This guide demonstrates the process of establishing a connection between an audio device, such as a speaker, and your computer either through an audio cable or via Bluetooth, provided the device supports this feature.
Procedures
Establishing Connection via Audio Cable

Locate the audio-out port on your computer. Typically, desktop PCs have this port at the rear of the CPU box, while iMacs feature a 3.5-millimeter headphone jack at the back of the monitor. Common audio-out options include:
- Optical - Identified by a pentagonal port. Optical cables are compatible with high-end, contemporary speakers.
- RCA - Comprising a red and white port. These ports accommodate 3.5-millimeter cables of corresponding colors.
- Headphone jack - The 3.5-millimeter headphone jack is commonly located on the side of laptops or at the rear of desktop computer cases. For speakers or headphones, the plug is color-coded in green and often bears a headphone symbol. The pink jack is designated for microphones, and the blue jack serves as Line-In, akin to an auxiliary input.
- HDMI - HDMI slots function similarly on computers as they do on TVs, facilitating audio transmission.
- Laptops typically feature the audio-out port as the headphone jack.
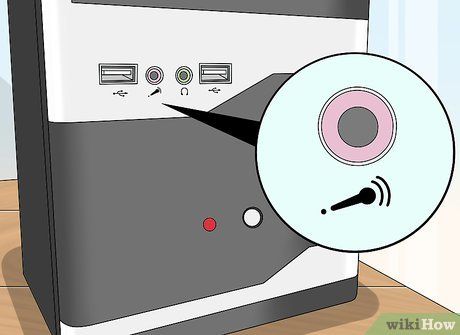
Locate the microphone jack if required. The microphone jack is usually the same size as the headphone jack (3.5 millimeters) and typically features a microphone icon. Knowing the location of the microphone port is essential, especially when connecting devices that necessitate separate microphone input, such as certain gaming headsets.
- USB ports can also serve as audio-in connections.
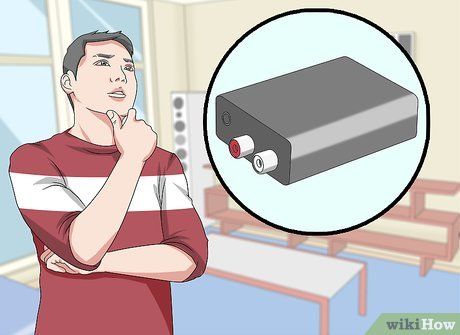
Determine the necessity of a converter. For instance, if you possess new speakers and an older computer, you might require an optical-to-RCA adapter since your computer likely supports RCA or headphone input exclusively.
- You can easily find audio converters, also referred to as 'audio extractors,' in most tech departments at retail outlets or online.
- If employing an audio extractor, you'll also need to procure a separate set of cables to connect the extractor to your computer.
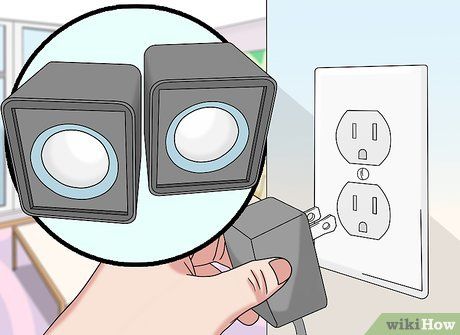
Connect your audio device to a power source if needed. Devices such as speakers and condenser microphones will typically necessitate a power source, such as a wall socket or your computer's USB port, to operate.
- You might also have to toggle an 'On' switch located on the rear of the primary speaker unit.

Link your device to your computer. The primary unit of your device (e.g., the headset or primary speaker) should feature an audio cable that plugs into your computer's audio output port.
- If required, initially connect your device to an audio extractor.

