RAM (Random Access Memory) is the memory your computer uses to store data from currently running programs. Generally, the more RAM you have installed, the more programs you can run simultaneously. However, the amount of RAM you can install is limited by both your computer's hardware and operating system. You'll need to check both to determine how much additional RAM your computer can support.
Steps
Check the Operating System
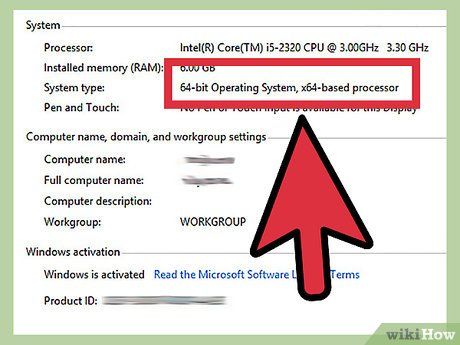
Determine if your Windows is 32-bit or 64-bit. The Windows operating system can only recognize a maximum amount of RAM. If you install more than the allowed RAM limit, the excess memory will not be utilized. This limit is determined by whether your Windows version is 32-bit or 64-bit.
- Refer to additional guides to learn how to check your Windows version. Typically, you can determine if your Windows is 32-bit or 64-bit from the System Properties window (⊞ Win+Pause)
- 32-bit systems can support up to 4 GB of RAM (for all versions).
- 64-bit systems can support up to 128 GB of RAM (Windows 10 Home) to 2 TB (Windows 10 Education, Enterprise, Pro)
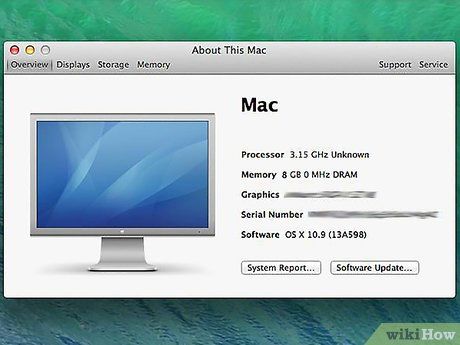
Check the model for MacBook. The total RAM capacity that a Mac computer can support depends on the specific model you are using. Many Mac computers have varying supported memory capacities. Refer to your MacBook's documentation for the exact RAM specifications. Some popular models include:
- iMac (27-inch, Late 2013) - 32 GB
- iMac (2009-Late 2012) - 16 GB
- iMac (2006-2009) - 4 GB
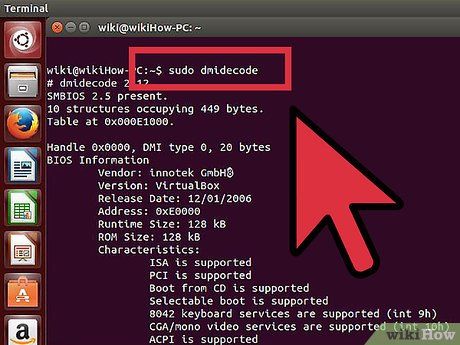
Determine the RAM capacity supported by the Linux operating system. A 32-bit Linux system can only support up to 4 GB, but if PAE (Physical Address Extension) is enabled (common in most modern distributions), a 32-bit system can support up to 64 GB of RAM. In theory, a 64-bit Linux system can support up to 17 billion GB of RAM, though practical limits are 1 TB (Intel) or 256 TB (AMD64).
- To determine the exact RAM capacity your system supports, open the Terminal by pressing Ctrl+Alt+T. Type sudo dmidecode -t 16. Enter the administrator password. Finally, look for the Maximum Capacity: entry.
Check the Motherboard

Identify your motherboard. Even if the operating system supports a massive amount of RAM, you are still limited by what the motherboard can handle. If you cannot access the motherboard's documentation, you may need to locate the motherboard or search for its specifications online.
- You might need to open your computer case and inspect the motherboard's model number.
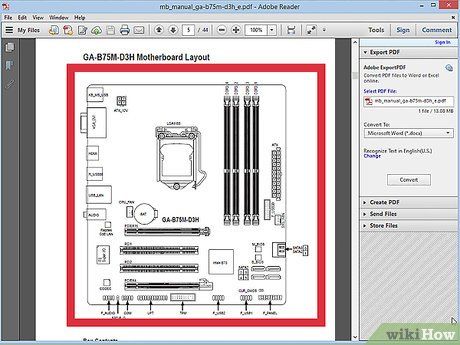
Review the motherboard documentation. Near the beginning of the motherboard's documentation, you can find a chart or technical specifications page. Look for the maximum RAM or system memory capacity that can be installed. You will also see the number of available slots on your motherboard.
- RAM is installed in pairs. If your motherboard supports 16 GB of RAM and has 4 slots (dual-channel), you can install four 4 GB sticks or two 8 GB sticks to reach the limit.
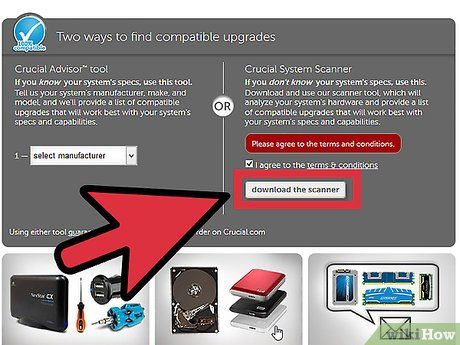
Use a system scanning tool. If you prefer not to open your computer or read through motherboard documentation, many online tools are available to scan your system and report how much memory is supported, as well as the type and speed.
- You can visit major manufacturer and retailer memory scanning websites, such as Crucial or MrMemory.
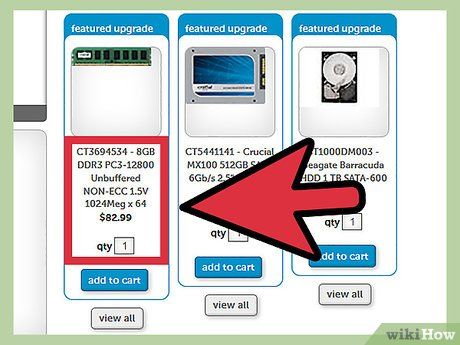
Upgrade your RAM. Once you determine the maximum RAM capacity your system supports, you can install additional memory. Ensure the clock speed matches the existing RAM if you are adding new RAM to the current setup.
