Eliminate corrupted files swiftly on your PC or Mac
This Mytour guide will show you how to remove corrupted files on Windows and Mac using the administrator account, Safe Mode, and command prompt on Windows, as well as Terminal and Safe Mode on Mac. Typically, you can drag the file you wish to delete into the recycling bin/trash can and empty it, but certain files (such as corrupted ones) might cause errors during deletion.
Essential Information
- On Windows, you can drag corrupted files to the Recycle Bin if you're logged in as an Administrator.
- On a Mac, you can delete corrupted files in Terminal using the command sudo rm -R filename.
- You can also delete corrupted files on both Windows and macOS by booting into Safe Mode.
Step-by-Step Guide
Admin Deletion Process on Windows
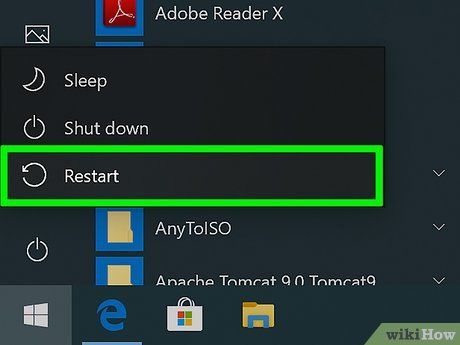
Close all running programs and reboot your computer. If your account lacks admin privileges, you might encounter difficulty deleting certain files, necessitating access to an administrator account.
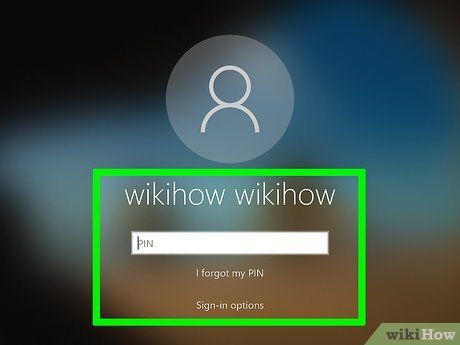
Access an administrator account. With administrative rights, deleting corrupted files becomes a breeze.
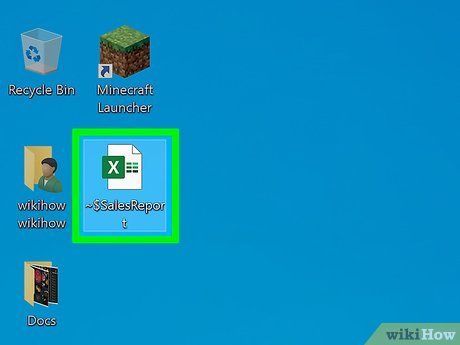
Locate the corrupted file you wish to remove. It can be found either on your desktop or in File Explorer.
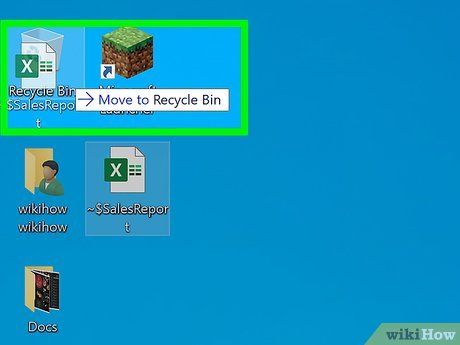
Drag the corrupted file to the Recycle Bin. Typically, this bin icon is situated on your desktop.
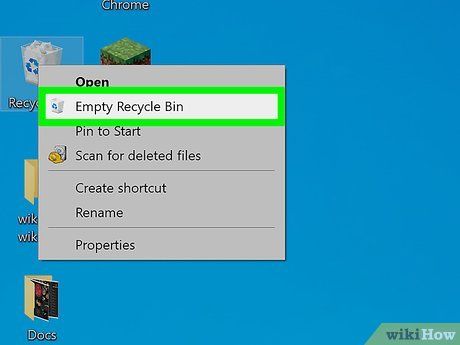
Right-click the Recycle Bin icon and choose Empty Recycle Bin. Typically, this is the second option in the list next to another recycling bin icon.