Assess your device. Play a video or some music to verify whether the audio output is functioning correctly, or attempt recording a voice memo with your new microphone (if applicable).
- You might need to alter the audio output, reboot your computer, or update your computer's software if your device does not initially function.
Pairing via Bluetooth on Windows

 ⊞ Win
⊞ Win
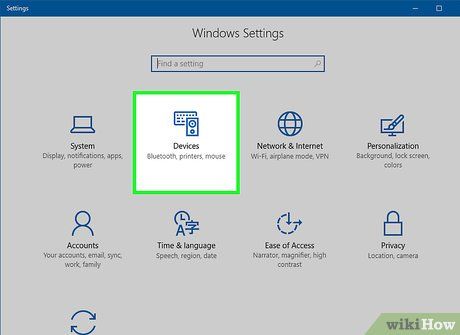
Access Devices. Look for this option among the top row of items on the Settings page.
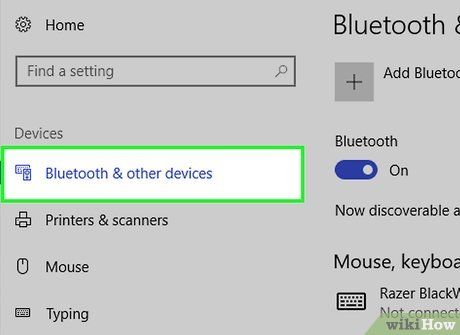
Go to Bluetooth & other devices. This tab is situated on the far-left side of the page.
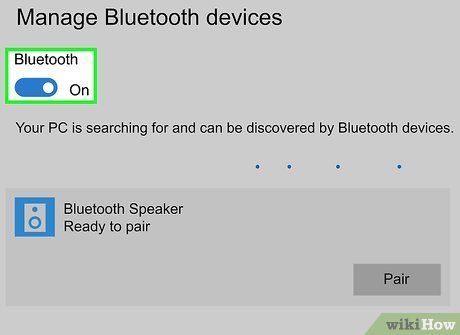

- If you notice 'On' beside the toggle, Bluetooth is activated.

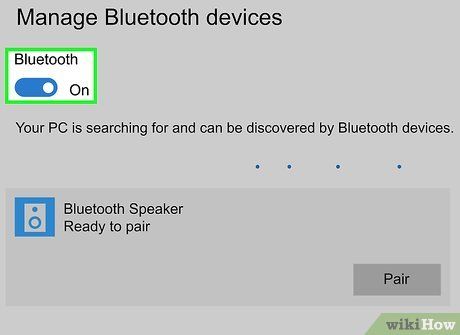
Activate your Bluetooth device and enable pairing mode. Switch on your Bluetooth audio device and ensure it's in either 'pairing' or 'discoverable' mode. If needed, connect it to a power source.
- As devices vary, consult the manual accompanying your audio device to learn how to enable 'pairing' mode if unsure.
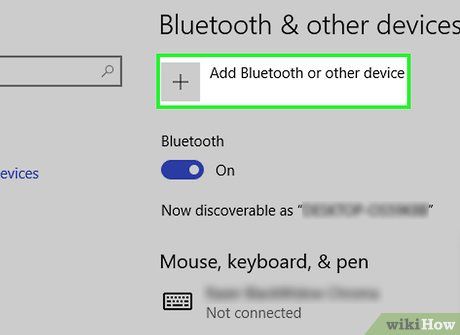
Click + Add Bluetooth or other device. Locate this button at the top of the page.
Click Bluetooth. It's the primary option within the Add a Device window.
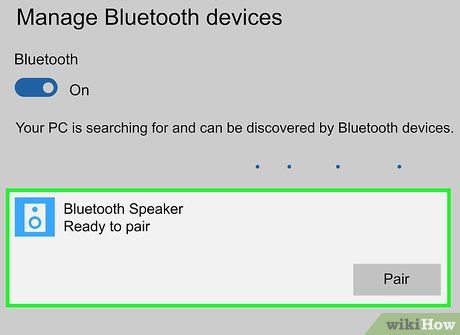
Choose your audio device's name. Look for it in the 'Add a Device' window; typically, its name will be a blend of the model number and the manufacturer's name. Upon selection, it will initiate pairing automatically.
- If the device doesn't appear, ensure it's in 'pairing' mode and rescan for nearby devices.
Click Done. This button will be situated in the bottom-right corner of the available Bluetooth devices window.
 audio
audio
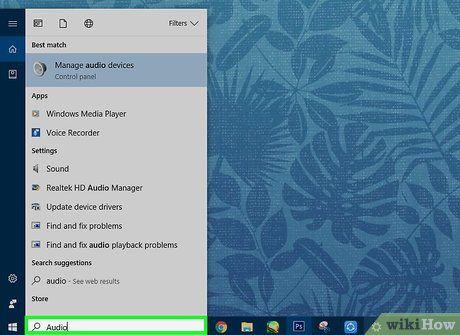
Access Manage Audio Devices. This option features a speaker symbol. Clicking it will open your audio manager.
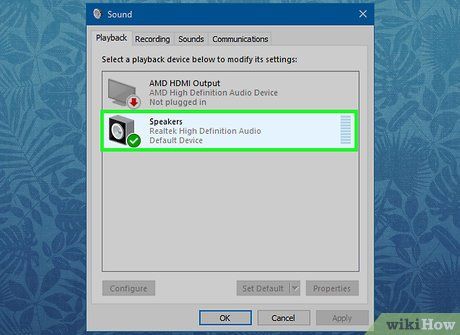
Choose your Bluetooth device. Its name should appear in the Sound window, alongside your laptop's default output device if applicable.
- If connecting a microphone, start by clicking the Recording tab at the window's top.
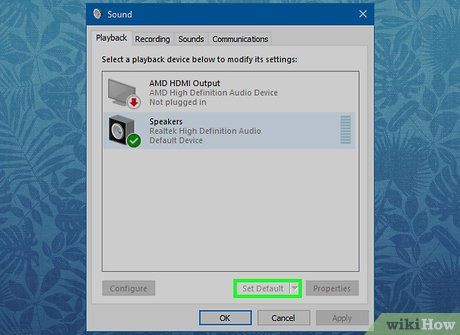
Click Set Default. It's situated in the window's bottom-right corner.
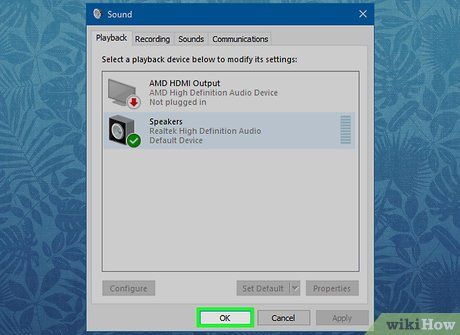
Click OK. Your device should now serve as the default within its category on your computer.

