 Curious about how a foldable phone screen operates? Are you familiar with its opening and closing procedures?
Curious about how a foldable phone screen operates? Are you familiar with its opening and closing procedures?Embracing the fusion of compactness and expansiveness, the realm of smartphones witnesses the emergence of foldable screens, epitomized by Samsung's Z Flip and Z Fold. Delve into the mechanics of folding displays with 24h Technology!
How do Foldable Screens Work?
Whether rigid or flexible, flat or curved, rollable or foldable, most screens operate on similar principles.
In reality, the images we perceive on screens are crafted from millions of pixels, achievable through various technologies. Thus, the market offers a plethora of display types such as OLED, LCD, micro-LED, and mini-LED, ensuring versatile and crisp visual experiences.
 Samsung phones feature foldable OLED displays. (Image Source: Trusted Reviews)
Samsung phones feature foldable OLED displays. (Image Source: Trusted Reviews)All those pixels are placed on a layer called the panel. Years ago, panels were thin glass sheets, fragile and prone to breakage. However, over the past decade, screen manufacturers have developed and produced flexible plastic panels that can bend without shattering.
The advent of plastic screens gave birth to the first unique curved-display phones, notably Samsung's Galaxy Note Edge, launched in 2014.
 Samsung's remarkable curved-display Galaxy Note Edge debuted in 2014. Source: Samsung.
Samsung's remarkable curved-display Galaxy Note Edge debuted in 2014. Source: Samsung.As technology advances, screen manufacturers continually research ways to safely increase the flexibility of plastic displays. This progress also addresses durability concerns, allowing screens to bend thousands of times without damage.
This advancement paves the way for today's foldable screens, enabling us to fold phones without worrying about screen breakage.
Flexible panels are just a small part of phone manufacturing. Scientists and engineers must also tackle other challenging issues, such as producing lightweight and flexible panels capable of withstanding mechanical pressure over extended periods. They must ensure that all bending and folding actions do not compromise display quality over time.
 Flexible OLED panels can bend seamlessly.
Flexible OLED panels can bend seamlessly.Engineers must develop a flexible protective layer for the screen and ensure that all other technologies applied to the screen continue to function normally.
Once all these requirements are met, another team must figure out how to integrate the flexible screen into a foldable phone while maintaining the extremely high standards demanded by manufacturers. It's truly a daunting task, so it's safe to say that to deliver the perfect foldable phone to users, manufacturers have invested a great deal of dedication.
Delve Deeper into How Foldable Screens Work
One thing you may not know is that all foldable screens on the market today are OLED. OLED screens do not have a backlight like LCDs; instead, pixels emit light on their own when powered.
That's why OLED panels are typically thinner and lighter, about 30% compared to LCDs. Additionally, OLED offers many other benefits, hence it's chosen for flexible displays, although flexible LCD displays still exist, but are relatively rare.
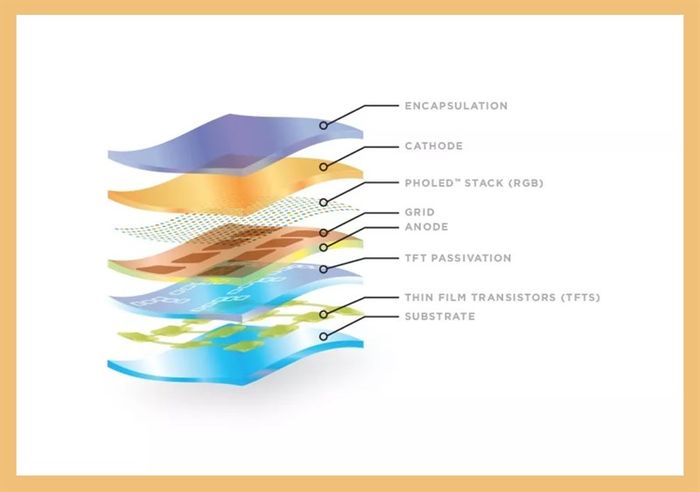 Structure of flexible OLED display. (Source: AndroidAuthority)
Structure of flexible OLED display. (Source: AndroidAuthority)To visualize how flexible OLED screens work, imagine them as a very thin layer cake. Each layer of this technology cake has a specific role, stacked together into an extremely thin package, just millimeters thick.
The substrate layer, also known as the motherboard, is the main layer of the screen, supporting all other layers. Most modern foldable devices use a substrate made of a flexible polymer called polyimide (PI). Due to its flexibility and insulation, particularly polyimide also boasts high mechanical strength and stable temperature.
The TFT layer is used on the surface of the screen, controlling energy supply to each pixel. It acts like an 'electrical grid' connecting all pixels on the screen. Unlike LCDs, on OLED screens, each pixel can be individually controlled, providing high contrast and low power consumption.
