects of beer drinking by engaging in appropriate exercise to burn off extra calories after drinking alcohol. Some entertaining yet effective physical activities you may consider include gym workouts, joining dance classes, yoga, or even swimming.
If you find yourself sensitive to gluten, you should switch to beers made with gluten-free compounds to eliminate the adverse effects of beer.
3. Conclusion
In conclusion, it's no surprise that beer consumption has both pros and cons. However, the side effects of daily beer drinking can be controlled if we lead an active lifestyle.
If you're already a moderate drinker and seeking high-quality beer options, Mytour.vn always provides information on various beer products you may be looking for. Compare beer prices on Mytour.vn before purchasing to save time considering and selecting.
