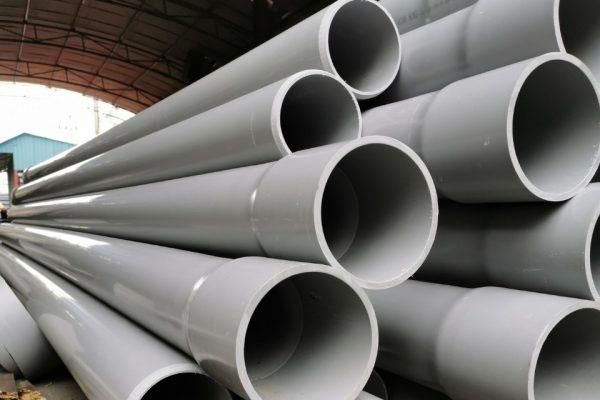
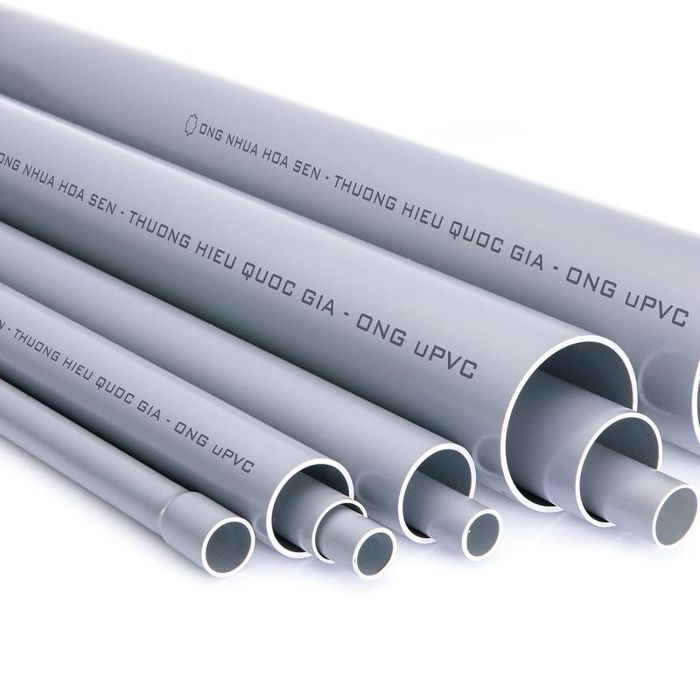
1. PVC Pipes
The first type among the most commonly used plastic pipes on the market today is PVC pipes. Typically, they are also referred to as rigid pipes.
Basic characteristics:
- When it comes to the composition of PVC pipes, you need to know that this type of plastic pipe does not use plasticizers in the mixing formula.
- The mixing composition of PVC pipes includes PVC resin powder with a K index of 65-66, heat stabilizers, internal lubricants, external lubricants, processing aids, fillers, colorants, etc...
- uPVC is a Polyvinyl Chloride that has not been plasticized.
Advantages of this type of pipe:
- Polymers Acrylic component creates durability, increasing the ability to withstand strong impacts.
- The application of stabilizing compounds helps uPVC plastic withstand the impact of heat and ultraviolet rays.
- uPVC plastic is shaped by wax, so it has an extremely smooth and shiny surface.
It is thanks to these advantages that PVC pipes have been chosen by many people. However, this is still not the highest quality or most durable type of pipe. If the requirements of the project are higher, you should consider other premium water pipes.