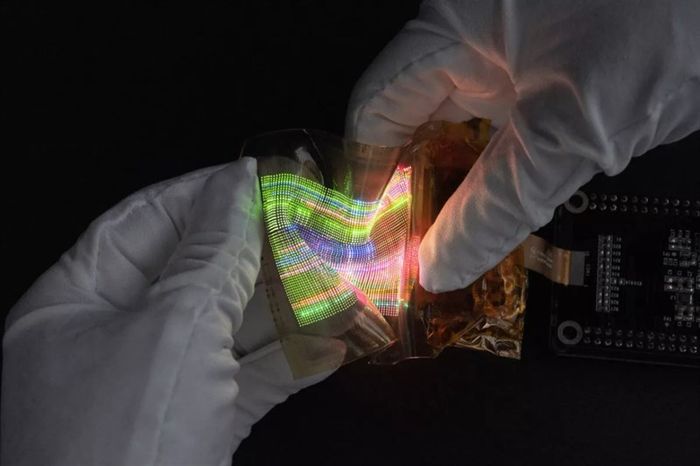 Royole's super flexible LED display 2. (Source: AndroidAuthority)
Royole's super flexible LED display 2. (Source: AndroidAuthority)The OLED layer is the light-emitting layer formed by individual pixel points, each pixel consisting of sub-pixels of 3 colors: red, green, and blue. Each pixel can achieve a specific color and brightness by adjusting the amount of power received by its sub-pixels. These pixels combine to form the images we see on the screen.
The cover layer, also known as the encapsulation layer, is the sealing and protective layer for other layers. It's also the layer that users directly touch when interacting with the foldable screen, typically made of polyimide. Recently, it's also manufactured from ultra-thin glass (UTG). Samsung has been using this material on its latest Z Flip and Z Fold phone series.
Other Interesting Facts about Foldable Screens
Foldable screens come in two types: inward folding and outward folding. Inward folding, like Samsung's Galaxy Z Flip series, hides the screen inside the device when folded, contributing to durability but may develop slight creases on the screen.
 Galaxy Z Flip4 features a convenient inward folding screen, compact in size.
Galaxy Z Flip4 features a convenient inward folding screen, compact in size.As for outward folding screens, the standout is the Huawei Mate XS 2, with its screen curved outward, leaving no creases on the display. However, there's a slight downside as the screen is prone to scratches, causing discomfort during use.
 The unique Huawei Mate XS 2 boasts an outward curved folding screen.
The unique Huawei Mate XS 2 boasts an outward curved folding screen.Most foldable phones on the market today can only fold once. However, Samsung once teased a phone that can fold two, three times - the Samsung Flex In & Out series, utilizing 'multi-foldable' technology.
 Samsung Flex In & Out utilizes 'multi-foldable' technology, capable of impressively folding up to two times. (Source: AndroidAuthority)
Samsung Flex In & Out utilizes 'multi-foldable' technology, capable of impressively folding up to two times. (Source: AndroidAuthority)There's also a type of foldable screen that doesn't require 'folding', which is extremely unique. They are designed to be flexible, capable of rolling up and almost disappearing inside the device. A prime example is the OPPO X 2021, teased by OPPO not long ago.
 OPPO X 2021 with a rollable screen, capable of retracting into the device. (Source: Frandroid.com)
OPPO X 2021 with a rollable screen, capable of retracting into the device. (Source: Frandroid.com)In addition to the screen, the hinge is also a crucial aspect of manufacturing foldable phones. Manufacturers have devoted a lot of effort and dedication to creating extremely sturdy, smooth-operating, consistent hinges that must also be compatible with phones without causing uncomfortable creases on the screen.
 The hidden hinge design on the Samsung Z Flip4 creates a seamless feel for the device.
The hidden hinge design on the Samsung Z Flip4 creates a seamless feel for the device.Another equally important factor is durability. In reality, the ability for the screen to fold may cause internal components to shift, leading to external elements such as water, dust, and pollutants easily infiltrating the device. There have been cases where multiple broken pieces were found beneath the screen, significantly affecting user experience, and screen damage is inevitable.
Nevertheless, with the relentless advancement of technology and the continuous evolution in user needs, electronic device manufacturers are all striving to develop and introduce more foldable screen technology products. Promisingly, in the future, we will experience a plethora of modern devices with unique foldable screens and high durability.
Conclusion
So there you have it, 24h Technology has explored with you how foldable screens work. Do you like this type of screen? Do you plan to get a phone with such a convenient screen? Leave a comment below and let us know!
See more:
- The first-generation Galaxy Z Flip has received the One UI 5.0 update!
- Hands-on with the Galaxy Z Flip4 Maison Margiela: Premium, luxurious look.
- Galaxy Z Fold series is on a shocking sale of over ten million, it's time to act!
