In today's era, we are familiar with terms like USB and USB Type-C, but USB Type A is often overlooked. Let's dive into what USB Type A is and unravel the design of the USB Type A charging port with Mytour Blog!
Details about USB Type A
USB Type A is one of the well-known USB ports that has been around for a while on computers, TVs, speakers, and various electronic devices. It has a rectangular shape and can only be inserted in one direction. Due to its familiarity among tech users, it's commonly referred to simply as USB, with no distinction between USB-A or USB Type A.
USB Type A has undergone various developmental stages, initially prevalent as USB 2.0, then upgraded to 3.0, 3.1, and 3.2. Subsequently, USB Type C emerged, replacing USB Type A, with the latest standard being USB4, leaving only USB Type-C.
Explore more:
Multi-functional genuine mini cameras
High-quality, budget-friendly computer keyboards
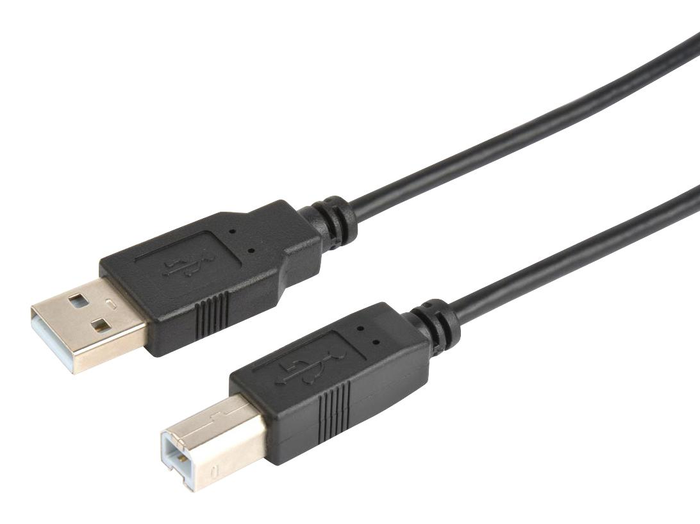 USB Type A connections often refer to the design of the USB port (Source: Internet)
USB Type A connections often refer to the design of the USB port (Source: Internet)What is USB Type A charging port?
The USB Type A charging port possesses the physical interface of the USB Type A with its characteristic rectangular shape. This was the prevalent charging port before the introduction of USB Type-C. USB Type A charging ports can be found in most removable charging adapters or the charging ports on laptops (used to charge mobile devices).
Typically, to establish data connections between computers, we use USB ports to connect devices together with cables. However, in the current era, all of this has been replaced by USB Type A ports.
Charging Speed of USB Type A Port
In reality, the USB Type A charging port is just a physical interface, and the charging speed, whether fast or slow, depends on the charging protocol and technology. Before the advent of USB Type C, Quick Charge by Qualcomm, Fast Charge by Samsung, and even the super-fast charging VOOC & Super VOOC were all based on the USB Type A charging port.
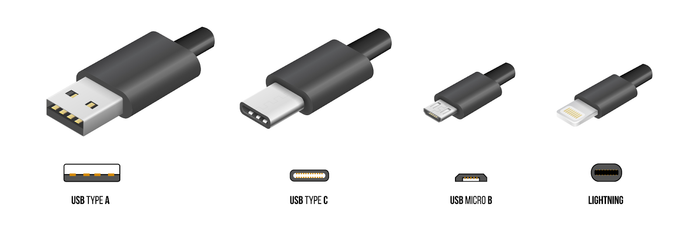 The plug types of current USB charging ports (Source: Internet)
The plug types of current USB charging ports (Source: Internet)How's the Connectivity?
USB Type A is widely used in most computer devices today, including desktops, laptops, tablets, etc. It is employed on computers to connect with wireless keyboards, mice, USB Flash drives, and to transfer data between devices. Additionally, USB Type A serves many other purposes.
Moreover, USB Type A is utilized for gaming devices like Xbox, Playstation, and can be found on speakers, Smart TVs, as well as numerous other devices.
Comparing USB-A and USB-C
Form, Design
The rectangular wide connection of USB-A has been updated with the USB-C design, aiming to save space for users and allowing electronic devices to be thinner than ever.