Evaluate your device. Assess its functionality by playing a video or some music to check the audio output, or by attempting to record a voice memo using your new microphone (if applicable).
- If the device doesn't function, you may need to reboot your computer or update its software.
Pairing via Bluetooth on Mac

Power on your Bluetooth device. Depending on its type, you might need to connect it to a power supply beforehand.

Activate Bluetooth if it's not already enabled. To view your Bluetooth device on your Mac, ensure that Bluetooth is turned on.
Choose your Bluetooth device's name. Look for a combination of the model number and the manufacturer's name.
- If the device's name isn't visible, press the 'pairing' button or power cycle it.
Initiate the connection. This action will trigger your Mac and the device to pair with each other.


Access System Preferences. This option is located near the center of the Apple drop-down menu.
Access Sound. Look for the speaker-shaped icon within the System Preferences window.
Access the Output tab. It's located at the top of the Sound window.
- If you're connecting a microphone, switch to the Input tab.
Double-click on your Bluetooth device's name. This action will designate it as your Mac's primary output (or input, if connecting a microphone).

Evaluate your device. Test its functionality by playing a video or music to check the audio output, or by recording a voice memo with your microphone (if applicable).
- If your device doesn't work, consider restarting your computer or updating its software.
Insights
-
When connecting a microphone to a sound card, use the Mic-In input instead of Line-In, as Line-In inputs may not handle microphone frequencies well. Instruments and DVD players should be connected to the Line-In input.
-
Most Bluetooth devices require occasional charging rather than constant connection to a power source.
Cautions
- Compatibility issues may arise with older or newer devices. If your computer cannot support a Bluetooth device and cannot use a traditional connection method (e.g., wired headset or speakers), consider upgrading your computer.
