
Key Takeaways |
|---|
Alternative transportation options Lựa chọn giao thông thay thế Backup measures Biện pháp dự phòng Carbon footprint Dấu chân carbon Contingency plans Kế hoạch dự phòng Cycling and pedestrian infrastructure Cơ sở hạ tầng cho đạp xe và đi bộ Dedicated lanes Làn đường riêng Demand management strategies Chiến lược quản lý nhu cầu Efficient commuting Di chuyển hiệu quả Equitable access Quyền tiếp cận công bằng Greenhouse gas emissions Khí thải nhà kính Induced demand Nhu cầu kích hoạt Intelligent traffic lights Đèn giao thông thông minh Intersection safety An toàn giao lộ Private vehicles Xe cá nhân Productivity losses Thiệt hại về năng suất Public transportation systems Hệ thống giao thông công cộng Real-time traffic information Thông tin giao thông thời gian thực Road expansion projects Dự án mở rộng đường Road layouts Bố trí đường Safety measures Biện pháp an toàn Smart city initiatives Các sáng kiến thành phố thông minh Supply chains Chuỗi cung ứng Sustainable modes of transportation Các phương thức vận tải bền vững System breakdown Sự hỏng hóc hệ thống Technical glitches Lỗi kỹ thuật Traffic bottlenecks Điểm tắc nghẽn giao thông Traffic disruptions Sự gián đoạn giao thông Traffic flow Luồng giao thông Traffic management systems Hệ thống quản lý giao thông Traffic volume Lưu lượng giao thông Transportation efficiency Hiệu quả giao thông Travel times Thời gian di chuyển Vehicle ownership Sở hữu phương tiện Vehicle-free days Ngày không có xe |
Các bài viết liên quan đến chủ đề này
Matching Some cities have vehicle-free days, when private cars, trucks, motorcycles are banned in the city center. Public transportation like buses, taxis and metros are advised. To what extent do you think the advantages outweigh the disadvantages?
The construction of new roads and highways is often seen as a solution to alleviate traffic congestion. Do you believe the advantages of this approach outweigh the disadvantages?
Urbanization and population growth are contributing factors to traffic congestion. What are the causes, and what are the effects?
The best way to solve traffic and transportation problems is to encourage people to live in cities rather than suburbs or countryside. Do you agree or disagree?
Public transportation systems can help alleviate traffic congestion. Do the advantages of this outweigh the disadvantages?
With the advancement of technology, smart traffic management systems have been implemented in some cities. Is this a positive or a negative development in addressing traffic congestion?
Collocations về vấn đề kẹt xe giao thông
Collocation | Type | Vietnamese Meaning | English Example Sentence |
|---|---|---|---|
Alternative transportation options | ADJ + NOUN | Lựa chọn giao thông thay thế | Providing alternative transportation options can reduce traffic congestion. |
Backup measures | NOUN + NOUN | Biện pháp dự phòng | Backup measures should be in place to ensure system reliability. |
Carbon footprint | NOUN + NOUN | Dấu chân carbon | Reducing our carbon footprint is crucial for environmental sustainability. |
Contingency plans | NOUN + NOUN | Kế hoạch dự phòng | Effective contingency plans are essential for crisis management. |
Cycling and pedestrian infrastructure | NOUN + CONJ + NOUN | Cơ sở hạ tầng cho đạp xe và đi bộ | Cities should invest in cycling and pedestrian infrastructure. |
Dedicated lanes | ADJ + NOUN | Làn đường riêng | Dedicated lanes for buses can improve public transportation. |
Demand management strategies | NOUN + NOUN | Chiến lược quản lý nhu cầu | Demand management strategies can help reduce traffic congestion. |
Efficient commuting | ADJ + NOUN | Di chuyển hiệu quả | Public transportation offers efficient commuting options. |
Equitable access | ADJ + NOUN | Quyền tiếp cận công bằng | Improving public transportation ensures equitable access for all. |
