Connecting a router to a modem enables internet access across multiple devices in your home and adds an extra layer of security to protect against hackers and third parties. The router and modem can be properly set up using two Ethernet cables, coaxial cables, and the included power cables. Today, Mytour will guide you through the steps of connecting your router to the modem.
Steps
Connecting the router to the modem
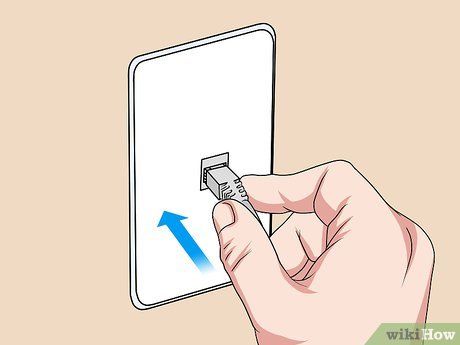
Plug the Internet cable into the wall port. If you’re using fiber optic cable, connect the coaxial cable to the wall port to transmit the internet. For a DSL modem, you need to plug the telephone line into the telephone port on the wall.
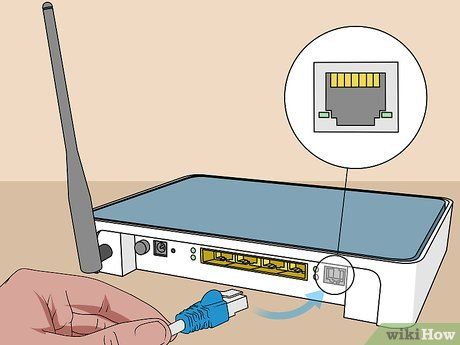
Plug the other end of the network cable into the modem. Connect the coaxial cable or phone line to the appropriate port on the modem. This will allow the modem to receive the Internet connection.
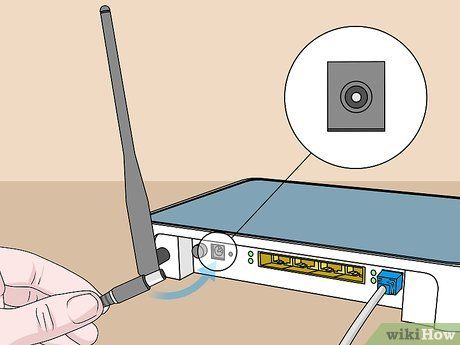
Connect the modem's power cable to the device. Locate the AC adapter port on the modem and plug in the AC adapter.
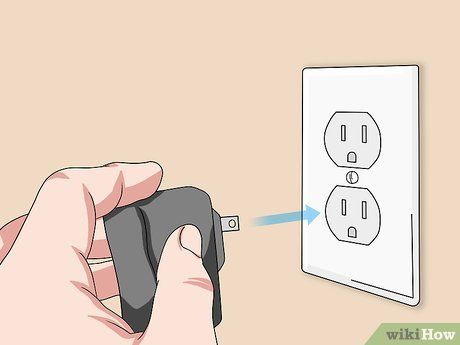
Plug the modem's power cable into a nearby electrical outlet. The modem will now receive power.

Turn on the modem. If the modem does not power on immediately after plugging it in, locate the power switch on the device and turn it on.
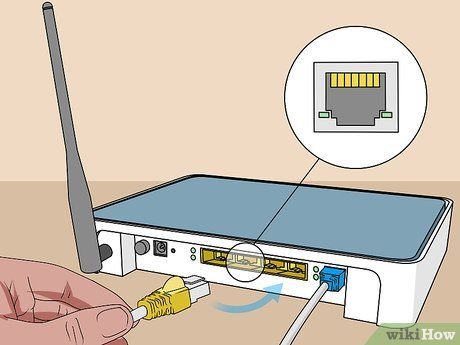
Insert the Ethernet cable into the "Ethernet" port on the modem. This port is used to connect other devices to the modem.

Plug the other end of the cable into the router. Insert the remaining Ethernet cable into the port labeled "WAN", "Internet", or something similar on the router. This port is typically located next to the four colored "LAN" ports on the router.

Connect the power cable to the router. Find the AC adapter port on the router and plug the power cable into it.
Plug the router's power cable into a nearby electrical outlet. The router will almost immediately power on after being plugged in and will require a few minutes to fully boot up.

Connect the second Ethernet cable to the router. Plug one end of the Ethernet cable into one of the "LAN" ports on the router.

Plug the Ethernet cable into the computer. Locate an available LAN port on your laptop or desktop and insert the remaining end of the Ethernet cable into the device.

