A. Câu điều kiện loại 1 và cách áp dụng
Nếu bạn muốn dự đoán một hành động hoặc sự việc có thể xảy đến trong tương lai, nếu nó đi kèm với một điều kiện nhất định khác thì hãy sử dụng câu điều kiện loại 1. Đây là dạng câu điều kiện căn bản nhất mà những người bắt đầu học Tiếng Anh cần phải nắm vững và sử dụng thành thạo.

1. Cấu trúc câu điều kiện loại 1
Các loại câu điều kiện nói chung đều bao gồm hai mệnh đề: mệnh đề “nếu” (mệnh đề điều kiện, đi kèm “if”) và mệnh đề “thì” (mệnh đề chính, đề cập đến hành động, sự việc sẽ xảy ra trong điều kiện đó.
If + S + V(s/es), S + will/can/shall + V(nguyên mẫu)
IF+ thì hiện tại đơn, Will + Động từ nguyên mẫu
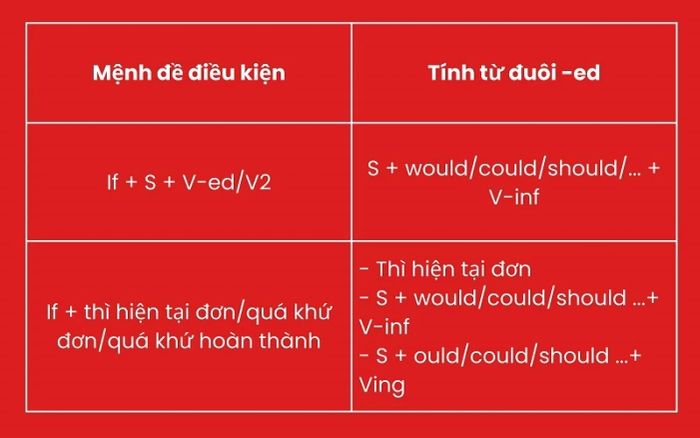
- Trong một số trường hợp, cấu trúc của câu điều kiện loại 1 có thể thay thế 'will' bằng 'must/should/have to/ought to/can/may'.
- Mệnh đề điều kiện (mệnh đề “if”) có thể đứng ở vế đầu hoặc vế sau câu và thường được sử dụng trong thì hiện tại đơn. Mệnh đề chính thường sử dụng trong thì tương lai đơn.
2. Cách sử dụng câu điều kiện loại 1
- Được dùng để biểu thị sự việc có thể xảy ra trong hiện tại hoặc tương lai:
Ví dụ về câu điều kiện loại 1: If I wake up early, I will arrive at work on time.
- Sử dụng để đề xuất hoặc gợi ý:
Ví dụ về câu điều kiện loại 1: If you require assistance, I am available to help.
- Sử dụng để cảnh báo hoặc ám chỉ hậu quả:
Ví dụ về câu điều kiện loại 1: If you skip your training sessions, your performance may suffer.
3. Điều cần lưu ý khi áp dụng câu điều kiện loại 1
- Trong một số trường hợp, cấu trúc của câu điều kiện loại 1 có thể chấp nhận thì hiện tại đơn trong cả hai mệnh đề.
Ví dụ: If I feel like dancing, join me, please.
- Mệnh đề “if” có thể được sử dụng trong thì hiện tại tiếp diễn hoặc thì hiện tại hoàn thành.
Ví dụ: If I continue to study, I'll complete my project by tomorrow.
- Mệnh đề chính có thể dùng trong thì tương lai tiếp diễn hoặc thì tương lai hoàn thành.
Ví dụ: If I arrive early at the restaurant, I'll order our meal in advance.
4. Câu điều kiện loại 1 phủ định
Công thức câu điều kiện loại 1 phủ định:
If + S1 + not / don’t / doesn’t + V-inf + O, S2 + will / can / may… + V-inf + O.
Ví dụ câu điều kiện loại 1 dạng phủ định: If you don’t understand the question, I can explain it to you.
Có thể sử dụng 'Unless + thì hiện tại đơn' thay cho 'If not + thì hiện tại đơn'.
For example: If we don't pass the driving test, we cannot obtain a driver's license.

5. Inverted form of conditional type 1
Inverting conditional type 1 helps to make the sentence more polite and is often used when making requests or asking for favors.
Inverted form with the verb to be in conditional type 1:
Should + S + (not) + be + … + S + will/may/can + V
Example of inverted form in conditional type 1:
If you are regularly late to work, you won’t get a bonus this month.= Should you be regularly late to work, you won’t get a bonus this month.