Greenhouse gas emissions | NOUN + NOUN | Khí thải nhà kính | Reducing greenhouse gas emissions is crucial for climate change mitigation. |
Induced demand | VERB + NOUN | Nhu cầu kích hoạt | Expanding road capacity may lead to induced demand for more vehicles. |
Intelligent traffic lights | ADJ + NOUN | Đèn giao thông thông minh | Intelligent traffic lights can optimize traffic flow. |
Intersection safety | NOUN + NOUN | An toàn giao lộ | Intersection safety measures should be implemented to reduce accidents. |
Private vehicles | ADJ + NOUN | Xe cá nhân | The number of private vehicles on the road has increased. |
Productivity losses | NOUN + NOUN | Thiệt hại về năng suất | Traffic congestion leads to productivity losses for businesses. |
Public transportation systems | ADJ + NOUN | Hệ thống giao thông công cộng | Public transportation systems play a crucial role in reducing traffic congestion. |
Real-time traffic information | ADJ + NOUN | Thông tin giao thông thời gian thực | Real-time traffic information can assist drivers in choosing less congested routes. |
Road expansion projects | NOUN + NOUN | Dự án mở rộng đường | Road expansion projects aim to improve traffic capacity. |
Road layouts | NOUN + NOUN | Bố trí đường | Effective road layouts can enhance traffic flow. |
Safety measures | NOUN + NOUN | Biện phápan toàn | Implementing safety measures is essential to reduce accidents. |
Smart city initiatives | ADJ + NOUN | Các sáng kiến thành phố thông minh | Smart city initiatives integrate technology to improve transportation efficiency. |
Supply chains | NOUN + NOUN | Chuỗi cung ứng | Traffic congestion can disrupt supply chains and increase costs. |
Sustainable modes of transportation | ADJ + NOUN + NOUN | Các phương thức vận tải bền vững | Encouraging sustainable modes of transportation can reduce carbon emissions. |
System breakdown | NOUN + NOUN | Sự hỏng hóc hệ thống | A system breakdown can cause significant disruptions in traffic flow. |
Technical glitches | ADJ + NOUN | Lỗi kỹ thuật | Technical glitches in the traffic management system should be minimized. |
Traffic bottlenecks | NOUN + NOUN | Điểm tắc nghẽn giao thông | Traffic bottlenecks can result in long delays and congestion. |
Traffic disruptions | NOUN + NOUN | Sự gián đoạn giao thông | Construction projects can cause traffic disruptions. |
Traffic flow | NOUN + NOUN | Luồng giao thông | Optimizing traffic flow is crucial to reduce congestion. |
Traffic management systems | NOUN + NOUN | Hệ thống quản lý giao thông | Advanced traffic management systems can improve traffic flow and reduce congestion. |
Traffic volume | NOUN + NOUN | Lưu lượng giao thông | High traffic volume during peak hours leads to congestion. |
Transportation efficiency | NOUN + NOUN | Hiệu quả giao thông | Smart traffic management systems aim to improve transportation efficiency. |
Travel times | NOUN + NOUN | Thời gian di chuyển | Efficient public transportation reduces travel times for commuters. |
Vehicle ownership | NOUN + NOUN | Sở hữu phương tiện | High vehicle ownership contributes to traffic congestion. |
Vehicle-free days | NOUN + NOUN | Ngày không có xe | Implementing vehicle-free days can alleviate traffic congestion. |
Bản đồ tư duy
Dưới đây là 2 mind maps mẫu và rất hữu ích đối với các học viên còn gặp vấn đề về phát triển ý. Các ý bao trùm có thể tạo ra câu luận điểm hay bởi tính khái quát của nó, và các ý nó sẽ tạo thành phần luận cứ chặt chẽ và thuyết phục.
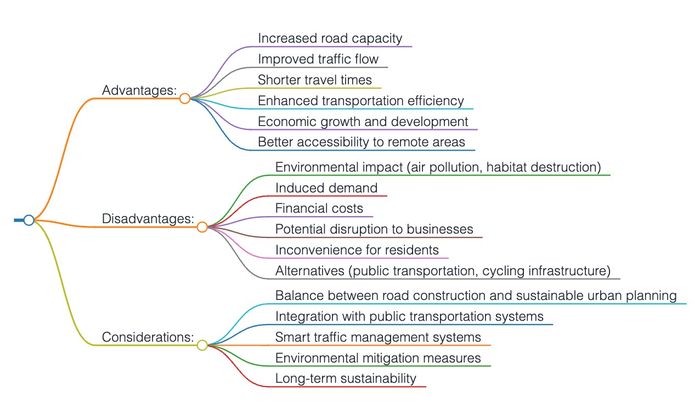
Biểu đồ tư duy 1: Các ưu điểm, nhược điểm của việc xây dựng thêm đường và xa lộ cùng những yếu tố cần xem xét thêm
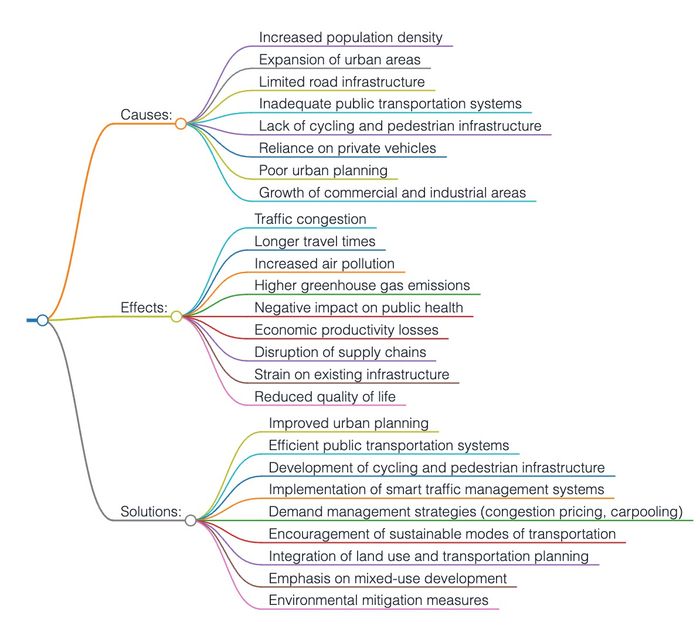
Biểu đồ tư duy 2: Nguyên nhân, hậu quả và phương pháp giải quyết vấn đề đô thị hóa và sự tăng trưởng dân số đối với tình trạng kẹt xe giao thông
Người học hoàn toàn có thể phối hợp các ý trong 2 mind maps trên để giải quyết các dạng bài khác nhau có liên quan.
