You can format a drive using the Disks utility pre-installed on Ubuntu. If the Disks tool reports errors or the partition is damaged, GParted can be used as an alternative for formatting. Additionally, GParted allows you to resize existing partitions, enabling you to create new partitions from unallocated space.
Steps
Perform a Quick Format
Launch the Disks application. You can quickly find it by opening Dash and typing disks. All drives connected to your computer will appear on the left side of the window.
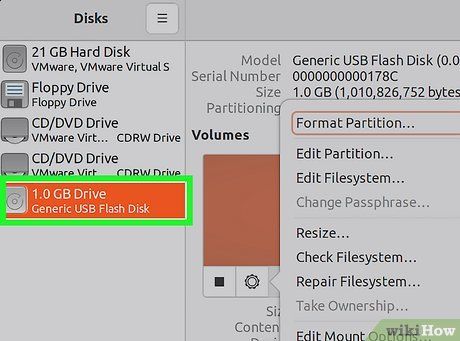
Select the drive you wish to format. All drives will be listed in the left panel. Be cautious when choosing a drive, as all data on the partition will be erased during formatting.
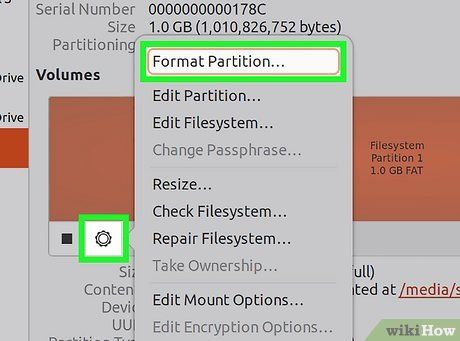
Click the Gear icon and select "Format Partition." A new window will open, allowing you to configure the file system settings.
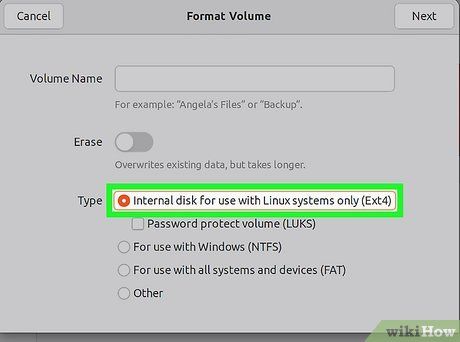
Choose the file system you want to use. Click the "Type" menu and select your desired file system.
- If you plan to use the drive for transferring files between Linux, Mac, Windows, or most USB-compatible devices, choose "FAT."
- If the drive will only be used on Linux systems, select "Ext4."
- For Windows-exclusive use, opt for "NTFS."
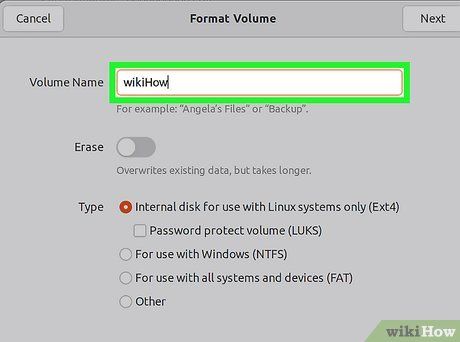
Assign a name to the drive. You can enter a label for the formatted drive in the empty field. This will help you easily identify the drive later.
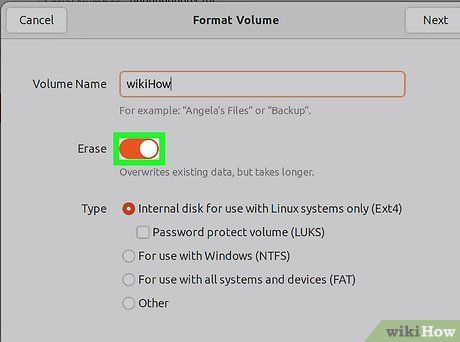
You can choose to securely erase the drive or not. By default, the formatting process will delete data without overwriting it. If you prefer a more secure deletion method, select "Overwrite existing data with zeroes" from the "Erase" menu. This option takes longer but ensures greater security.
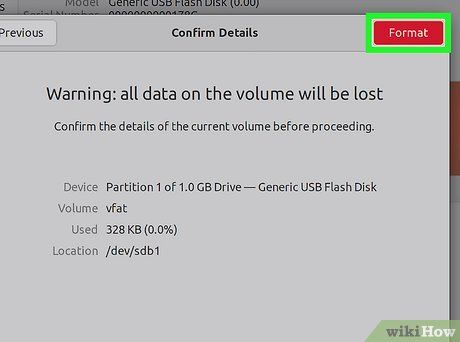
Click the "Format" button to begin. You’ll be prompted to confirm before proceeding. Formatting may take longer for larger drives or if you’ve selected the secure erase option.