(If you frequently come to work late, you won't receive a bonus this month.)
If the children are fine, their parents will be happy.= Should the children be fine, their parents will be happy.
(If all the children are healthy, their parents will be happy.)
Inversion with the main verb in conditional type 1:
Should + S + (not) + V + … + S + will/may/can + V
Example of inverted form in conditional type 1:
If you go to work late regularly, you won’t get a bonus this month.= Should you go to work late regularly, you won’t get a bonus this month.
(If you frequently arrive late to work, you won't receive a bonus this month.)
If the children feel happy, their parents will be satisfied.= Should the children feel happy, their parents will be satisfied.
(If the children are happy, their parents will be satisfied.)
Note:
– The use of 'should' in the inversion of conditional type 1 does not mean 'should'; using 'should' does not change the meaning of the IF clause.
– If the original IF clause does not contain 'should', we borrow the modal verb 'should' and perform inversion according to the structure above.
– If the IF clause contains 'should', simply move 'should' to the beginning of the sentence.
Example:
If your students should need my help, I’ll be there in 10 minutes. = Should your students should need my help, I’ll be there in 10 minutes.
(Should your students need my assistance, I will be there in 10 minutes.)
6. Rewrite conditional type 1 sentences
Types of exercises for rewriting conditional type 1 sentences:
1) Verb form changing exercises
At the most basic level, the exercise will provide one clause, and you simply need to determine the type of conditional and apply the correct formula.
2) Exercises rewriting using IF
In this exercise type, you will be given two separate sentences, and your task is to combine them into a compound sentence using IF or connecting words like so = that’s why, because.
For this type, if you notice:
– Both sentences are in the future tense, use conditional type 1 (not negative).
– One is in the present, the other in the future / present, use conditional type 2 (negative).
– If there is a past involved, use conditional type 3 (negative).
Note:
– Negating a sentence with 'not' means we use it without 'not' and vice versa.
– If 'because' is present, replace 'if' immediately with 'because'.
– If 'so' or 'that’s why' is used, place 'if' opposite to their positions.
3) Rewriting sentences using unless instead of if
4) Rewriting sentences changing from without to using if
Replace Without = If…. not…., keep the rest as is (depending on the specific sentence meaning).
5) Rewriting sentences changing from Or, otherwise to using if
This type often has the structure of an imperative sentence + or, otherwise + S will…
Proceed as follows:
If you don’t (rewrite, remove or otherwise)
6) Rewriting sentences changing from But for to using if
Use: if it weren’t for instead of but for, keep the rest the same
Types of conditional sentences imply:
Provided (that), providing (that) (as long as) = if
In case = in the event of
C. Exercises Application
The exercises below help you practice using conditional sentence structures type 1 and 2. Let's refer to them.
1. Conditional Sentence Type 1 Exercise: Choose the correct option
1.1. If I (were/was/would be) ____ rich, I (will try/would try/tried) ____ to help the orphans.
1.2. What (would you do/will you do/did you do) ____ in the event of encountering a snake in your garden?
1.3. If I (was/would be/were) ____ you, I (would ask/will ask/would ask) ____ for her assistance.
1.4. If he (found/would find/had found) ____ a child in the street, he (would take/took/would take) ____ him to the police.
1.5. If she (were/was/would be) ____ a color, she (would be/was/were) ____ blue.
2. Conditional Sentence Type 1 Exercise: Choose the correct option
2.1. If I (had/have had/had had/should have had) __________ the same problem you had as a child, I might not have succeeded as well as you have.
2.2. I (would have visited/visited/had visited/would visit) __________ my mom sooner had someone told me she was in the hospital.
2.3. (Should I need/Should I have needed/I have needed/If I needed) __________ more help, I would call my sister.
2.4. (Had I known/Did I know/If I knew/If I had known) __________ then what I know today, I would have saved myself a lot of time and trouble over the years.
2.5. Do you think there would be less misunderstanding in the world if all people (spoke/speak/had spoken/were to speak) __________ the same language?
Để hiểu và áp dụng đúng cấu trúc câu điều kiện loại 1 và 2, bạn cần thường xuyên làm các bài tập dạng chọn lựa đáp án, hoàn thành câu… Thực hành hàng ngày không chỉ giúp bạn nhớ tốt kiến thức mà còn phát triển khả năng phản ứng nhanh với các bài tập cụ thể. Thường xuyên đọc các bài viết từ Mytour để học thêm nhiều kiến thức Tiếng Anh chính xác và thú vị nhé!