Bài tập
Collocations | Vietnamese Meaning |
1. Public transportation systems | A. Hệ thống quản lý giao thông |
2. Traffic volume | B. Cơ sở hạ tầng cho đạp xe và đi bộ |
3. Traffic flow | C. Cơ sở hạ tầng cho đạp xe và đi bộ |
4. Traffic management systems | D. Giao thông bền vững |
5. Sustainable transportation | E. Thời gian đèn giao thông |
6. Travel times | F. Hệ thống giao thông công cộng |
7. Greenhouse gas emissions | G. An toàn giao lộ |
8. Cycling and pedestrian infrastructure | H. Thời gian di chuyển |
9. Contingency plans | I. Sự hỏng hóc hệ thống |
10. Road expansion projects | J. Lưu lượng giao thông |
11. Intersection safety | K. Bố trí đường |
12. System breakdown | L. Biện pháp dự phòng |
13. Traffic signal timings | M. Lỗi kỹ thuật |
14. Road layouts | N. Dự án mở rộng đường |
15. Technical glitches | O. An toàn giao lộ |
Ex 2: Fill in the blanks with the appropriate collocation
Adverse effects High decibel sounds Metropolitan cities Public awareness
Quiet zones Urban ecosystems Vehicular traffic
Noise generation Rapid urbanization Well-being concerns
_____________ is a common problem in densely populated cities.
The high dependence on __________ contributes to increased traffic congestion in urban areas.
Long _____________ are a major issue during peak hours.
_____________ refers to the amount of carbon dioxide emitted by vehicles, contributing to air pollution and climate change.
_____________ are experienced due to traffic congestion, leading to delays and inefficiencies.
_____________ refers to the number of vehicles owned by individuals or households in a particular area.
_____________ can help optimize traffic flow and reduce congestion at intersections.
_____________ involve expanding existing road infrastructure to accommodate the growing number of vehicles.
_____________ are temporary solutions implemented to manage traffic flow, such as detours or alternative routes.
_____________ are areas where traffic flow is severely restricted, leading to congestion.
Ex 3: Fill in the appropriate collocations in the blanks
sustainable transportation physical activity carbon footprint vehicle-free days
traffic flow private vehicles limited access travel time public health
The implementation of (1)_______________ in certain cities, where private cars, trucks, and motorcycles are prohibited in the city center, has become a subject of debate regarding its advantages and disadvantages. This essay will analyze the extent to which the benefits outweigh the drawbacks of such an approach.
One of the primary advantages of vehicle-free days is the reduction in traffic congestion. By eliminating private cars, trucks, and motorcycles from the city center, (2)_______________ can be significantly improved. This allows for smoother movement of public transportation vehicles such as buses, taxis, and metros, facilitating efficient commuting for residents and visitors alike. The decrease in congestion also contributes to a reduction in (3)_______________ and enhances overall transportation efficiency.
Additionally, vehicle-free days promote sustainable modes of transportation. With (4)_______________ being banned, individuals are encouraged to utilize public transportation options. This not only reduces the (5)_______________ and air pollution associated with private cars but also promotes a greener and more environmentally friendly city. The increased usage of buses, taxis, and metros also leads to a more efficient use of resources, as fewer vehicles are required to transport a larger number of people.
Furthermore, vehicle-free days can enhance (6)_______________. By reducing the number of vehicles in the city center, air quality improves, leading to a decrease in respiratory illnesses and other health issues associated with pollution. Moreover, the promotion of walking, cycling, and using public transportation encourages (7)_______________, contributing to a healthier lifestyle for residents.