Using Command Prompt on Windows
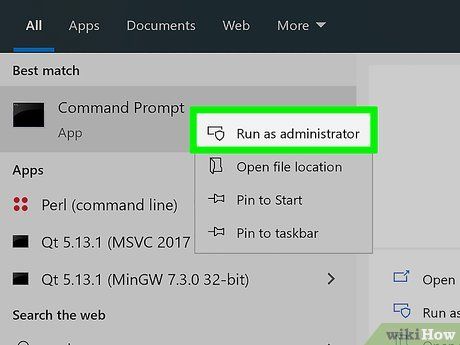
Launch Command Prompt as an Administrator. You can click the Start menu icon, type 'cmd' to view a list of search results, then select the Command Prompt program and click Run as administrator.
- For this approach, you'll need the file path of the file you wish to delete. If you're unsure how to obtain a file's file path, refer to How to Find a File's Path on Windows.
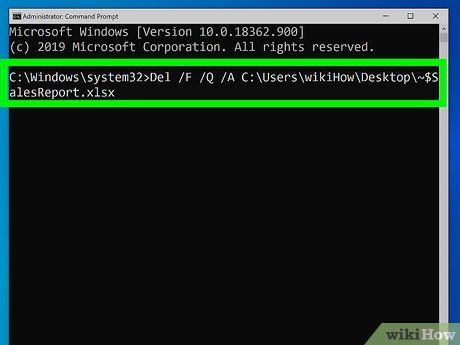
Type the following command into the command prompt window:
'Del /F /Q /A <filepath>'
- Replace <filepath> with the location of your file. For instance, you might input 'Del /F /Q /A C:\Users\John\Downloads'.
- '/F' is for forcefully deleting files, '/Q' is for deleting read-only files, and '/A' is for selecting files with the archiving attribute.
Press ↵ Enter. Your file should be deleted.
Utilizing Safe Mode on Windows
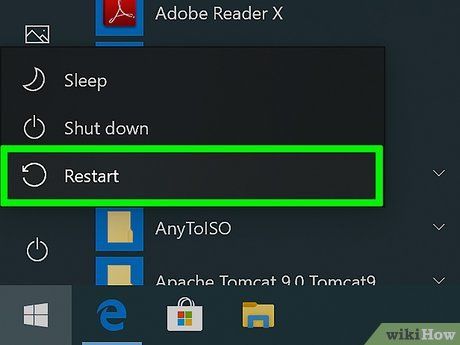
Close all active programs and restart your computer. This method is advisable if previous attempts have failed.
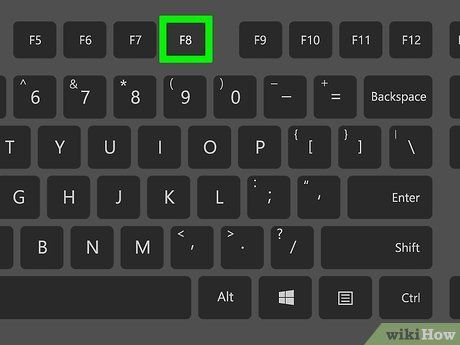
Press F8 before the Windows logo appears. You might miss this initially, requiring another computer restart. For additional guidance, refer to How to Activate Safe Mode in Windows 10 Using F8, How to Activate Safe Mode in Windows 10 using the Power Menu, and How to Start Windows in Safe Mode for older Windows versions.