2. PPR Plastic Pipes
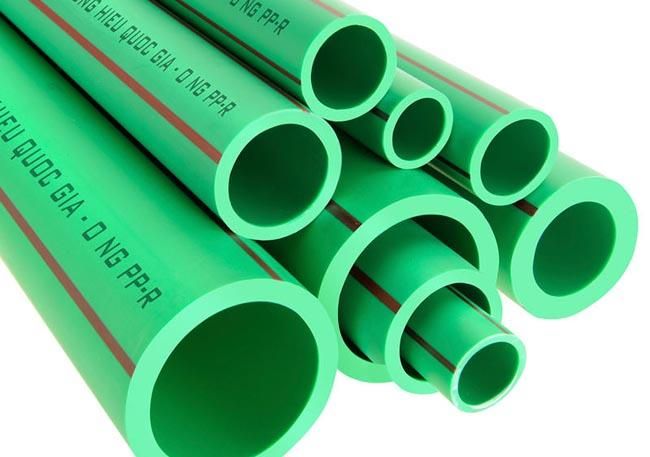
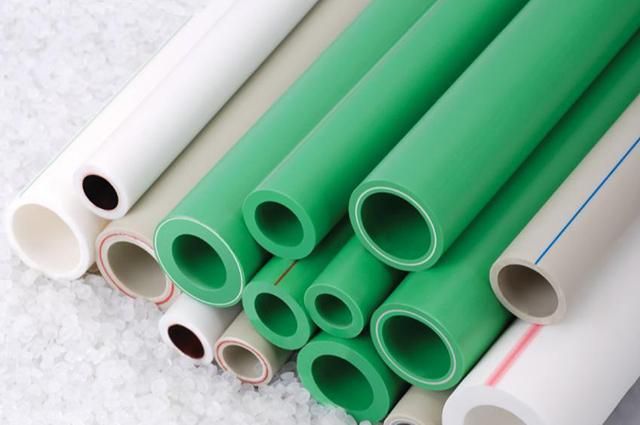


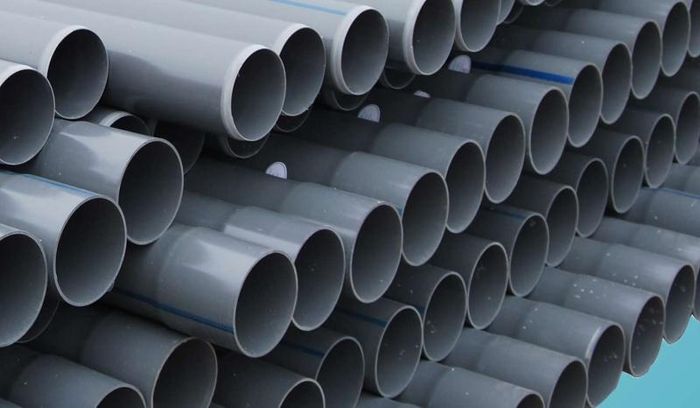
Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) pipes are formed from the polymerization reaction of vinyl chloride. The composition of flexible PVC pipes includes PVC resin powder (K65-K66), heat stabilizers, lubricants, colorants, plasticizers, etc. PVC pipes are manufactured using extrusion machines, either twin-screw or single-screw. Generally, PVC pipes produced on twin-screw extruders yield higher-quality products compared to single-screw extruders. This is because twin-screw extruders have better melting capabilities, allowing for direct use of the PVC resin mixture without pre-processing. Conversely, single-screw extruders require pre-made PVC resin pellets or additives in the mixing formula for proper melting.
PVC pipes find diverse applications in various aspects of life, from water supply pipes from water treatment plants to distribution stations, pipes delivering water from water treatment plants to households, sewage pipes in high-rise buildings, irrigation pipes in rubber, coffee, pepper, cashew, and tea plantations, and pipes supplying water in hydroelectric plants, etc.

PEX pipes, made from high-density cross-linked polyethylene (PEX-A), form a three-dimensional network, meeting the latest standards for clean water supply pipes in developed countries such as the United States, Europe, Singapore, etc.
PEX pipes boast several advantages, including high heat resistance, withstanding temperatures up to 90°C during normal operation and up to 100°C for short durations. They also excel in handling high pressure, withstanding 10 bars at 70°C and 20 bars at 20°C. Additionally, PEX pipes offer 99% UV resistance, outperforming PPR pipes with a dual-layer UV resistance of 99.9% thanks to a platinum protective layer. Their flexible design allows for easy installation even in tight spaces, and they save 30% installation time compared to traditional pipes. PEX pipes can reach lengths of up to 100 meters in coil form. This PEX piping system is considered the most robust and convenient water supply system, meeting the highest standards of hygiene and hydraulic performance.