On the other hand, there are some disadvantages to consider. One major concern is the potential impact on businesses in the city center. With (8)_______________ for private vehicles, customers may find it inconvenient to reach shops, restaurants, and other establishments. This could result in a decline in sales and economic activity for businesses located in the affected area. Additionally, residents living in the city center who rely on private vehicles for various reasons, such as mobility challenges or transportation of goods, may face difficulties in their daily routines.
In conclusion, vehicle-free days have several significant advantages that outweigh the disadvantages. They effectively reduce traffic congestion, promote (9)_______________, and improve public health. While potential drawbacks, such as the impact on businesses and inconvenience for certain residents, should be acknowledged, the overall benefits to the environment, transportation efficiency, and public health make vehicle-free days a worthwhile approach. By implementing proper measures to mitigate the negative effects, such as providing alternative transportation options and supporting affected businesses, the advantages of vehicle-free days can be maximized, creating a more sustainable and livable city.
Ex 4: Create an outline and write a comprehensive answer for this topic. Write a minimum of 250 words.
Traffic congestion not only affects the environment but also has adverse effects on public health. What are the causes of traffic congestion, and what measures can be taken to mitigate its impact?
Key
Bài 1
Public transportation systems - F. Hệ thống giao thông công cộng
Traffic volume - J. Lưu lượng giao thông
Traffic flow - C. Luồng giao thông
Traffic management systems - A. Hệ thống quản lý giao thông
Sustainable transportation - D. Giao thông bền vững
Travel times - H. Thời gian di chuyển
Greenhouse gas emissions - G. Khí thải nhà kính
Cycling and pedestrian infrastructure - P. Cơ sở hạ tầng cho đạp xe và đi bộ
Contingency plans - B. Biện pháp dự phòng
Road expansion projects - N. Dự án mở rộng đường
Intersection safety - O. An toàn giao lộ
System breakdown - I. Sự hỏng hóc hệ thống
Traffic signal timings - E. Thời gian đèn giao thông
Road layouts - K. Bố trí đường
Technical glitches - M. Lỗi kỹ thuật
Bài 2
Traffic congestion is a common problem in densely populated cities.
The high dependence on private vehicles contributes to increased traffic congestion in urban areas.
Long travel times are a major issue during peak hours.
Carbon footprint refers to the amount of carbon dioxide emitted by vehicles, contributing to air pollution and climate change.
Productivity losses are experienced due to traffic congestion, leading to delays and inefficiencies.
Vehicle ownership refers to the number of vehicles owned by individuals or households in a particular area.
Intelligent traffic lights can help optimize traffic flow and reduce congestion at intersections.
Road expansion projects involve expanding existing road infrastructure to accommodate the growing number of vehicles.
Backup measures are temporary solutions implemented to manage traffic flow, such as detours or alternative routes.
Traffic bottlenecks are areas where traffic flow is severely restricted, leading to congestion.
Bài 3
vehicle-free days
traffic flow
travel time
private vehicles
carbon footprint
public health
physical activity
limited access
sustainable transportation
Bài 4
Outline gợi ý:
I. Introduction
Introduce the topic of traffic congestion and its adverse effects on the environment and public health.
Present the purpose of the essay: to explore the causes of traffic congestion and propose mitigation measures.
II. Causes of Traffic Congestion
Paragraph 1:
Discuss the primary cause of traffic congestion: exponential increase in private vehicle ownership.
Explain the relationship between rising personal incomes and increased traffic volume.
Highlight the impact of inadequate public transportation systems on reliance on private vehicles.
Paragraph 2:
Explore the contributing factors to traffic congestion: urbanization and population growth.
Discuss how population density affects road infrastructure and leads to congestion.
Emphasize the challenges posed by urbanization and increasing demands on transportation.
III. Measures to Mitigate Traffic Congestion
Paragraph 3:
Introduce the first measure: improving public transportation systems.
Explain the importance of enhancing quality, efficiency, and accessibility of public transportation modes.
Discuss how these improvements can incentivize individuals to choose public transport over private vehicles.
Paragraph 4:
Introduce the second measure: implementing congestion pricing strategies.
Explain how charging higher fees during peak hours can discourage private vehicle use.
Discuss the potential benefits of reinvesting the generated revenue in public transportation infrastructure.
IV. Conclusion
Summarize the adverse effects of traffic congestion on the environment and public health.
Recap the causes discussed in the body paragraphs.
Highlight the proposed measures to mitigate traffic congestion's impact.
Conclude with a call to action for implementing these measures to create sustainable and healthier urban environments.