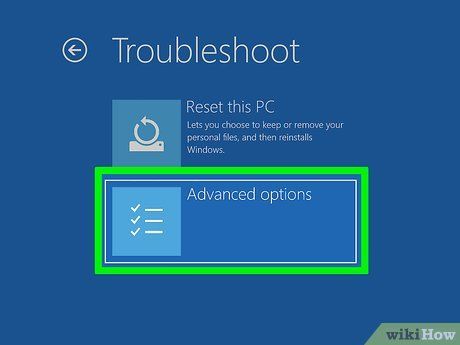
Choose Advanced options. This will appear on the right side of your screen.
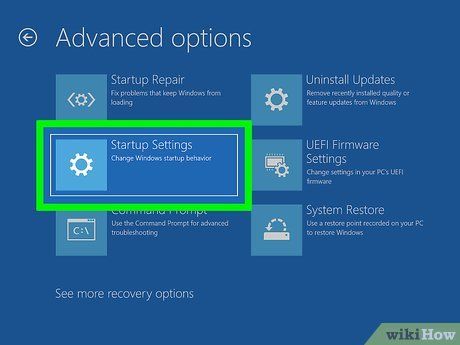
Select Startup Settings and Restart. Your computer will reboot with Startup Settings.
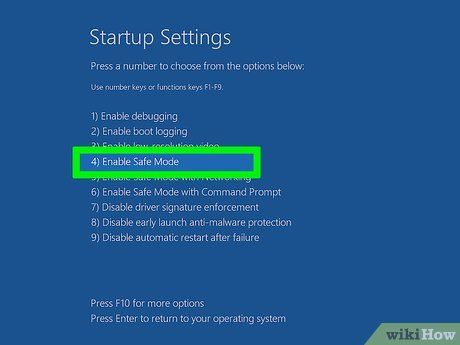
Activate Safe Mode. You'll need to press the corresponding number (1-9) or function key (F1-F9) to select it.

Locate the file you wish to remove. You'll find it either on your desktop or in your file explorer.
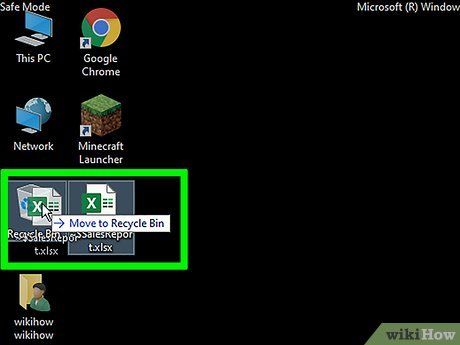
Drag the file to the Recycle Bin. Typically, you'll find this recycling bin icon on your desktop.
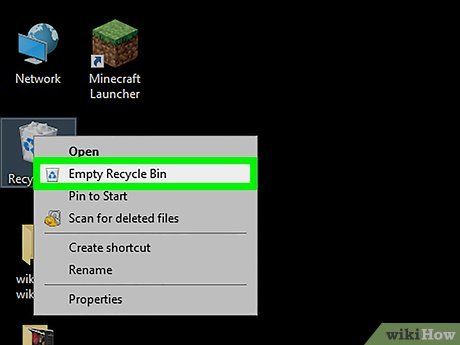
Right-click the Recycle Bin icon and choose Empty Recycle Bin. The files within the Recycling Bin should be deleted; if you still encounter an error, proceed to other methods.
Utilizing Terminal on Mac
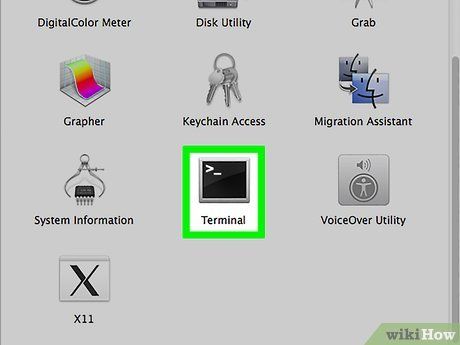
Launch Terminal. You can locate the Terminal app icon in the Utilities folder of Finder.
