1. Human Intelligence Boosted by Brain Folds
Have you ever wondered why humans are always smarter than other animals despite cohabiting on Earth? The answer lies in the folds of your brain. Unlike a flat surface, the brain's cortex is full of creases and folds of varying depths.
These folds, called sulci for shallow ones and gyri for deeper ones, enable our brains to process information more efficiently while conserving space.
2. Each Brain Contains Approximately 86 Billion Neurons
This number is truly impressive! With such a large quantity of cells, our brains ensure timely reception and processing of information to sustain bodily functions.
However, compared to African monkeys, humans have a modest number of brain cells, as these primates possess over 100 billion neurons.
3. Human Brain Isn't the Largest
Among Earth's inhabitants, humans are deemed the most intelligent species, leading many to believe we possess the largest brains.
However, that's not the case. The human brain typically accounts for about 2% of body weight (approximately 1.3 - 1.4 kg). Compared to creatures like sperm whales, our brains are much smaller, as their brains weigh between 7 - 8 kg.
4. Brain Doesn't Feel Pain
When you stub your toe or break your arm, the first sensation you feel is sharp pain, signaling injury and the need for immediate attention. This intense sensation is due to nerve cells transmitting information to the brain for analysis, allowing humans to have clear reactions to bodily touch.
However, surprisingly, the brain itself doesn't feel pain. More accurately, there are no pain receptors in the brain. Even feelings of dizziness or headaches are results of numerous tissues, nerves, and blood vessels surrounding the brain receiving warning signals of pain from nerve cells.
5. Brain Consumes 20% of Body's Energy
Despite comprising only 2 – 3% of body mass, due to excessive workload and duration, the brain consumes up to 20% of the body's energy.
Scientific research from the United States indicates that to maintain optimal bodily functions and accurate information processing, the brain requires the consumption of 25% of the body's glucose and 20% of its oxygen.
6. Human Brain Comprises Fat
Sixty percent of the human brain is made up of fat. This not only makes it the fattiest organ in the human body but these fatty acids also play a crucial role in brain function.
It's essential to ensure you're providing appropriate energy with nutrient-rich foods to enhance brain health.
7. Memory Capacity Surpasses Any Modern Machine
With its remarkable ability to memorize, the brain can help humans store data accurately, even surpassing the Encyclopedia Britannica fivefold. However, human forgetfulness often stems from infrequent mental exercises and the impact of harmful habits.
Although there's no precise research on brain capacity, some scientists estimate it ranges from 3 to 1,000 terabytes.


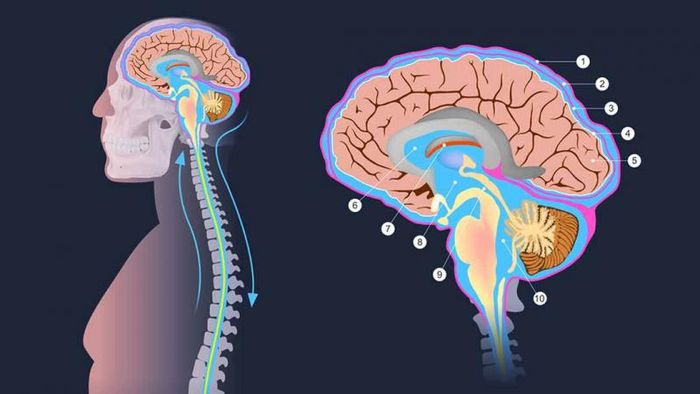
8. Spinal Cord: Key Communication Link Between Brain and Body
The spinal cord serves as the primary communication link between the body and the brain. Conditions like ALS or amyotrophic lateral sclerosis, a type of motor neuron disease, affect nerve cells in the brain and spinal cord, disrupting controlled movements. Another condition impacting both the brain and spinal cord is multiple sclerosis.
In this condition, the immune system attacks the protective covering of nerve fibers, causing communication issues between the brain and the human body. The human spinal cord stops growing by the age of 4.
9. Information Transmits to the Brain at Remarkable Speed
Information transmits to the brain at remarkable speed, traveling at about 431 km/h. When a nerve cell is stimulated, it generates an electrical impulse that propagates from one cell to another. Moreover, interruptions in this process can often lead to seizures.
10. Human Brain Can Generate 23W of Electricity
The human brain can generate approximately 23W of electricity, enough to power a light bulb. To achieve this remarkable feat, certain essentials are required. Simply maintaining a regular sleep schedule helps sustain the pathways in your brain.
On the other hand, sleep deprivation may increase the accumulation of a type of protein in the brain, linked to Alzheimer's disease.