Bài mẫu tham khảo
Traffic congestion has emerged as a critical concern in modern society, posing significant challenges not only to the environment but also to public health. This essay will delve into the causes of traffic congestion and propose measures that can be taken to mitigate its impact.
One of the primary causes of traffic congestion is the exponential increase in private vehicle ownership. As personal incomes rise, more individuals can afford cars, resulting in a surge in traffic volume. Furthermore, inadequate public transportation systems force people to rely heavily on private vehicles, exacerbating congestion on the roads. Another contributing factor is urbanization and population growth, as cities become more densely populated, road infrastructure struggles to keep pace with the increasing demands, leading to congestion.
To mitigate the impact of traffic congestion on the environment and public health, several measures can be implemented. Firstly, governments should prioritize the improvement of public transportation systems. By enhancing the quality, efficiency, and accessibility of buses, trains, and subways, individuals would be incentivized to opt for public transport over private vehicles. Additionally, investing in the development of cycling and pedestrian infrastructure would encourage people to use sustainable modes of transportation, reducing traffic congestion and promoting a healthier lifestyle.
Furthermore, implementing congestion pricing strategies can be an effective solution. By charging higher fees during peak hours in congested areas, drivers would be deterred from using their vehicles, resulting in reduced traffic congestion. The revenue generated from these fees can be reinvested in public transportation infrastructure, further improving its quality and expanding its reach.
In addition to infrastructure improvements, adopting smart traffic management systems can significantly alleviate congestion. Intelligent traffic lights that dynamically adjust signal timings based on traffic flow can optimize traffic movement and minimize congestion. Furthermore, real-time traffic information through smartphone applications can assist drivers in choosing less congested routes, dispersing traffic and reducing bottlenecks.
Education and awareness campaigns should also be employed to change individual behavior. Promoting carpooling, ride-sharing, and flexible work hours can incentivize people to share rides and travel during off-peak hours, thereby reducing the number of vehicles on the road. Public awareness campaigns can highlight the environmental and health consequences of traffic congestion, encouraging individuals to choose alternative modes of transportation whenever possible.
To conclude, traffic congestion poses serious threats to both the environment and public health. The causes of congestion are multifaceted, including increased vehicle ownership, inadequate public transportation, urbanization, and population growth. Mitigating its impact requires a multi-faceted approach, including improving public transportation systems, implementing congestion pricing, adopting smart traffic management systems, promoting sustainable modes of transportation, and raising public awareness. By implementing these measures, we can effectively combat traffic congestion and create more sustainable and livable cities for the future.
Bản mẫu tham khảo cho các bài viết luận trong bài.
1. Question: "Some cities have vehicle-free days, when private cars, trucks, motorcycles are banned in the city center. Public transportation like buses, taxis and metros are advised. To what extent do you think the advantages outweigh the disadvantages?"
The implementation of vehicle-free days in certain cities, where private cars, trucks, and motorcycles are prohibited in the city center, has become a subject of debate regarding its advantages and disadvantages. This essay will analyze the extent to which the benefits outweigh the drawbacks of such an approach.
One of the primary advantages of vehicle-free days is the reduction in traffic congestion. By eliminating private cars, trucks, and motorcycles from the city center, traffic flow can be significantly improved. This allows for smoother movement of public transportation vehicles such as buses, taxis, and metros, facilitating efficient commuting for residents and visitors alike. The decrease in congestion also contributes to a reduction in travel time and enhances overall transportation efficiency.
Additionally, vehicle-free days promote sustainable modes of transportation. With private vehicles being banned, individuals are encouraged to utilize public transportation options. This not only reduces the carbon footprint and air pollution associated with private cars but also promotes a greener and more environmentally friendly city. The increased usage of buses, taxis, and metros also leads to a more efficient use of resources, as fewer vehicles are required to transport a larger number of people.
Furthermore, vehicle-free days can enhance public health. By reducing the number of vehicles in the city center, air quality improves, leading to a decrease in respiratory illnesses and other health issues associated with pollution. Moreover, the promotion of walking, cycling, and using public transportation encourages physical activity, contributing to a healthier lifestyle for residents.
On the other hand, there are some disadvantages to consider. One major concern is the potential impact on businesses in the city center. With limited access for private vehicles, customers may find it inconvenient to reach shops, restaurants, and other establishments. This could result in a decline in sales and economic activity for businesses located in the affected area. Additionally, residents living in the city center who rely on private vehicles for various reasons, such as mobility challenges or transportation of goods, may face difficulties in their daily routines.
In conclusion, vehicle-free days have several significant advantages that outweigh the disadvantages. They effectively reduce traffic congestion, promote sustainable transportation, and improve public health. While potential drawbacks, such as the impact on businesses and inconvenience for certain residents, should be acknowledged, the overall benefits to the environment, transportation efficiency, and public health make vehicle-free days a worthwhile approach. By implementing proper measures to mitigate the negative effects, such as providing alternative transportation options and supporting affected businesses, the advantages of vehicle-free days can be maximized, creating a more sustainable and livable city.
