Zucchini (also known as Japanese cucumber) is extremely easy to grow, making it a great vegetable to inspire children to take up gardening. Once the fruit begins to develop, it's not long before it’s time to harvest, and the young gardeners will be delighted with their efforts.
Steps
Preparing to Plant
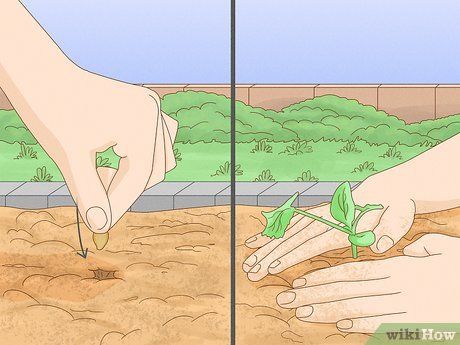
Consider how you want to begin growing zucchini. There are two primary methods for propagating zucchini – either sowing seeds or purchasing young plants to place in your garden. If you opt for growing from seeds, you'll need to start sowing them 4-6 weeks before the outdoor planting season in your area. Purchasing pre-planted seedlings in pots is always the easiest and quickest method, though it may not be as exciting as planting seeds.
- There are several varieties of zucchini, but in general, they are quite similar to each other. Zucchini can be categorized as either 'bushy' or 'vining', referring to how the plant's leaves grow (spreading/crawling or bushy).
- Most bushy zucchinis are considered summer squash, while vining zucchinis are regarded as winter squash.
- The color of zucchini naturally ranges from pale yellow to deep green, and some may even appear nearly black. Some zucchinis may have faint stripes or spots, which is completely normal and nothing to worry about.
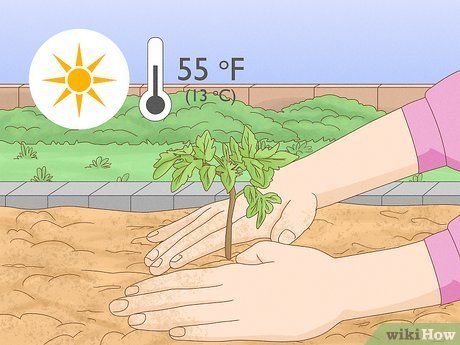
Understand the planting timing. Zucchini is typically considered a summer squash because it grows best and produces the highest-quality fruit during the summer. Some zucchini varieties are considered winter squash, but this term refers to the harvest period rather than the planting period. Zucchini thrives in sunny conditions and doesn't grow well in cold soil, so it’s important to plant it when the outdoor soil temperature reaches at least 13°C. This usually happens after the first or second week of spring, once the last frost has passed.
- If you're unsure about when to plant zucchini, contact your local agricultural development office for more information on the best planting times for your area.
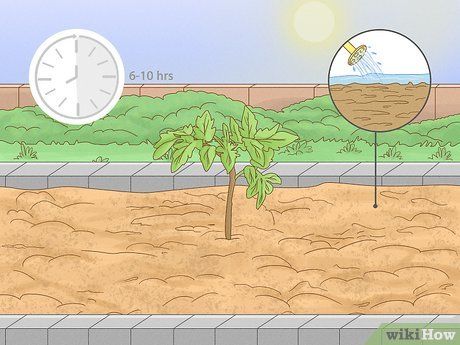
Find the best planting location. Zucchini grows best in areas with full sunlight and plenty of space to spread out. Choose a spot in your garden that gets at least 6-10 hours of sunlight each day. Be sure to pick a location with good drainage, as zucchini prefers moist but well-drained soil.
- If necessary, improve the drainage by planting zucchini on raised mounds or making adjustments to the soil and drainage system.
- Plant in a south-facing area to maximize sunlight exposure (or north-facing if you're in the southern hemisphere).
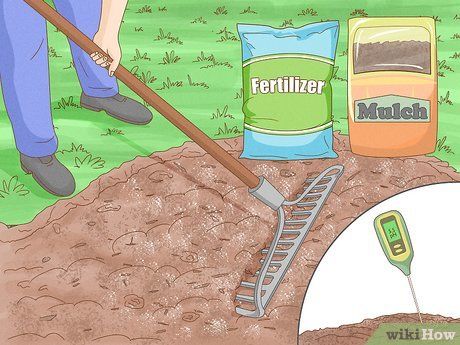
Prepare the soil. While not everyone has time for extensive soil preparation, taking a few months before planting can provide the best conditions for zucchini to grow. Start by mixing garden mulch and fertilizer to enrich the soil. Check the soil pH and adjust if necessary; zucchini prefers soil with a pH between 6 and 7.5. To make the soil more acidic (lower pH), you can mix in peat moss or pine needles. To make the soil more alkaline (raise pH), add lime.
- To add nutrients and organic matter, incorporate compost into the soil one month before planting, and then apply garden mulch until planting time.
- If your soil doesn’t drain well, you can mix in sand to improve drainage.

Sow the seeds. If you prefer not to plant seeds directly into the ground, you can start them indoors 4-6 weeks before moving them outside. Prepare a seed tray, a soil-free planting mix, and your seeds. Place one seed per tray, cover with a 0.3 cm layer of the planting mix, and water generously! Make sure the tray is placed in a sunny area with a temperature of at least 16°C. Once the second set of leaves emerges, you can transplant the seedlings outdoors.
Planting Zucchini

Prepare the planting area. Use a garden hoe to dig small holes for planting. If you're sowing seeds, press each seed into the soil at a depth of no more than 1.2 cm. For seedlings, dig holes slightly larger than the root ball. Maintain a spacing of 75-100 cm between plants (similar to the distance between rows). You can thin out the seedlings if necessary.