Check the lights on the modem and router to see if they are illuminated. A lit light indicates that the devices are connected properly. The way the lights behave may vary based on the brand and model of the router. Consult the user manual or the manufacturer's website for additional details.
Open a web browser. After properly setting up the internet connection, you will be able to browse the web using a web browser.
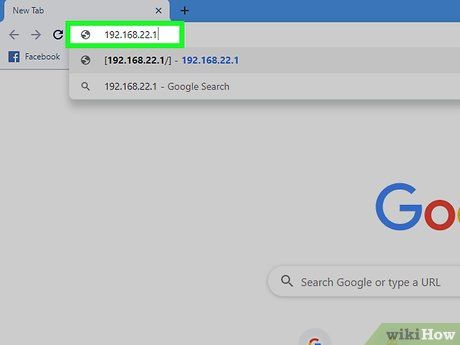
Enter the router's IP address in the browser's address bar. The router's default IP address may vary based on the manufacturer and model. You can refer to the user manual or the manufacturer's website to find the router's IP address.
- Common default IP addresses include 192.168.0.1, 192.168.1.1, and 10.0.0.1
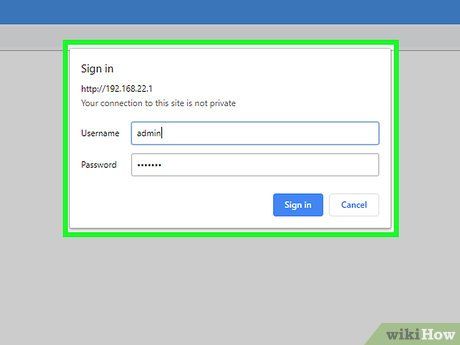
Enter the default username and password. You will need to log in to the router using the default account credentials. Check the user manual or the manufacturer's website to determine the username and password for your router.
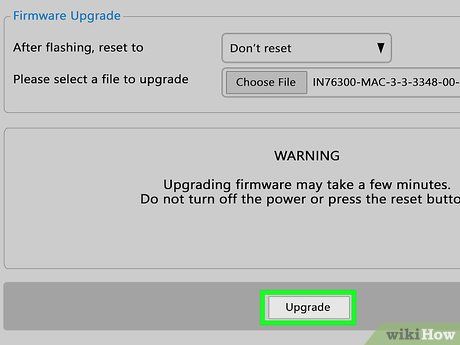
Update the router's firmware. Once connected to the router, the next step is to update the device. On the web interface, find the option to update the router and click it. The process for updating the router’s firmware may vary depending on the manufacturer and model.
- You can also use the router's web interface to set up port forwarding and block websites.
Set up your wireless network configuration
Launch a web browser. After properly connecting to the internet, you should be able to browse the web using your browser.
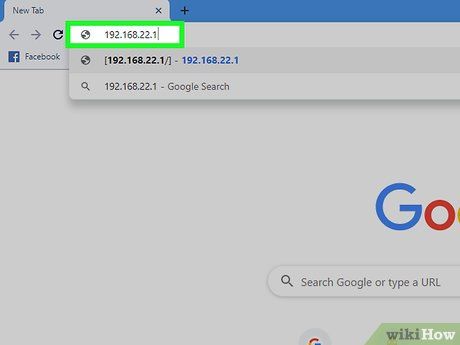
Enter the router's IP address in the browser's address bar. The default IP address for your router may vary depending on the manufacturer and model of the device. You can refer to the user manual or the manufacturer's website to find the correct IP address for your router.
- Common default IP addresses include 192.168.0.1, 192.168.1.1, and 10.0.0.1
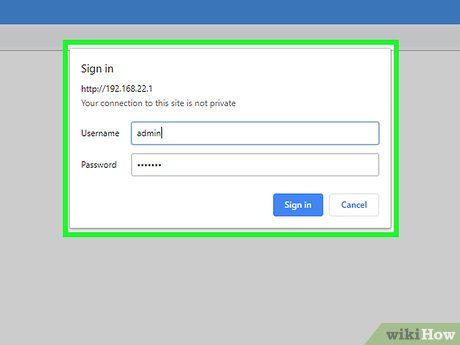
Enter the default username and password. To log in to the router, you will need to use the default account details. Check the user manual or the manufacturer's website to find the default username and password for your router.
- Common default login credentials are "admin" for the username and "password" for the password.
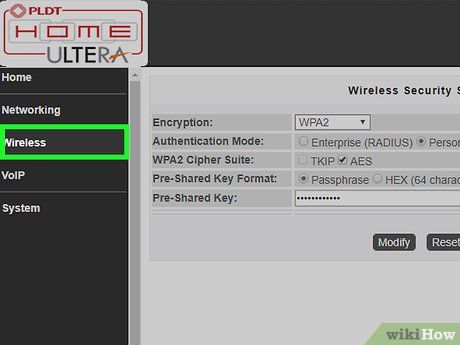
Locate the wireless settings section. The layout of the web interface may differ between manufacturers and router models. Look for the wireless settings section in the router's interface. It could be listed under titles like "System", "Settings", "Configuration", or something similar.
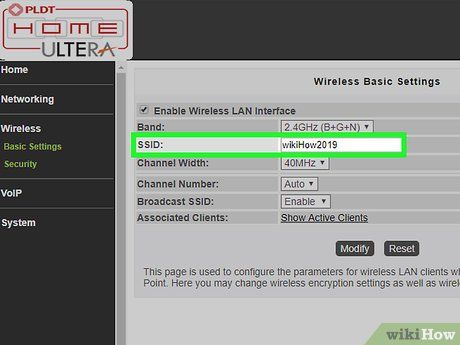
Set a name for your Wi-Fi network. Locate the SSID settings in your router's web interface. Enter the desired name for your wireless network in the SSID field.
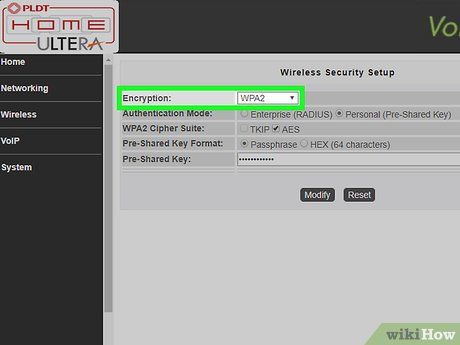