2. Question: "The construction of new roads and highways is often seen as a solution to alleviate traffic congestion. Do you believe the advantages of this approach outweigh the disadvantages?"
The construction of new roads and highways is often proposed as a potential solution to alleviate traffic congestion in many cities. This essay will critically evaluate whether the advantages of this approach outweigh the disadvantages.
One of the key advantages of constructing new roads and highways is the potential to increase road capacity. With additional lanes and routes, there is a higher likelihood of reducing traffic congestion, particularly during peak hours. This can lead to smoother traffic flow and shorter travel times for commuters, improving overall transportation efficiency. Additionally, the construction of new roads and highways can enhance connectivity between different regions, facilitating economic growth and development.
Moreover, new roads and highways can provide improved accessibility to remote areas. These areas may have previously been poorly connected, resulting in limited economic opportunities and reduced access to essential services. By constructing new road networks, communities in remote regions can benefit from improved access to jobs, education, healthcare, and other services, leading to enhanced quality of life.
Furthermore, the construction of new roads and highways can stimulate economic activity. It creates employment opportunities in the construction industry and generates a demand for materials and equipment, providing a boost to the local economy. Additionally, improved transportation infrastructure can attract businesses and investments to an area, leading to increased trade and economic growth.
However, there are significant disadvantages associated with the construction of new roads and highways that must be considered. One major drawback is the potential environmental impact. Building new roads often involves clearing land, which can lead to deforestation and habitat destruction. Moreover, increased vehicle usage resulting from improved road connectivity can contribute to air and noise pollution, as well as greenhouse gas emissions, exacerbating the challenges of climate change and adversely affecting public health.
Another disadvantage is the potential for induced demand. Constructing new roads and highways may initially alleviate traffic congestion, but it can also lead to increased vehicle ownership and usage over time. This phenomenon occurs when improved road capacity attracts more drivers, ultimately offsetting the initial congestion reduction. Consequently, the benefits of new road construction may be short-lived, and the cycle of congestion could continue.
Additionally, the financial costs of constructing new roads and highways should not be overlooked. Building and maintaining extensive transportation infrastructure require substantial investments from the government. These funds could be allocated to other critical sectors such as healthcare, education, or public transportation systems, which might have a more significant long-term impact on the overall well-being of the population.
In conclusion, while the construction of new roads and highways can offer advantages such as increased road capacity, improved accessibility, and economic growth, the disadvantages cannot be ignored. The potential environmental impact, induced demand, and financial costs pose significant challenges. Therefore, a comprehensive evaluation of the specific context, including the existing transportation infrastructure, urban planning strategies, and environmental considerations, is necessary to determine whether the advantages of new road construction outweigh the disadvantages. Moreover, a holistic approach that combines the construction of roads with investment in public transportation, sustainable urban planning, and effective traffic management strategies may provide a more balanced and sustainable solution to alleviate traffic congestion.
3. Question: "Urbanization and population growth are contributing factors to traffic congestion. What are the causes, and what are the effects?"
Urbanization and population growth are undeniably significant contributors to traffic congestion in cities. This essay will explore the causes of traffic congestion resulting from urbanization and population growth, as well as its effects on various aspects of urban life.
One of the primary causes of traffic congestion in urban areas is the increase in population density. As cities experience population growth, the number of vehicles on the roads escalates. This surge in private vehicle ownership, combined with limited road infrastructure, leads to overcrowded streets and traffic congestion. Additionally, urbanization often results in the expansion of commercial and industrial areas, attracting more commuters and exacerbating congestion during peak hours.
Furthermore, urban planning plays a crucial role in traffic congestion. Poorly designed road networks, inadequate traffic management systems, and a lack of alternative transportation options can all contribute to increased congestion. Insufficient public transportation systems, limited cycling and pedestrian infrastructure, and inadequate parking facilities force individuals to rely heavily on private vehicles, intensifying traffic congestion in urban areas.
The effects of traffic congestion are manifold and extend beyond inconvenience and frustration for commuters. Firstly, it has a detrimental impact on the environment. The increased number of vehicles on the road leads to elevated air pollution levels, including higher emissions of greenhouse gases and harmful pollutants. This not only contributes to climate change but also poses serious health risks to urban residents, causing respiratory problems and other pollution-related illnesses.
Moreover, traffic congestion has economic implications. The excessive time spent in traffic results in productivity losses for individuals and businesses. Delays in the transportation of goods and services can disrupt supply chains and increase costs, negatively affecting the economy. Additionally, the high fuel consumption associated with stop-and-go traffic contributes to increased expenses for individuals and businesses alike.