Alongside the changes in shape and design, modern USB-C ports also enable users to plug USB-C connectors in any direction. This is due to the symmetrical pin orientation on both the top and bottom of the USB-C connector.
In contrast, USB-A pins are only allocated to the bottom part of the USB-A port, preventing the reversal of the connector when plugged in.
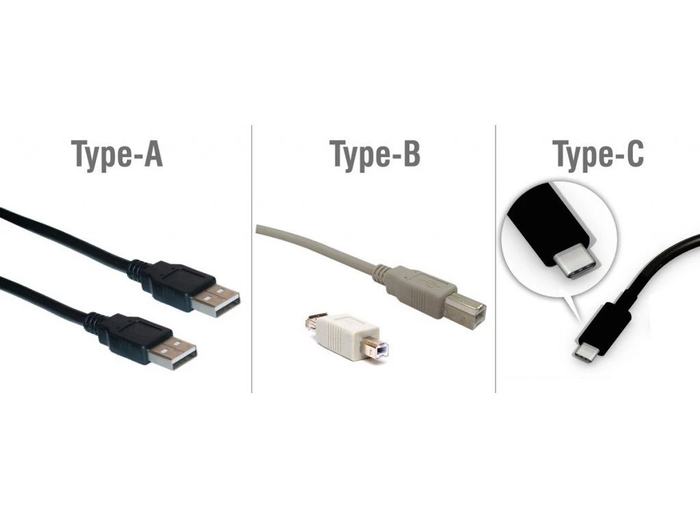 Distinguishing shapes and designs between USB-A and USB-C (Source: Internet)
Distinguishing shapes and designs between USB-A and USB-C (Source: Internet)USB Standards Compatibility
The latest USB 4.0 standard now mandates USB-C connectors while phasing out USB-A. USB 4.0 boasts data speeds of up to 40Gbps, enabling bidirectional power delivery of around 100W (powering large tech devices, from laptops to certain types of printers).
As a result, this is significantly more powerful than the recent USB 3.1 standard, with a maximum data transfer speed of 10Gbps.
Alternate Modes Support
The Alternate Mode feature, also known as USB-C's replacement mode, allows USB-C ports to be compatible with a broader range of data protocols. However, its support depends on whether hardware manufacturers decide to integrate it into their electronic devices.
This feature can be strategically arranged to become a single USB-C port incorporating Thunderbolt, HDMI, DisplayPort, Mobile High-Definition Link, and VirtualLink. You can integrate all these connections into a single USB-C port, allowing electronic devices to be thinner. All you need is a suitable adapter to access the Alternate Mode feature you want from the USB-C port.
You can integrate all these connections into a single USB-C port, allowing electronic devices to be thinner. All you need is a suitable adapter to access the Alternate Mode feature you want from the USB-C port.
In contrast to USB-C, USB-A does not support Alternate Mode. However, both USB types are designed to be compatible with the devices they connect to.
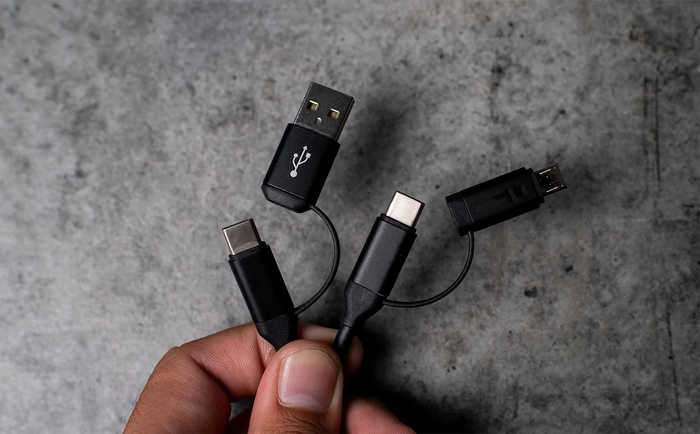 USB-A lacks support for Alternate Mode (Source: Internet)
USB-A lacks support for Alternate Mode (Source: Internet)Above are the fundamental insights into USB Type A that Mytour has compiled for our dear readers. We hope this article brings you valuable and interesting knowledge about USB types, especially USB Type A!
