Have you mistakenly erased some files from your SD card or encountered data loss due to a corrupted card? Acting promptly and refraining from further card usage could facilitate file recovery using data retrieval software. There are free options available on every operating system, as well as paid programs that may offer more user-friendly interfaces.
Steps
Utilizing PhotoRec (Compatible with Any Operating System)
Avoid accessing the SD card. Even if the files have been deleted, there's still a chance that the data remains intact but has been marked for overwrite by new data. By refraining from accessing the SD card, you enhance the likelihood of data preservation.
- Until you're prepared to attempt file recovery, it's advisable to remove the SD card from any device.
Get PhotoRec Software. PhotoRec is a free, open-source tool for recovering files that functions across Windows, OS X, and Linux platforms.
Extract the Application. There's no need to install PhotoRec. Simply unzip the photorec_os program from the ZIP file. The os will vary based on your operating system. For instance, the Windows version is photorec_win.
Insert Your SD Card. Place your SD card into your computer using an SD card reader or connect it via USB by inserting it into your camera.
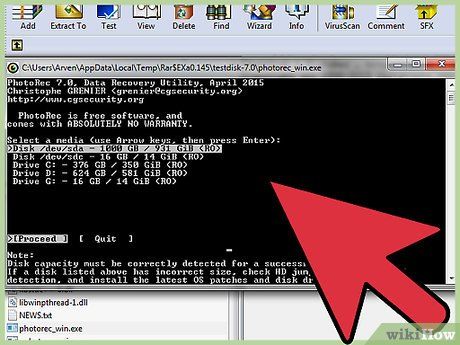
Launch PhotoRec. PhotoRec initiates within a command line interface. You'll navigate the program using your arrow keys.
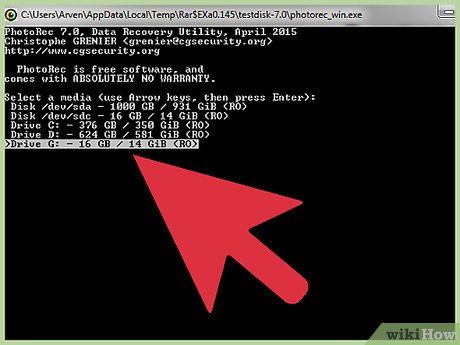
Choose Your Drive. Locate your SD card from the list of available drives and press ↵ Enter.
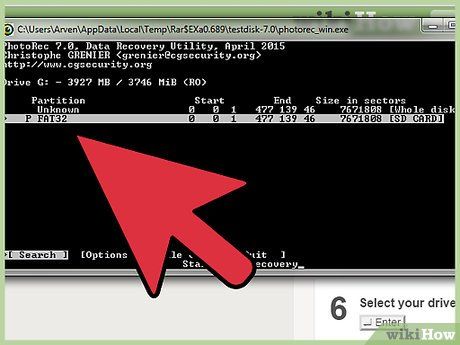
Choose the Partition. Your SD card likely has only one partition. Use the arrow keys to select it.
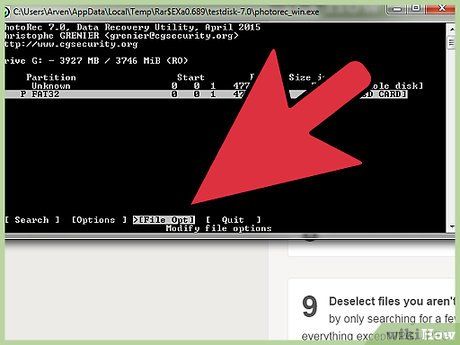
Access the File Opt Menu. Look for this option at the bottom of the window.
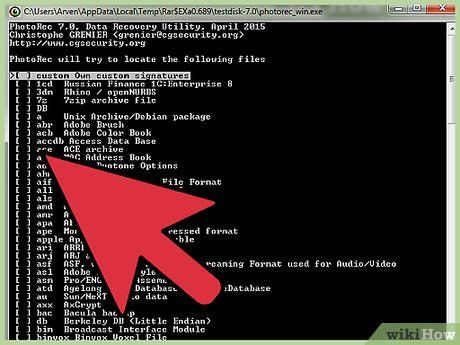
Unselect Unwanted Files. To expedite the search process, narrow down the file types. If you're aiming to recover images, deselect all except JPG, JPEG, RAW, CR2, PNG, TIFF, GIF, BMP, SR2, and DNG.
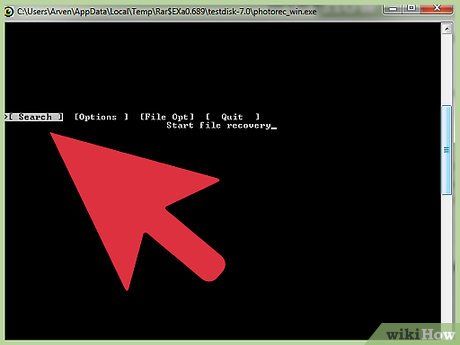
Proceed with the Search Option. This action will bring up the file system menu.