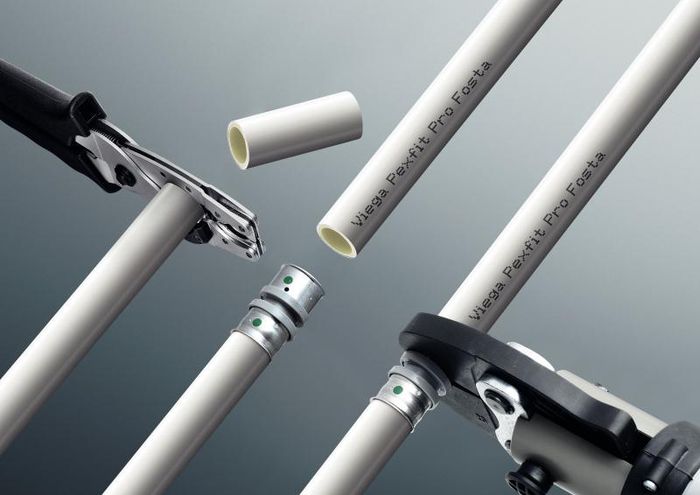
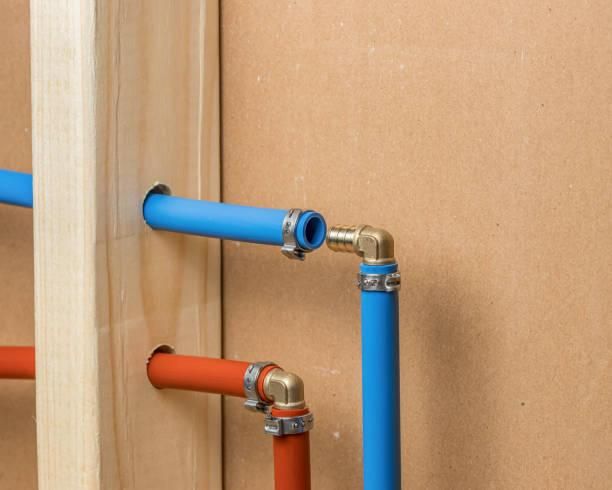


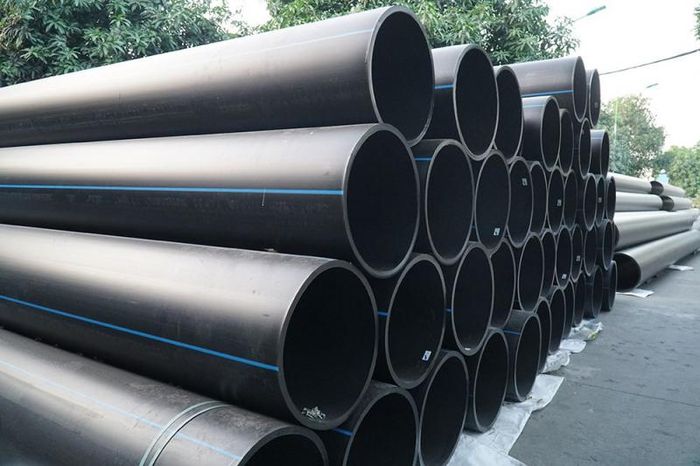
High-Density Polyethylene (HDPE) pipes are renowned for their strength and resilience, making them ideal for demanding applications in infrastructure and construction projects.
HDPE pipes are manufactured from high-density polyethylene plastic. This type of plastic is derived from crude oil, then purified using catalysts such as chromium, silica,... to create a high-density polyethylene with greater density and tensile strength compared to LDPE or PVC. Various additives are also incorporated to enhance the chemical properties of HDPE plastic.