Select "WPA/WPA2" as your encryption key. This is the most secure encryption key for your Wi-Fi password.
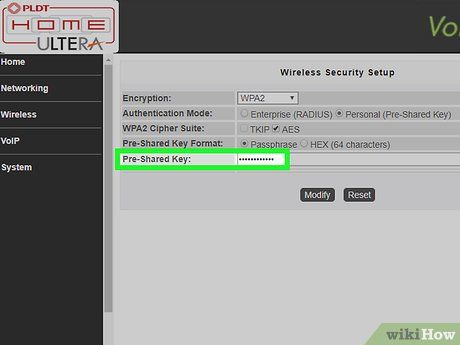
Enter your Wi-Fi password. This field may be labeled as "key", "wireless key", or "pass key". This is the password you'll enter on other devices to connect to your wireless network.
- A strong password should be at least 8 characters long and include a mix of letters and numbers.
- Ensure that the password you use is one you're comfortable sharing with guests, but avoid using the same password as your personal accounts.
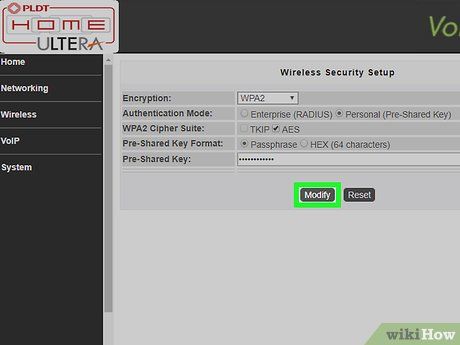
Save the changes to the system. Look for the option to save changes in your router settings. This button will vary depending on the manufacturer and model of the router.
Troubleshooting setup issues
Try disconnecting the modem for 15 seconds. If you're suddenly unable to access the Internet, try unplugging the modem for a few seconds and then reconnecting it. This action allows the modem to fully power off and reset for a stronger connection. After 15 seconds, plug the modem back in and wait at least two minutes before attempting to reconnect to the Internet.
Try restarting both the modem and the router. If you're having trouble connecting to the Internet, turn off the entire system and reboot the devices. This will help refresh the devices and strengthen the Internet connection for longer-lasting service.
- Turn off the computer and unplug the modem.
- Unplug the router's power source. Then, make sure both the Ethernet cable and coaxial cable are securely plugged into the devices.
- Reconnect the modem's power cable, followed by the router's power cable.
- Wait two minutes, then power on your computer. You should now be able to access the Internet.

Try using a different Ethernet cable and coaxial cable. This process helps rule out equipment issues when you're unable to access the Internet. In most cases, if the cables are frayed or damaged, you might experience difficulty connecting to the Internet.

Check if there is a power outage in your area. If the service is interrupted, contact your service provider. In some cases, temporary service disruptions can occur due to maintenance or local power outages.
Verify if the modem is compatible with the router. If you're unable to establish a connection, contact your service provider to check whether the router is compatible with the modem. Some modems may be outdated and therefore incompatible with the router provided by your service provider.

Check if the modem requires any special configuration. If you're unable to connect to the Internet, contact your ISP to inquire whether the modem requires any special setup. Some cable modems may need an Ethernet port configuration before they work properly with the network router.
What you will need
- Router
- Modem
- 2 Ethernet cables
- Coaxial cable
- Router power cable
- Modem power cable