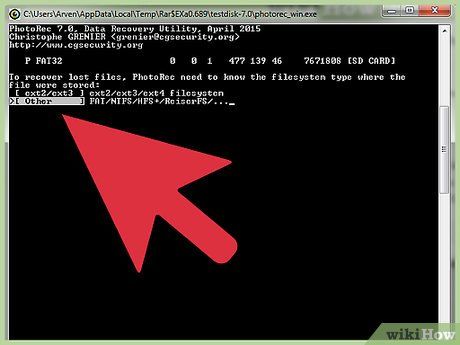
Choose the File System Format. For SD card file recovery, opt for Other.
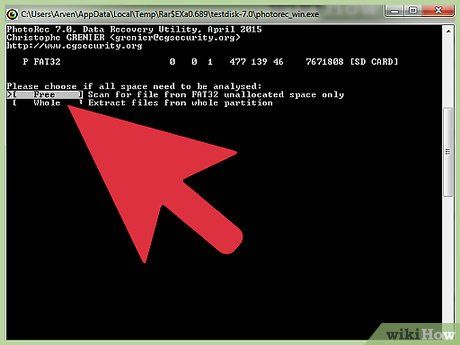
Specify the Area for Analysis. Opt for Free if you're recovering deleted files, or choose Whole if you're dealing with a corrupt card.
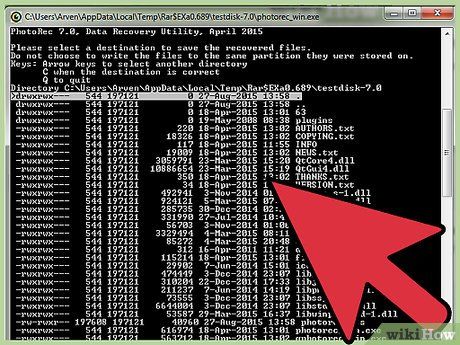
Select a Destination for Recovered Files. Establish a new directory if you require a convenient location for storing the retrieved data.
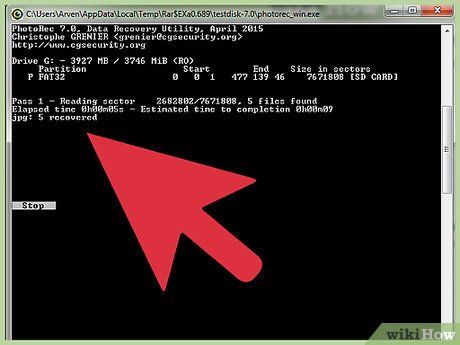
Patience for File Recovery. This phase might consume a considerable amount of time. You'll witness the number of recovered files updating in real-time.
Review the Retrieved Files. Due to corrupted file names, manual searching is necessary to locate the desired ones. If the images you seek aren't found, consider exploring alternative data recovery methods.
Utilizing ZAR (Windows)
Avoid accessing the SD card. If files are deleted, there's still a chance the data remains but is set to be overwritten. By refraining from accessing the SD card, you enhance the likelihood of data preservation.
- Until ready to attempt file recovery, remove the SD card from any device.
Get ZAR (Zero Assumption Recovery). ZAR's full version requires purchase, but the demo version permits image file recovery. Download ZAR solely from the developer's site.
- Visit the ZAR site and click the 'image recovery' link at the page's bottom to install the free demo for image recovery.
Insert the SD card. Place your SD card into your computer via an SD card reader or connect it via USB through your camera.
- Your computer may prompt you to format the card or label it unreadable. Disregard this formatting prompt as it could overwrite your picture data on the card.
Launch the Image Recovery tool in ZAR. Open ZAR and click on Image Recovery (Free). For other software, look for a similar option. Some programs may skip this step entirely.
Choose your SD card. Under 'Disks and partitions,' select your SD card, typically labeled as such. Click Next to initiate the recovery scan.
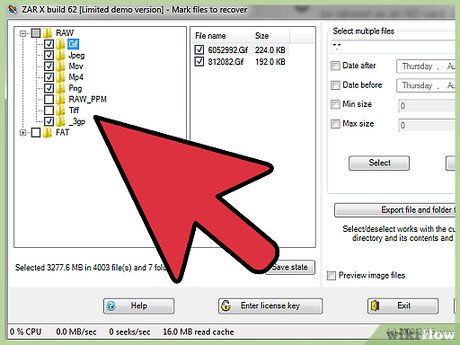
Select the files you wish to retrieve. You'll encounter a list of images located on your SD card. Pick the images you want to recover, or opt to restore all lost images. Previews may not be available, and filenames are likely to be lost.