- If you encounter issues during the formatting process, consider using GParted in the next step.
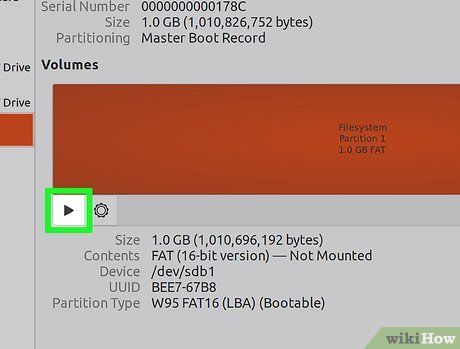
Mount the drive after formatting. Once the drive is formatted, click the "Mount" button that appears below the Volumes chart. The partition will be mounted, allowing you to access the file system for storage. Click the displayed link to open the drive in the file browser, or open the Files application and locate the drive in the left panel.
Using GParted

Open the Terminal. You can launch Terminal from Dash or press Ctrl+Alt+T.
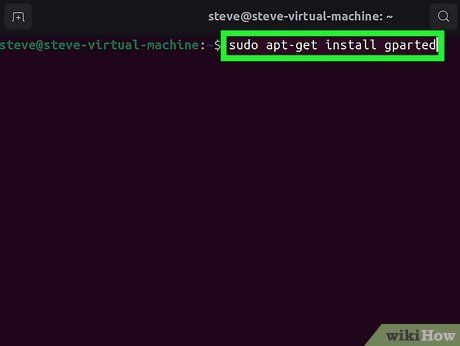
Install GParted. Enter the following command to install GParted. You’ll be asked to enter your user password, which won’t be displayed as you type:
- sudo apt-get install gparted
- Press Y when prompted to proceed.
Launch GParted from Dash. Open Dash and type "gparted" to locate GParted Partition Editor. You’ll see a bar representing the current disk partitions and the available free space.
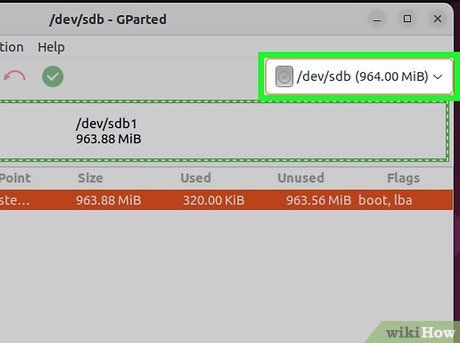
Select the drive you want to format. Click the dropdown menu in the top-right corner to choose the drive you wish to format. If unsure, identify the drive by its size.

Unmount the partition you intend to modify or delete. To make changes in GParted, you must first unmount the partition. Right-click the partition in the list or chart and select "Unmount."
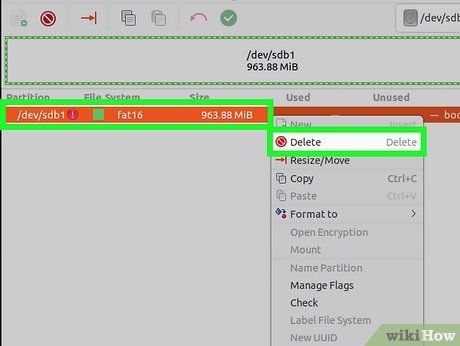
Delete the existing partition. The partition will be removed and marked as unallocated space. You can then create a new partition from this space and format it with your desired file system.
- Right-click the partition you want to remove and select "Delete."
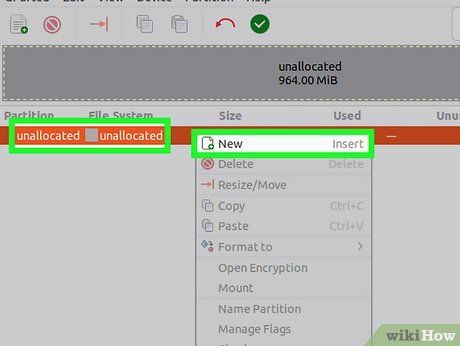
Create a new partition. After deleting the partition, right-click the unallocated space and choose "New." This will initiate the process of creating a new partition.
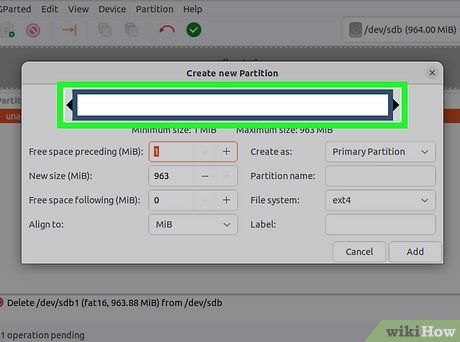
Select the partition size. When creating a new partition, use the slider to allocate the desired amount of space to the partition.