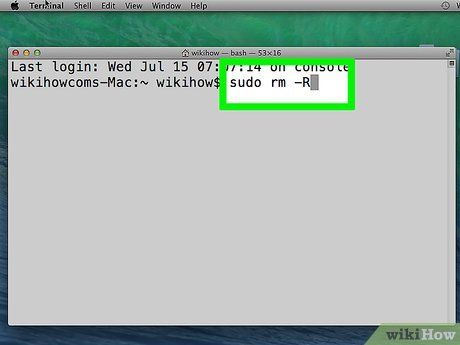
Input the following code into the Terminal window, but refrain from pressing ⏎ Return:
'sudo rm -R '. Ensure you leave a space after the final 'R' in the code.
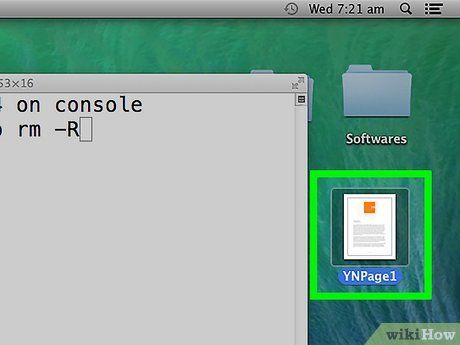
Find the file you wish to delete in Finder. Ensure that you can view your Terminal window simultaneously.
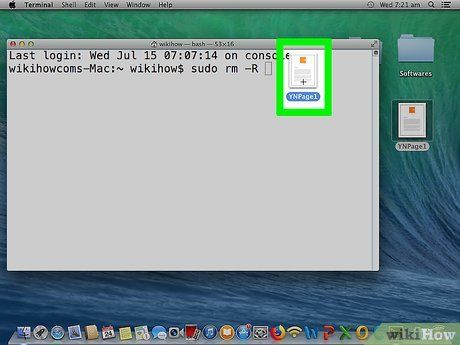
Drop the file you intend to delete from Finder into the Terminal window. The file's location and name will be appended to the end of your command.
- Press the Return key to execute the deletion.
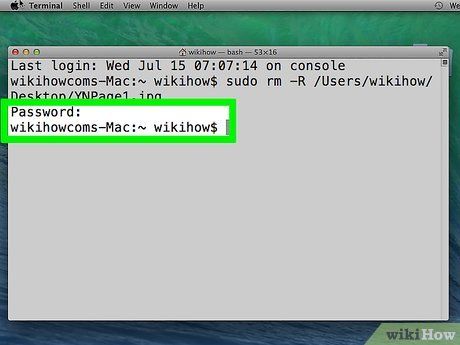
Input the Admin password and hit ⏎ Return. This action will prompt Terminal to permanently erase the file.
Activating Safe Mode on Mac

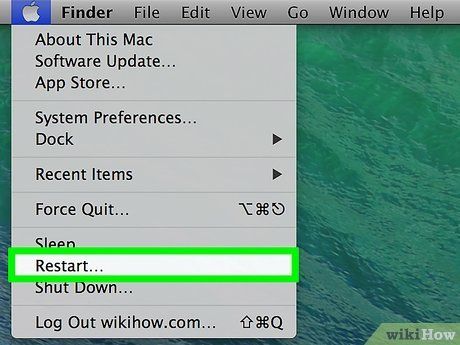
Click Restart and press ⇧ Shift. Hold down the Shift key as your Mac restarts to enable Safe Mode.
- You can release the Shift key at the login window, as Safe Mode has been activated.
Log into your account and locate the file you wish to delete. While your Mac is in Safe Mode, you might be able to delete the corrupted file.
Drag the file to the Trash. Alternatively, you can click to select the file in Finder, then navigate to the menu and choose Move to Trash.
Empty the Trash. Click and hold the Trash icon. After a moment, a menu will appear, allowing you to select Empty Trash.
- Restart your Mac once more to exit Safe Mode. If the previous steps still trigger an error, proceed to the next method.