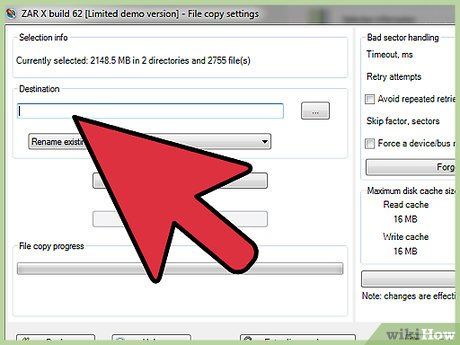
Choose where to save the recovered images. If your SD card is damaged, avoid saving them back to the card. Instead, designate or create a folder on your computer for saving the pictures. This ensures your pictures remain safe in case of future SD card issues.
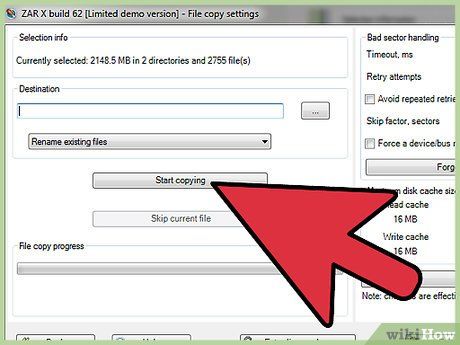
Transfer the files. Click Start copying the selected files to initiate picture restoration. The selected files will be saved to the specified location.
- Some pictures may not be fully recoverable. Even if the thumbnail appears intact, the picture itself may be partially or entirely damaged.
Using Data Rescue 3 (Mac)
Avoid accessing the SD card. If files are deleted, there's still a chance the data remains but is set to be overwritten. By refraining from accessing the SD card, you enhance the likelihood of data preservation.
- Until ready to attempt file recovery, remove the SD card from any device.
Download and install Data Rescue 3. Although Data Rescue 3 requires payment, it stands out as one of the most robust data recovery tools for OS X. You can acquire Data Rescue 3 from the website or the Mac App Store.
- If you're seeking a free alternative, consider PhotoRec.
Insert your SD card. Place the SD card into your Mac. If your Mac lacks an SD card slot, obtain an external USB card reader or insert the card into a camera and connect the camera to your computer.
Launch Data Rescue 3. Locate it in your 'Applications' folder, then choose 'Start New Scan' from the main menu.
Select your SD card. In the Data Rescue window, a list of drives will appear. Pick your SD card from the list.
- You might also need to select the volume. Most SD cards contain only one volume, but if there are multiple volumes, simply choose the entire SD card.
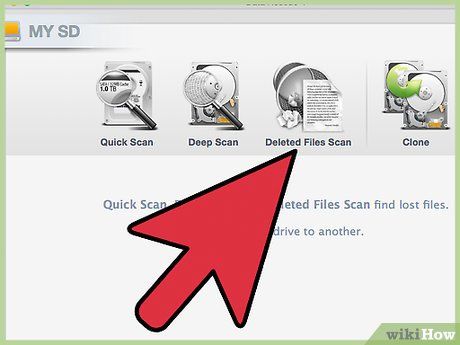
Choose your scanning method. For the initial attempt, opt for the 'Deleted Files Scan'. This method scans the free space to locate files deleted from the SD card. If this approach yields no results, you can return and try a 'Quick Scan' followed by a 'Deep Scan'. Click Start once you've selected your scan type.
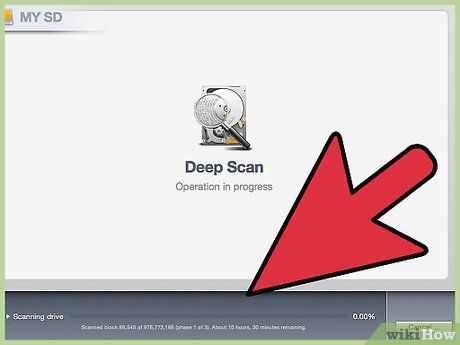
Allow the scan to finish. Depending on the type of scan, particularly if it's a Deep Scan, it may take a considerable amount of time. If necessary, you can pause the scan by clicking the Suspend button.
Choose the files you wish to recover. Once the scan finishes, a list of potential files to recover will be displayed. Tick the boxes next to the files or folders you want to recover.
- If you conducted a Quick or Deep Scan, files will appear in the 'Found Files' section of the results.
- If you performed a Deleted Files or Deep Scan, files will be listed under the 'Reconstructed Files' section. File names may be lost.
- You can preview files by selecting them from the list and clicking 'Preview'. Note that not all file types are previewable.
Initiate the recovery process. After selecting the desired files, click Recover and specify a location on your computer to save the files. Once you've identified a suitable location, click Open.
Helpful Advice
Precautions
- Not all lost photos can be recovered. If your memory card is severely damaged or reformatted, or if the deleted photos have been replaced with new ones, you may not be able to retrieve your lost images.