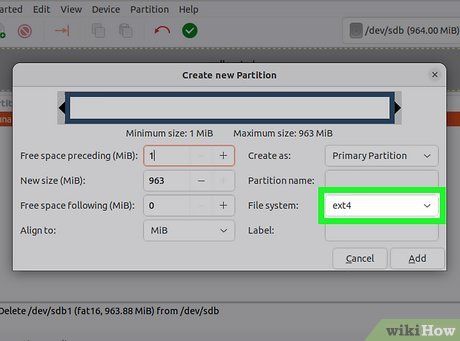
Choose the file system for the partition. Use the "File system" menu to select the format for the partition. If you plan to use the drive across multiple operating systems and devices, choose "fat32." For Linux-only use, select "ext4."
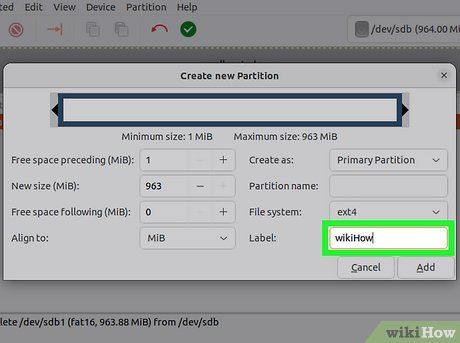
Assign a name to the partition. This will help you easily identify the partition on your system.
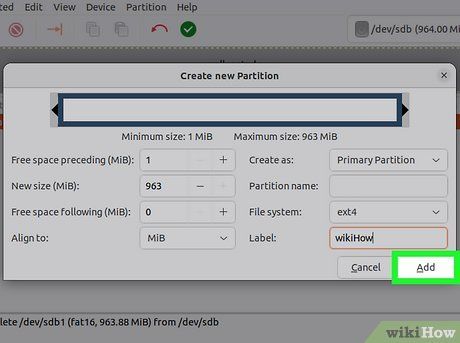
Click "Add" once you’ve configured the partition. The partition will be added to the operation queue at the bottom of the screen.
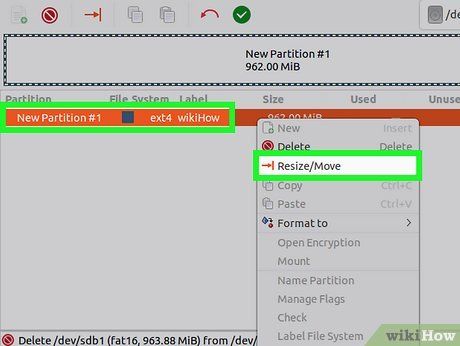
Resize the partition (optional). One of GParted’s key features is the ability to resize partitions. Resizing creates unallocated space, allowing you to create additional partitions. This essentially lets you divide the drive into multiple sections without affecting existing data.
- Right-click the partition you want to resize and select "Resize/Move."
- Drag the edges of the partition to create free space before or after it.
- Click "Resize/Move" to confirm the changes. You’ll need to create a new partition from the unallocated space as described earlier.
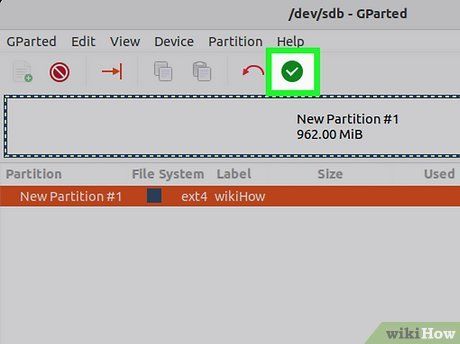
Click the green checkmark to apply the changes. No changes will be made to the drive until you click this button. Once clicked, all partitions marked for deletion will be removed along with their data. Ensure everything is correct before proceeding.
- The process may take some time, especially if you’re working with multiple partitions or large-capacity drives.
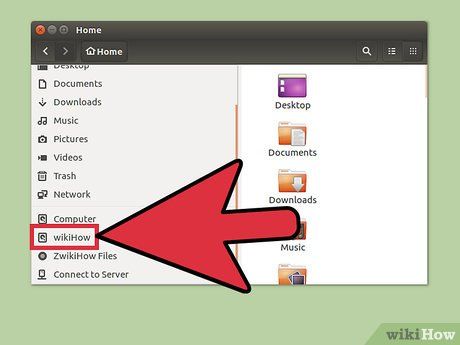
Locate the newly formatted drive. Once formatting is complete, you can close GParted and find the drive in the list of available drives within the Files application.