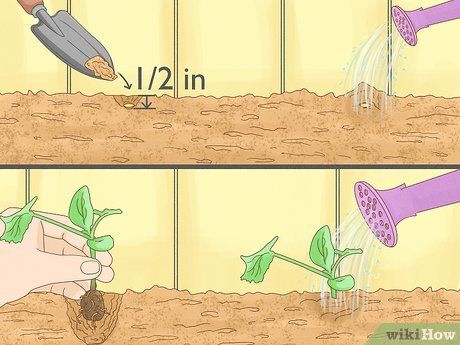
Plant the seeds. Place each seed or seedling in its own hole. Cover the seeds with a soil layer of approximately 0.6 or 1.2 cm, allowing them to receive the necessary light and water for germination. For seedlings, cover the root ball without touching the plant’s stem. Water generously to complete the planting process!
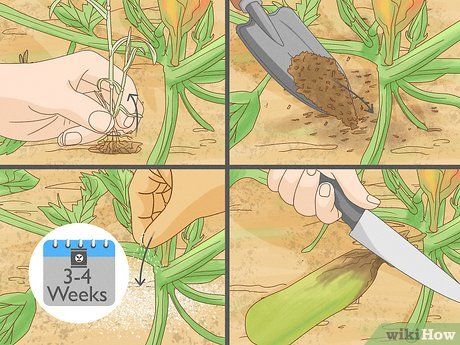
Caring for the plants. Keep an eye on your zucchini plants as they begin to grow. Zucchini is relatively low-maintenance, but it still needs some care to thrive. Remove any weeds around the plants and apply mulch if weeds continue to spread. Add liquid growth fertilizer every 3-4 weeks to encourage healthy growth. Prune any diseased or dying leaves and branches to prevent the spread of disease and help the plant continue to thrive.
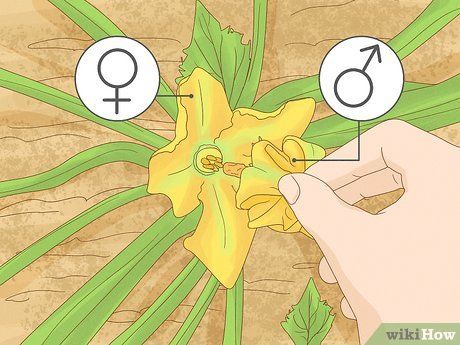
Support fruit production. Zucchini needs pollination to set fruit. If your garden lacks bees or other pollinating insects, or if your zucchini plants seem to be failing to produce fruit, you can hand-pollinate them. Find a male flower with a long, slender stem and the stamens in the center. Carefully pull off the male flower and dip its stamens into the female flower. Female zucchini flowers have short stems, a swollen base beneath the flower, and no stamens.
- You can pollinate multiple flowers or just a few, depending on your available time and the number of fruits you want to harvest.
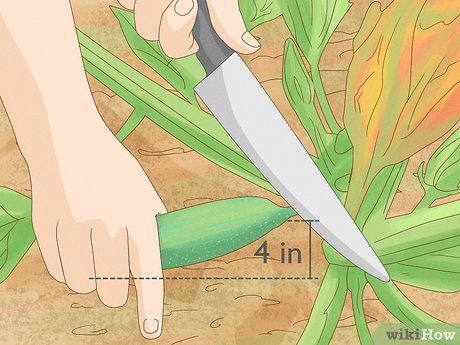
Harvest the zucchini. Zucchini is ready for harvest when it reaches about 10 cm in length. Harvesting frequently will encourage the plant to produce more fruit, so if you want plenty of zucchini, be sure to pick all the mature fruits. If you're not concerned with harvesting a large quantity, leave one or two fruits on the vine throughout the growing season to slow down the plant's fruiting. Use a sharp knife to cut the zucchini from the stem, which can be quite tough.
- Enjoy zucchini flower salad. Zucchini flowers are edible, but picking them will prevent the plant from producing as much fruit.
- If the plant has done well throughout the spring, it will continue to produce zucchini until the first frost appears.
- You can simply cut the stem of a zucchini to allow the plant to continue growing if you're not ready to harvest the entire crop.
Lời khuyên
- Bí ngòi vàng và xanh có hương vị như nhau, nhưng bí vàng thường dễ tìm hơn nếu bạn trồng nhiều!
- Bí ngòi là nguyên liệu rất tuyệt để làm món nhồi, thêm vào món sốt mì và để nấu canh. Bí ngòi cũng có thể dùng trong món rau trộn và thường được bào sợi để làm món "mì bí ngòi".
- Bí ngòi rất háo nước, vì vậy bạn nhớ tưới nhiều nước cho cây!
Cảnh báo
- Nếu cây không ra quả đúng mức thì nghĩa là hoa cái không được thụ phấn. Bạn có thể hái hoa đực và thụ phấn cho các hoa cái bằng cách thủ công để xử lý vấn đề này.
- Ở nhiều vùng Bắc Mỹ, sâu đục thân bí là loại dịch hại chủ yếu của cây bí ngòi. Các dấu hiệu nhiễm sâu bệnh bao gồm: lá héo úa, xuất hiện nhiều lỗ trên gốc cây và một chất như mạt cưa trên thân cây. Các loài dịch hại khác bao gồm ruồi trắng, rệp, nhện đỏ, giụn tròn, mốc sương, mốc và virus.
Những thứ bạn cần
- Zucchini seeds
- Soil digging tools
- A suitable space in your garden