Furthermore, traffic congestion has social consequences. It leads to increased stress levels and decreased quality of life for urban dwellers. The frustration and fatigue caused by long commutes and congestion can affect mental health and overall well-being. Additionally, traffic congestion hinders social interactions and community engagement, as people are less inclined to engage in activities outside their immediate vicinity due to the challenges of transportation.
In conclusion, urbanization and population growth are key factors contributing to traffic congestion in cities. The causes of congestion include population density, urban planning deficiencies, and a lack of alternative transportation options. The effects of traffic congestion encompass environmental degradation, economic losses, and negative impacts on mental health and community engagement. To address this issue, comprehensive strategies are needed, including improved urban planning, investment in efficient and sustainable public transportation systems, the development of cycling and pedestrian infrastructure, and the implementation of traffic management measures. By adopting a holistic approach, cities can mitigate the causes and effects of traffic congestion, resulting in more sustainable and livable urban environments.
4. Question: "The best way to solve traffic and transportation problems is to encourage people to live in cities rather than suburbs or countryside. Do you agree or disagree?"
In recent years, traffic and transportation problems have become increasingly prevalent, particularly in urban areas. Some argue that the most effective solution to address these issues is to encourage people to live in cities rather than in suburbs or the countryside. This essay will present arguments both in favor and against this viewpoint and ultimately argue that while encouraging urban living may be beneficial, it is not the sole solution to traffic and transportation problems.
Supporters of encouraging city living argue that by concentrating the population in urban areas, there would be a reduced need for long commutes. This would lead to shorter travel distances, decreased traffic congestion, and improved transportation efficiency. Additionally, living in cities often provides residents with better access to public transportation networks, including buses, subways, and trains. This accessibility encourages the use of sustainable modes of transport, reducing reliance on private vehicles and alleviating traffic congestion. Moreover, urban living promotes walkability and cycling as viable transportation options, contributing to healthier lifestyles and reducing environmental impact.
On the other hand, there are valid arguments against solely promoting city living as the solution to traffic and transportation problems. Firstly, cities already face significant challenges in terms of overcrowding, limited housing availability, and high living costs. Encouraging more people to live in cities could exacerbate these issues and put additional strain on already overburdened infrastructure. Furthermore, urban areas may not be suitable or desirable for everyone due to factors such as personal preferences, work locations, or family requirements. For some individuals, the suburbs or countryside provide a more peaceful and suitable living environment.
Instead of focusing solely on encouraging urban living, a comprehensive approach that addresses multiple aspects of traffic and transportation problems is necessary. Firstly, improving public transportation systems in both urban and suburban areas is essential. Enhancing the quality, coverage, and frequency of bus, train, and subway services would provide viable alternatives to private vehicles and reduce traffic congestion. Additionally, investing in cycling and pedestrian infrastructure in both urban and suburban areas can encourage active transportation and reduce the need for motorized travel.
Furthermore, smart city initiatives and technology can play a pivotal role in optimizing transportation networks. Intelligent traffic management systems, real-time traffic information, and data-driven planning can help mitigate traffic congestion by identifying bottlenecks, optimizing signal timings, and providing efficient routing options. Employing demand management strategies such as congestion pricing during peak hours can also discourage unnecessary travel and incentivize the use of public transportation.
In conclusion, while encouraging people to live in cities can offer advantages in terms of reducing travel distances, promoting sustainable transportation, and improving access to public transportation, it is not the sole solution to traffic and transportation problems. A comprehensive approach is necessary, which includes improving public transportation systems, investing in cycling and pedestrian infrastructure, and implementing smart city initiatives. By addressing multiple factors contributing to traffic congestion and transportation challenges, we can create more sustainable and efficient transportation systems that cater to the diverse needs and preferences of individuals in both urban and suburban areas.
5. Question: "Public transportation systems can help alleviate traffic congestion. Do the advantages of this outweigh the disadvantages?"
Public transportation systems have long been regarded as a potential solution to alleviate traffic congestion in urban areas. This essay will evaluate whether the advantages of public transportation systems outweigh the disadvantages in terms of alleviating traffic congestion.
One of the primary advantages of public transportation systems is their capacity to move a large number of people efficiently. Buses, subways, and trains can accommodate a significant number of passengers, thereby reducing the number of private vehicles on the roads. This leads to decreased traffic congestion, smoother traffic flow, and shorter travel times for commuters. Furthermore, public transportation often operates on dedicated lanes or tracks, allowing for more predictable travel schedules and reducing delays caused by traffic congestion.
Another advantage of public transportation systems is their potential to reduce environmental impact. Public transportation vehicles, particularly those powered by electricity or alternative fuels, produce fewer emissions compared to individual cars. By encouraging people to use public transportation, air pollution and greenhouse gas emissions can be mitigated, leading to improved air quality and reduced carbon footprint. This, in turn, contributes to efforts in combating climate change and promoting sustainable urban environments.
Furthermore, public transportation systems promote equitable access to transportation services. They cater to a wide range of individuals, including those who do not own private vehicles, cannot drive, or choose not to drive. Public transportation ensures that everyone, regardless of income or physical ability, has the opportunity to access education, employment, healthcare, and other essential services. This inclusivity helps to foster a more equitable society and reduces the reliance on private vehicles, which can be costly to own and maintain.
However, there are some disadvantages associated with public transportation systems that should be considered. Firstly, public transportation may not be as flexible or convenient as using a private vehicle. Fixed schedules and predetermined routes may not cater to the specific needs or preferences of individuals, leading to potential inconveniences or longer travel times. Additionally, crowded conditions during peak hours and limited seating capacity can make public transportation less comfortable for some passengers.
Another disadvantage is the financial cost of implementing and maintaining public transportation systems. Establishing an efficient and extensive network requires significant investments in infrastructure, vehicles, and operational expenses. This can pose financial challenges for governments, potentially leading to increased taxes or fares for users. Furthermore, if public transportation systems are not well-maintained or properly managed, it can result in unreliable service, further deterring individuals from utilizing these modes of transport.
In conclusion, the advantages of public transportation systems in alleviating traffic congestion outweigh the disadvantages. They contribute to reduced traffic congestion, improved air quality, and equitable access to transportation services. While public transportation may have drawbacks such as limited flexibility and associated costs, these can be mitigated through effective planning, investment, and management. By prioritizing and enhancing public transportation systems, cities can create sustainable, efficient, and inclusive transportation networks that benefit both individuals and the environment.
6. Question: "With the advancement of technology, smart traffic management systems have been implemented in some cities. Is this a positive or a negative development in addressing traffic congestion?"
The advancement of technology has paved the way for the implementation of smart traffic management systems in some cities. This essay will critically evaluate whether the adoption of such systems is a positive or negative development in addressing traffic congestion.
One of the key advantages of smart traffic management systems is their potential to improve traffic flow and alleviate congestion. These systems utilize advanced technologies, such as sensors, cameras, and real-time data analysis, to monitor traffic conditions and optimize signal timings. By dynamically adjusting signal durations based on real-time traffic patterns, smart traffic management systems can reduce delays, minimize bottlenecks, and improve overall traffic efficiency. This not only leads to shorter travel times for commuters but also reduces fuel consumption and emissions, contributing to a greener and more sustainable urban environment.
Moreover, smart traffic management systems enable better utilization of existing road infrastructure. By collecting and analyzing traffic data, these systems can identify areas with high congestion and propose targeted solutions. This may involve implementing changes to road layouts, such as introducing dedicated lanes for buses or bicycles, or adjusting traffic signal timings to accommodate the demand during peak hours. Through these proactive measures, smart traffic management systems optimize the use of available road space and reduce the need for costly road expansion projects.
Another advantage is the potential for improved safety. Smart traffic management systems can incorporate features like intelligent traffic lights, pedestrian detection systems, and vehicle-to-infrastructure communication. These technologies enhance safety by minimizing the likelihood of accidents, especially at intersections, and improving the coordination between different modes of transportation. Additionally, the availability of real-time traffic information can assist drivers in making informed decisions, avoiding congested areas, and reducing the risk of collisions.
However, there are some potential downsides to consider when evaluating the impact of intelligent traffic control systems. Firstly, implementing these systems requires significant investments in infrastructure, equipment, and upkeep. The expenses associated with establishing and maintaining a comprehensive intelligent traffic control network can be considerable, presenting financial obstacles for cities, especially those with limited resources.
Another issue is the risk of excessive reliance on technology. While intelligent traffic control systems aim to optimize traffic flow, they are susceptible to technical glitches or system failures. In the event of a system malfunction, there is a potential for disturbances and delays that could worsen congestion rather than alleviate it. Hence, it is crucial to have backup plans and contingency strategies in place to address any potential risks.
In summary, the deployment of intelligent traffic control systems represents a generally positive step in addressing traffic congestion. These systems hold promise for enhancing traffic flow, reducing congestion, improving safety, and promoting sustainable transportation. Nonetheless, the associated expenses and the necessity for contingency plans should be thoroughly evaluated. By striking a balance between technological progress and comprehensive planning and maintenance, cities can leverage the benefits of intelligent traffic control systems to create more efficient and livable urban landscapes.
